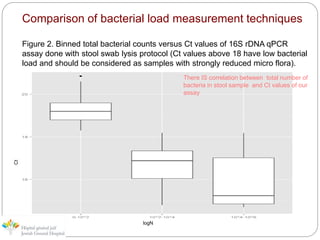
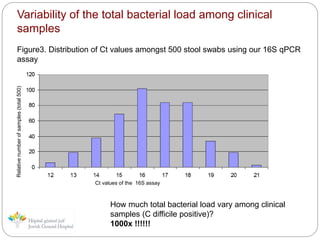
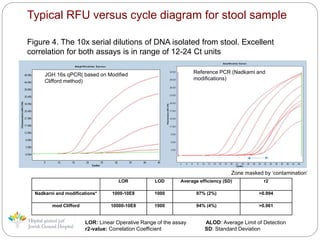
The document describes a new method developed by Jewish General Hospital in collaboration with McGill University for determining Clostridium difficile infections using quantitative PCR. The method detects the total bacterial load in stool samples using a 16S rDNA qPCR assay, which provides a measurement of total microbiota as a means of normalizing results. This allows distinguishing symptomatic patients from asymptomatic carriers by establishing a threshold of relative pathogen concentration. The method was tested on 500 stool samples and showed variability in total bacterial loads between individuals. It provides advantages over current qualitative PCR methods and could be incorporated into diagnostic assays.