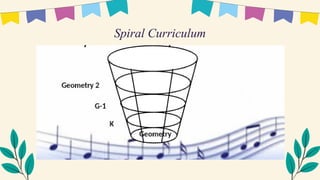
The document discusses Jerome Bruner's constructivist theory, highlighting the development of a child's knowledge representation through enactive, iconic, and symbolic stages. It emphasizes the importance of a spiral curriculum that allows students to build upon prior knowledge while developing problem-solving skills. Additionally, it outlines key principles of discovery learning and effective instruction, including the organization of knowledge and the sequencing of lessons.