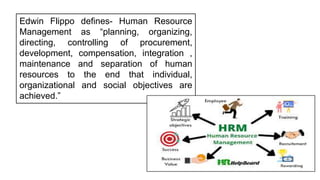
The document discusses human resource management and the importance of HR functions for organizations. It defines HRM as planning, organizing, and managing human resources to achieve individual and organizational goals. Key HR functions include recruitment and staffing, compensation, training, employee relations, and compliance. Common organizational structures for HR departments include functional, flat, and matrix structures. The document also recommends readings on innovative HR practices and the structure of HR departments.