This document summarizes a presentation on knowledge management and its application to healthcare commissioning.
The presentation covers:
1) An introduction to knowledge management and the speakers.
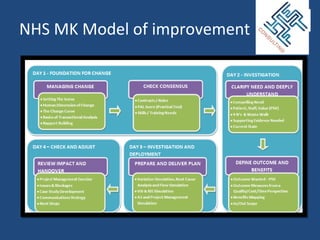
2) An overview of how knowledge management can be applied, from applying existing knowledge to continuing to learn.
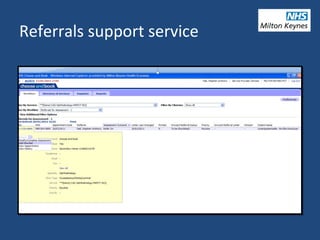
3) An example of how data on referrals is being used to improve referrals management.
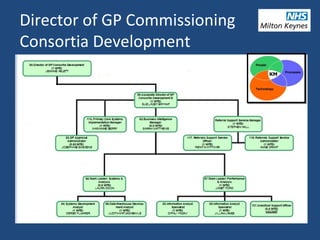
4) A discussion of how knowledge management supports various stages of the commissioning process.
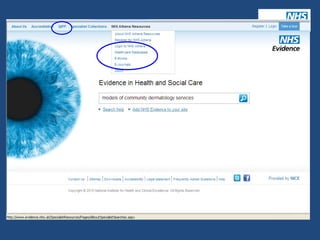
5) A librarian discusses resources for sourcing evidence to inform clinical practice and commissioning decisions.
The overall message is that systematically capturing and sharing knowledge can improve healthcare outcomes and save costs by ensuring the right knowledge reaches decision-makers