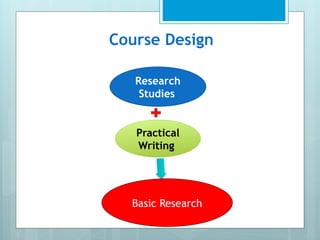
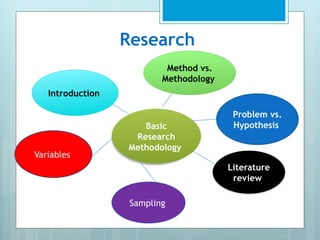
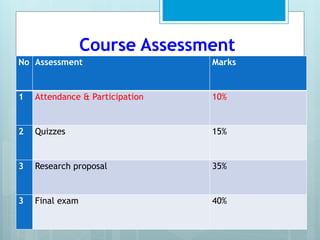
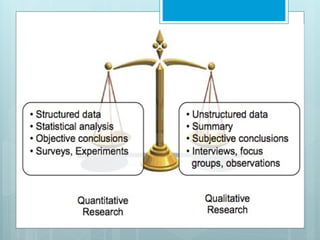
The document outlines a course on Basic Research Method taught by Abdirahman M. at the Somaliland Civil Service Institute, covering key concepts in research methodology, design, and assessment methods. It includes topics such as types of research, qualitative vs. quantitative approaches, and the components of a research thesis. The course aims to equip students with the necessary skills for conducting their own research projects.