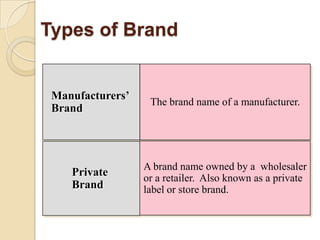
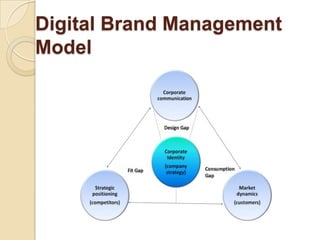
This document provides an overview of brand communication. It defines brand communication as activities that influence customer opinions of a company and its products. It discusses objectives of brand communication such as clearly conveying messages, connecting with prospects emotionally, and building loyalty. The document outlines a 10 step process for brand communication and discusses strategies, brand awareness, elements, and types of brands. It also introduces a digital brand management model focusing on design, consumption, and fit gaps.