The document provides an overview of the evolution of the C# programming language, detailing features introduced in versions 7.x and 8.0, including improvements in pattern matching, async programming with streams, and nullable reference types. It emphasizes enhanced code efficiency and safety, while also discussing innovations such as default interface methods. The presentation by Christian Nagel encourages experimenting with new features using Visual Studio 2019 Preview.

















![C# 7.3
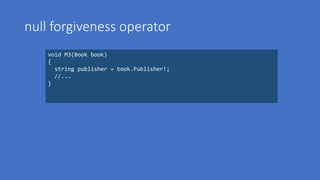
• Auto Property Field Attributes
• Generic constraints
• unmanaged, Enum, Delegate
• Expression Variables in Initializers
• Pattern-based fixed statement
• Ref local reassignment
• Stackalloc array initializers
[Serializable]
public class Foo
{
[field: NonSerialized]
public string MySecret { get; set; }
}
void Hash<T>(T value) where T : unmanaged
{
}
var d1 = stackalloc int[3] { 1, 2, 3 };
var d2 = stackalloc int[] { 1, 2, 3 };
var d3 = stackalloc[] { 1, 2, 3 };](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpv8-190227081421/85/C-What-s-next-7-x-and-8-0-20-320.jpg)




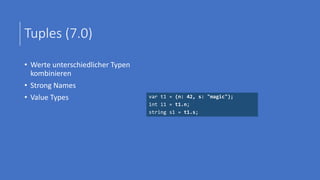
![Smallish Features (3)
• Caller expression attribute
• prototype
• Target-typed new
• prototype
• Pattern-based using
• VS Preview
• using declarations
• VS Preview
// C# 7
private Dictionary<string, List<int>> field =
new Dictionary<string, List<int>>()
{
{ "item1", new int[] { 1, 2, 3 } }
};
// C# 8
private Dictionary<string, List<int>> field =
new()
{
{ "item1", new() { 1, 2, 3 } }
};
public static class Debug
{
public static void Assert(bool condition,
[CallerArgumentExpression("condition")] string message = null);
}
Debug.Assert(array.Length == 1);
Debug.Assert(array.Length == 1, "array.Length == 1");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpv8-190227081421/85/C-What-s-next-7-x-and-8-0-25-320.jpg)








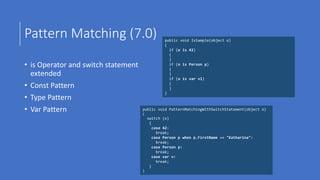
![Hat Operator
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3 };
int lastItem = arr[^1];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpv8-190227081421/85/C-What-s-next-7-x-and-8-0-35-320.jpg)
![Slice
string text1 = "the quick brown fox jumped over the lazy dogs";
string text2 = text1[4..8];
string text3 = text1[^4..^1];
string text4 = text1[10..];
string text5 = text1[..8];
string text6 = text1[..];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpv8-190227081421/85/C-What-s-next-7-x-and-8-0-36-320.jpg)

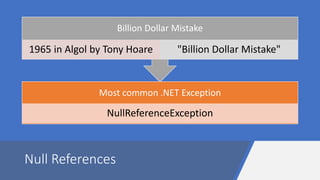
![Null Conditional Operator (C# 6)
• Reduce Null-Checks
int? length = customers?.Length;
Customer first = customers?[0];
int? count = customers?[0]?.Orders?.Count();
public void OnPropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] string propertyName = null) =>
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csharpv8-190227081421/85/C-What-s-next-7-x-and-8-0-42-320.jpg)