This document provides information about bridges, including:
1) It discusses the history of bridge construction from early wooden bridges built by humans to more advanced stone and iron bridges built by ancient Romans and others.
2) It outlines the importance of bridges for transportation and society.
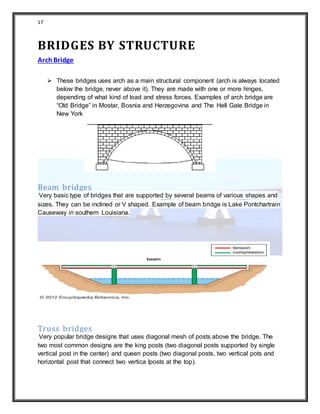
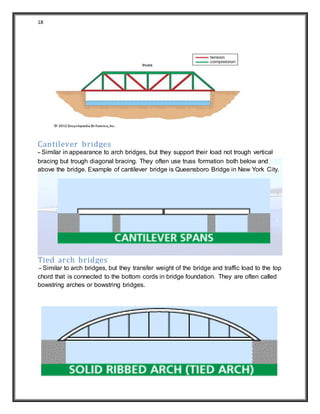
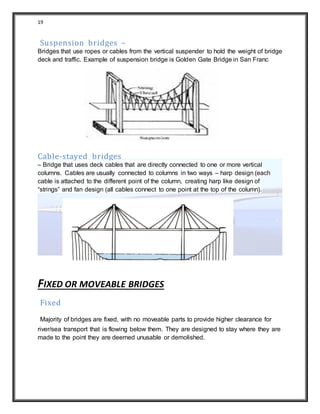
3) It describes different types of bridges based on their structure, materials used, and whether they are fixed or movable. The types discussed include arch, beam, truss, and cantilever bridges.