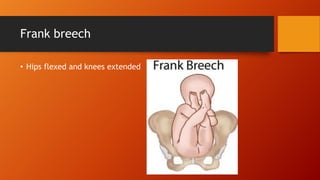
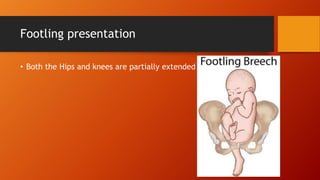
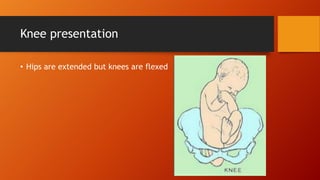
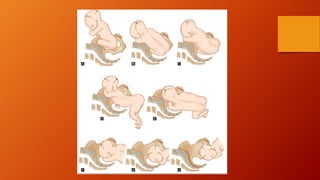
This document discusses breech presentation during childbirth. It defines breech presentation as when the fetus is positioned longitudinally with the buttocks or feet facing the birth canal. It classifies breech presentations as complete breech, incomplete breech (frank breech or footling), or knee presentation. Common causes of breech presentation include prematurity, factors preventing fetal version, and fetal abnormalities. Breech presentation is diagnosed through clinical examination including abdominal and vaginal palpation as well as ultrasound. The mechanism of labor in breech presentation and management options like external cephalic version, vaginal delivery, and cesarean section are also described.