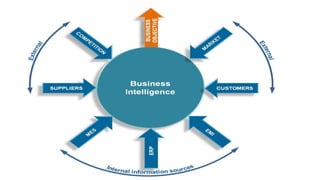
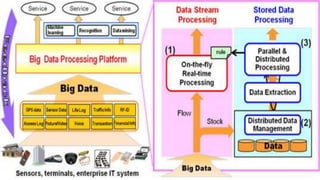
Business intelligence (BI) involves strategies and technologies used to analyze business data and present information to support decision-making. Big data refers to extremely large datasets that require advanced analytics to derive insights. BI technologies provide historical, current, and predictive views of business operations through reporting, analytics, and data mining. While BI helps with reporting, budgeting, forecasting, and promotions, it can be costly and expose information to risks. Big data allows for detecting fraud, gaining competitive insights, and improving customer service and profits through real-time analysis, but poses logistical and privacy challenges.