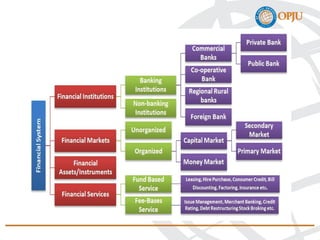
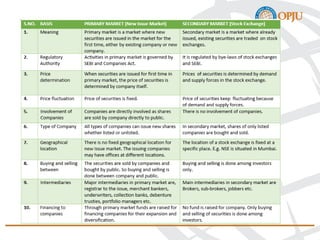
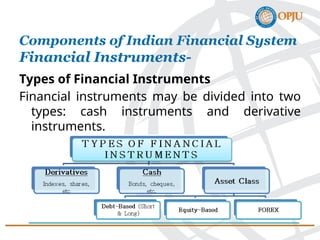
The document provides an overview of the Indian financial system, defining it as a complex network of institutions, practices, and markets that facilitates the transfer of funds between savers and borrowers. It outlines key components such as financial institutions, financial markets, financial instruments, and financial services, detailing their roles and classifications. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of these elements in promoting economic growth and efficient allocation of resources.