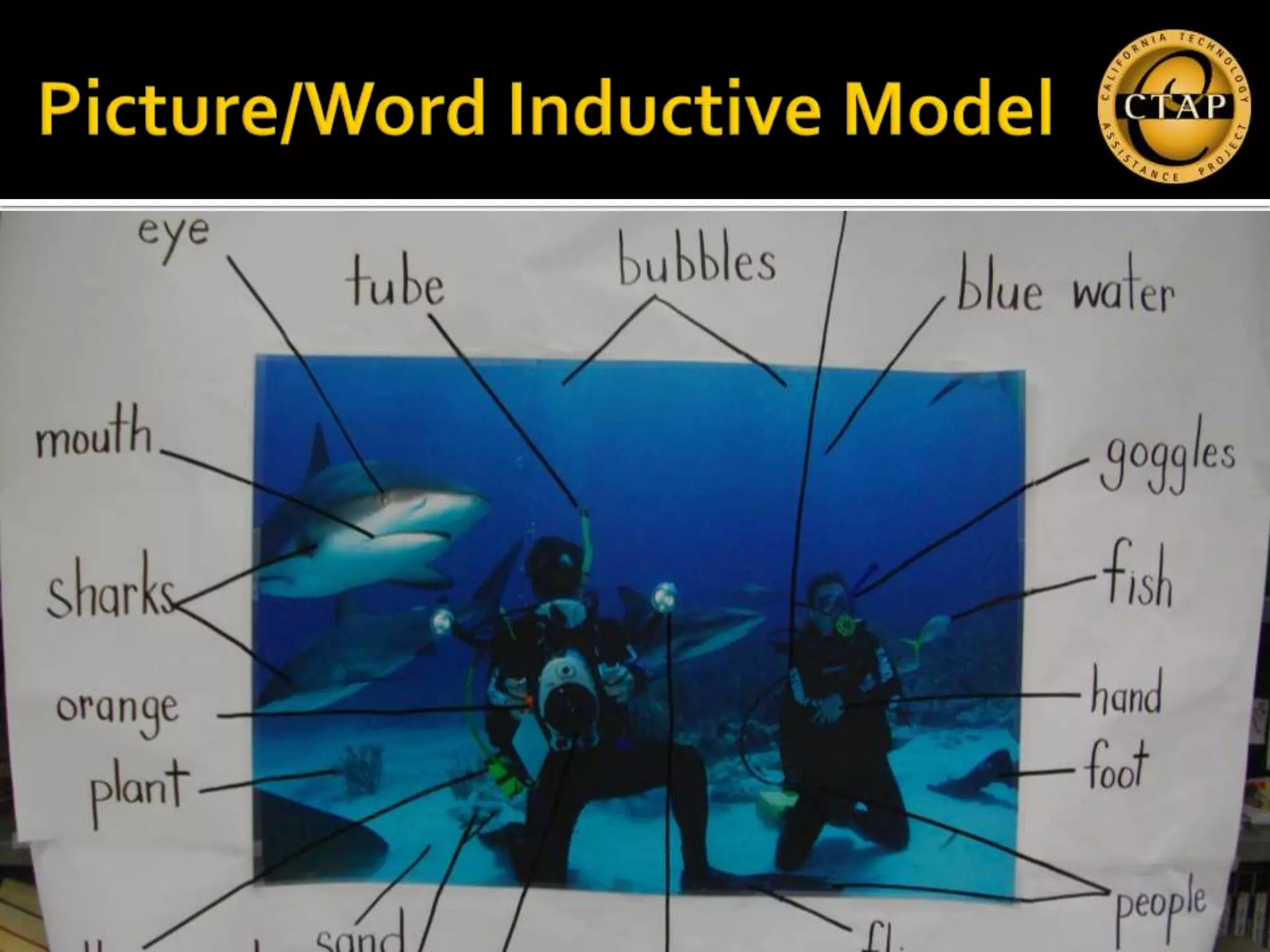
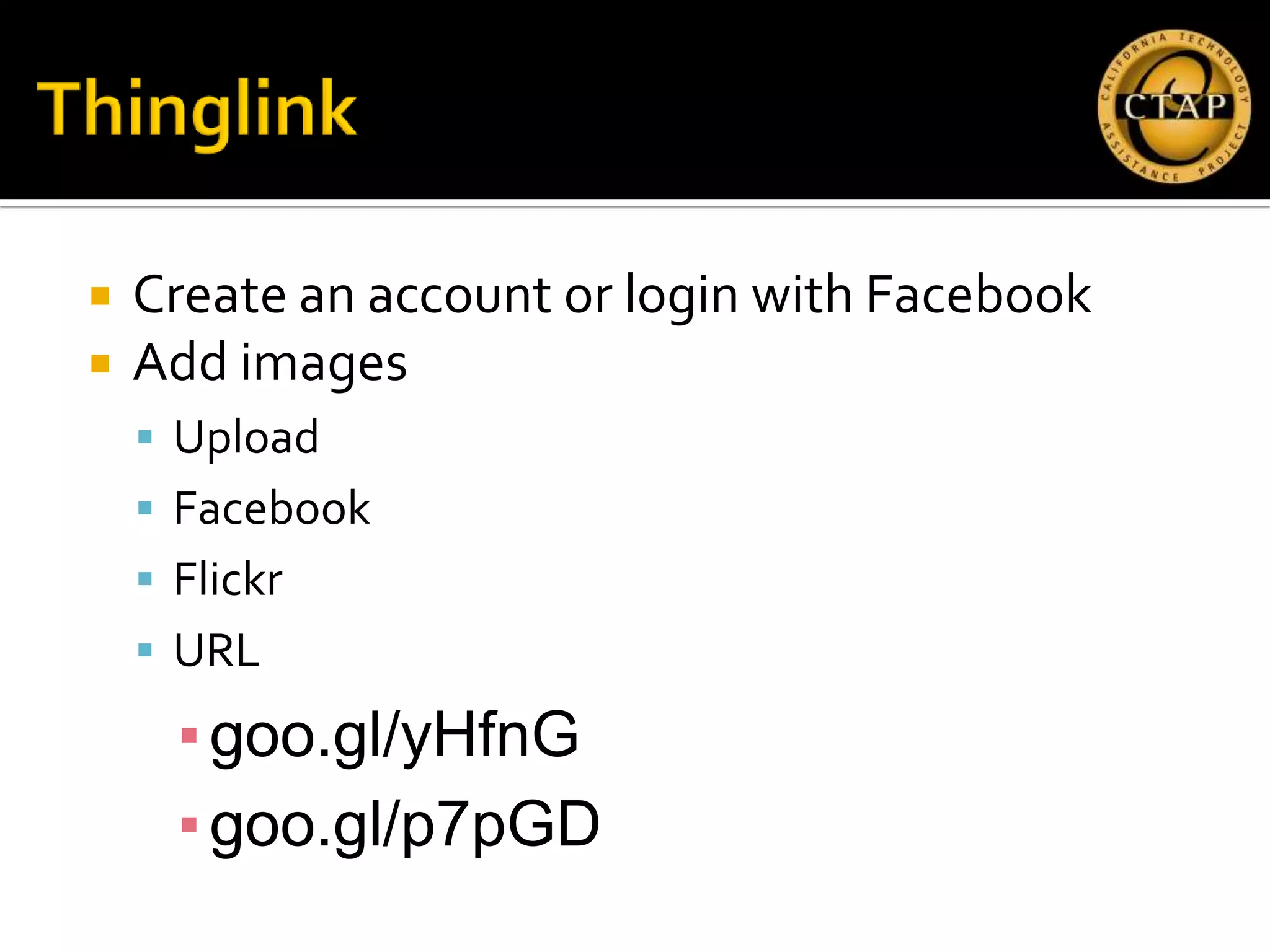
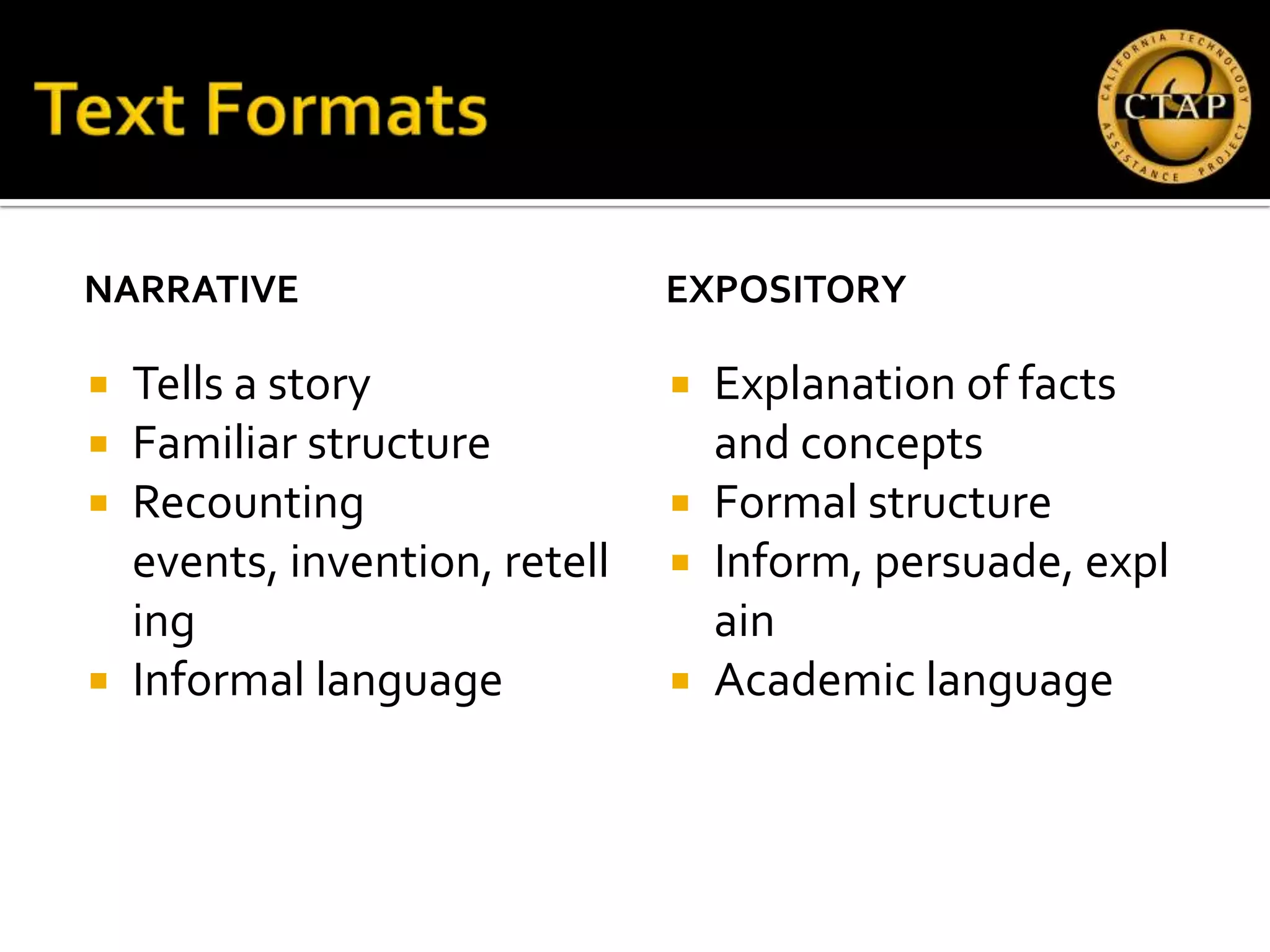
The document discusses the integration of Web 2.0 tools in promoting second language acquisition, specifically focusing on technologies like Fotobabble, Voki, and Thinglink for enhancing linguistic and discourse competencies. It emphasizes using digital media for vocabulary development and engaging students through interactive presentations and collaborations. Various methods and strategies for effective communication, language structuring, and audience interaction are also highlighted.