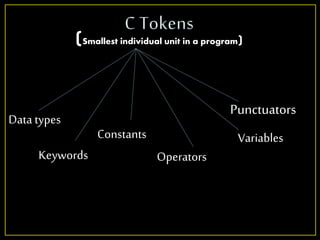
The document provides an overview of the C programming language, detailing its development at AT&T's Bell Labs and key features such as identifiers, keywords, and data types. It explains the rules for naming identifiers and variables, emphasizing case sensitivity and restrictions on character usage. Additionally, it outlines how to declare and initialize variables in C, highlighting the structure and types involved.