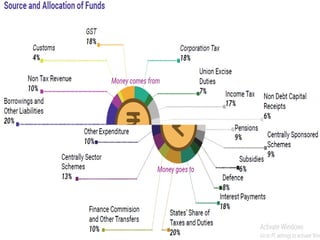
The document summarizes key announcements from the Indian Union Budget 2020-21 across several sectors:
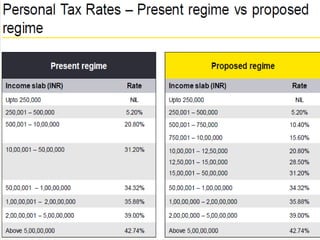
- Individual tax proposals include a new optional simplified personal tax regime, changes to residency rules, and taxation of employer contributions to provident funds above Rs. 750,000. Dividend income will now be taxed in the hands of recipients.
- Measures to stimulate growth include tax exemptions for sovereign wealth funds, no change in corporate tax rates but a reduced 15% rate for new power sector companies. Concessional borrowing rates were extended.
- Key sectors highlighted include agriculture and food processing, education and skill development, and infrastructure, transport, and power, with increased allocations and policy initiatives outlined