The document discusses the critical role of big data and business analytics in optimizing organizational processes and enhancing decision-making across various industries. It emphasizes the use of descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics to improve operational efficiency, increase revenue, and achieve competitive differentiation. While big data adoption in India is expected to grow, challenges such as data quality, privacy concerns, and organizational inertia remain significant barriers to its effective implementation.

![society as the Internet has become as more data may lead to more accurate analyses and
hence better decisions”: as per SAS, one of the global market leaders in this segment.
Analytics2
is the methodology that uses statistical & operations research (OR)
techniques, IT (Information Technology) software to make sense of trends, visualize
them and to predict outcomes with a high degree of accuracy. There are 3 types of
analytics:
1. Descriptive analytics: The use of simple statistical techniques to describe what is
contained in a data set/database e.g. a bar chart to depict number of shoppers
segmented by tiered levels of purchases (small/medium/high value). Techniques
include measures of central tendency, measures of dispersion, charts, graphs,
sorting methods, frequency distributions, probability distributions, and sampling
methods.
2. Predictive analytics: It involves the use of advanced statistical, OR (Operations
Research) and IT (information Technology) software to identify variables whose
behavior can be predicted and to build models to identify/predict trends not
observed in descriptive analysis e.g. using techniques like multiple regression to
identify the presence or absence of a relationship between selected variables that
can help explain/predict their behavior due to interdependence if any. You may
use statistical methods like multiple regression and ANOVA (Analysis of
Variance), information system methods like data mining and sorting, operations
research methods like forecasting models.
3. Prescriptive analytics: It is the use of decision science, management science and
applied mathematical techniques to help make optimal use of allocated resources
e.g. linear programming models may be used to optimally allocate budgets for a
big retail store that wants to get an optimal amount of customers with a limited
campaign budget. Operations research methodologies like linear programming
and decision theory.
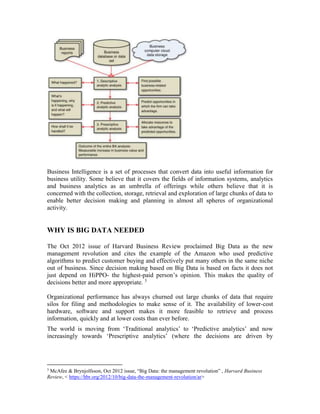
Business Analytics follows the same methodology as plain analytics but with the
caveat that the outcome of the analytic analysis must make a clear and measurable
impact on business performance. It reports results like business intelligence but in
addition also explains that why the results have occurred apart from just the storage
and reporting. (Refer Figure 1)
Figure 1: Business Analytics Process [Business Analytics: Principles, Concepts &
Applications by Schniederjans & Starkey (Pearson)]
2
Schniederjans & Starkey, 2015, “Business Analytics: Principles, Concepts & Applications”, Pearson,
USA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cdc-consultingahead-230102091749-f76c4ceb/85/BIG-DATA-BUSINESS-ANALYTICS-2-320.jpg)