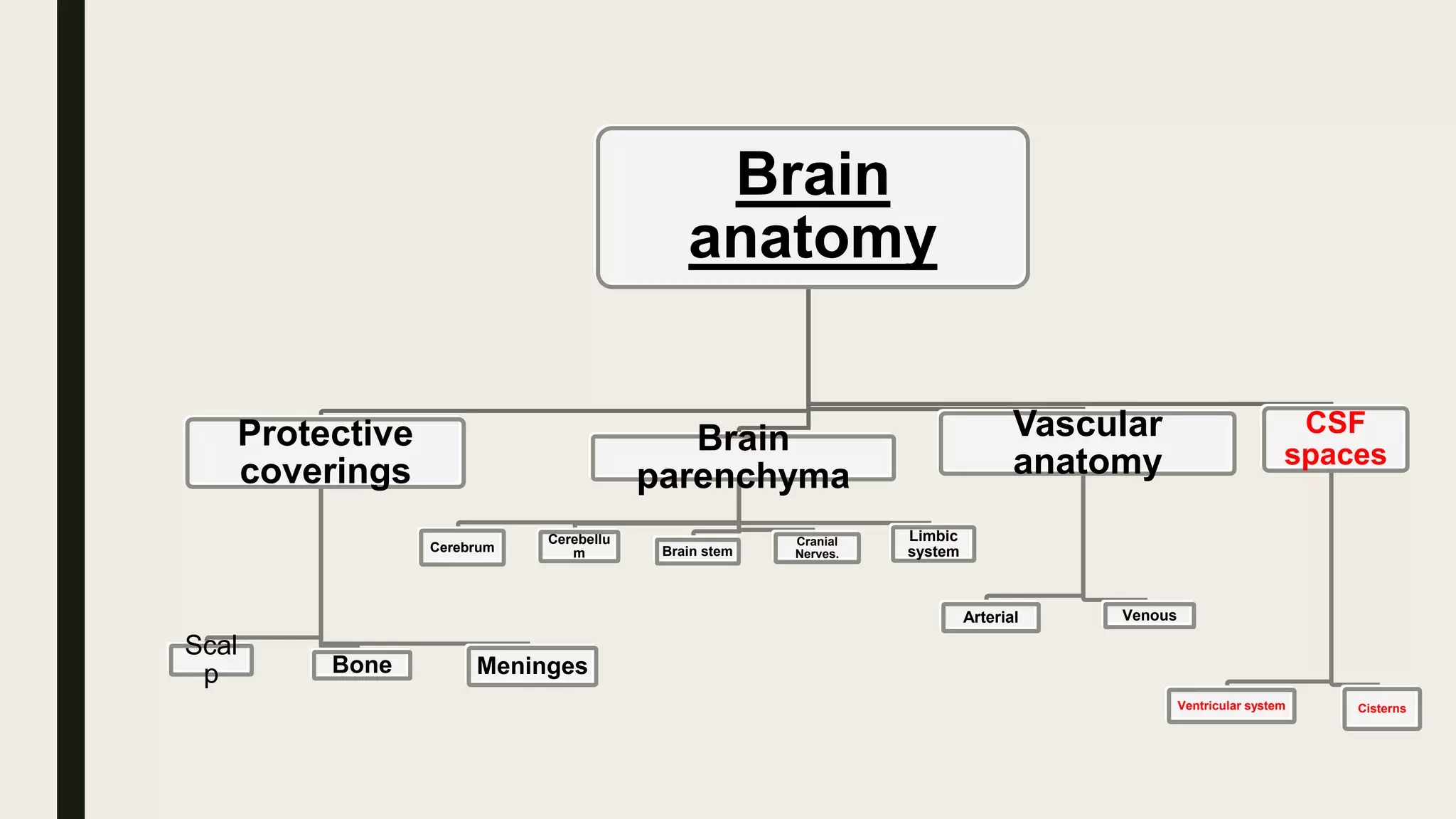
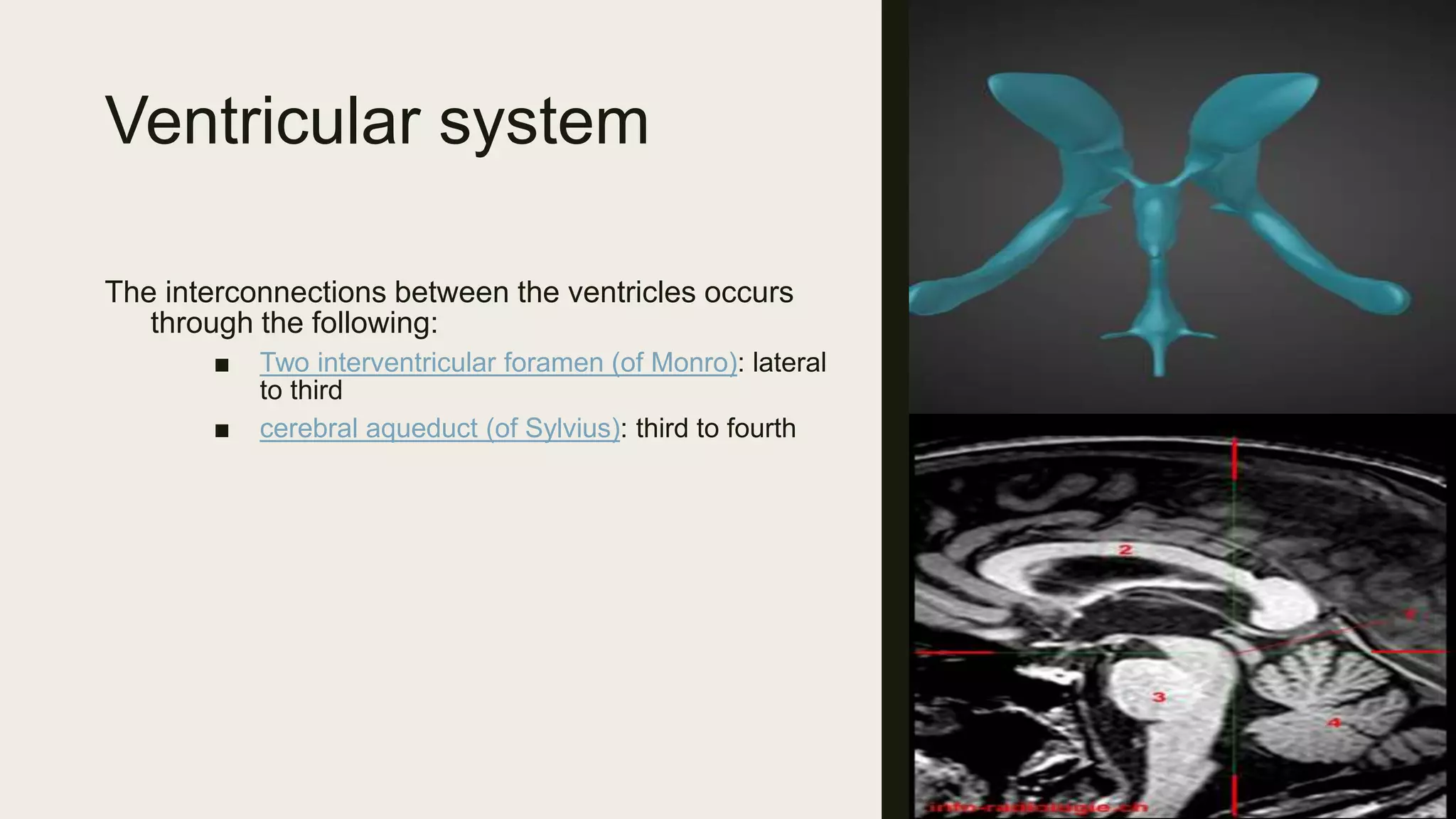
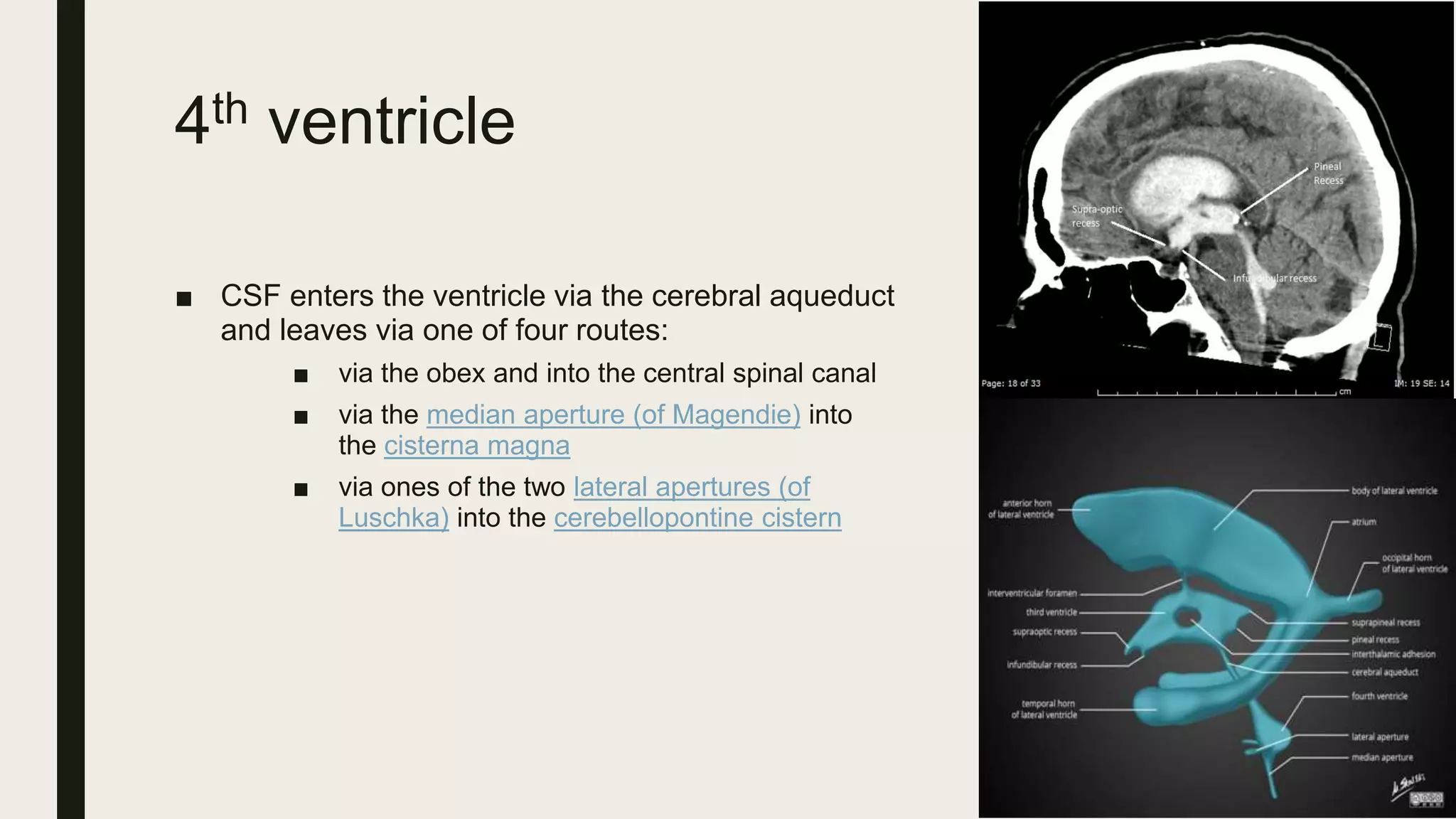
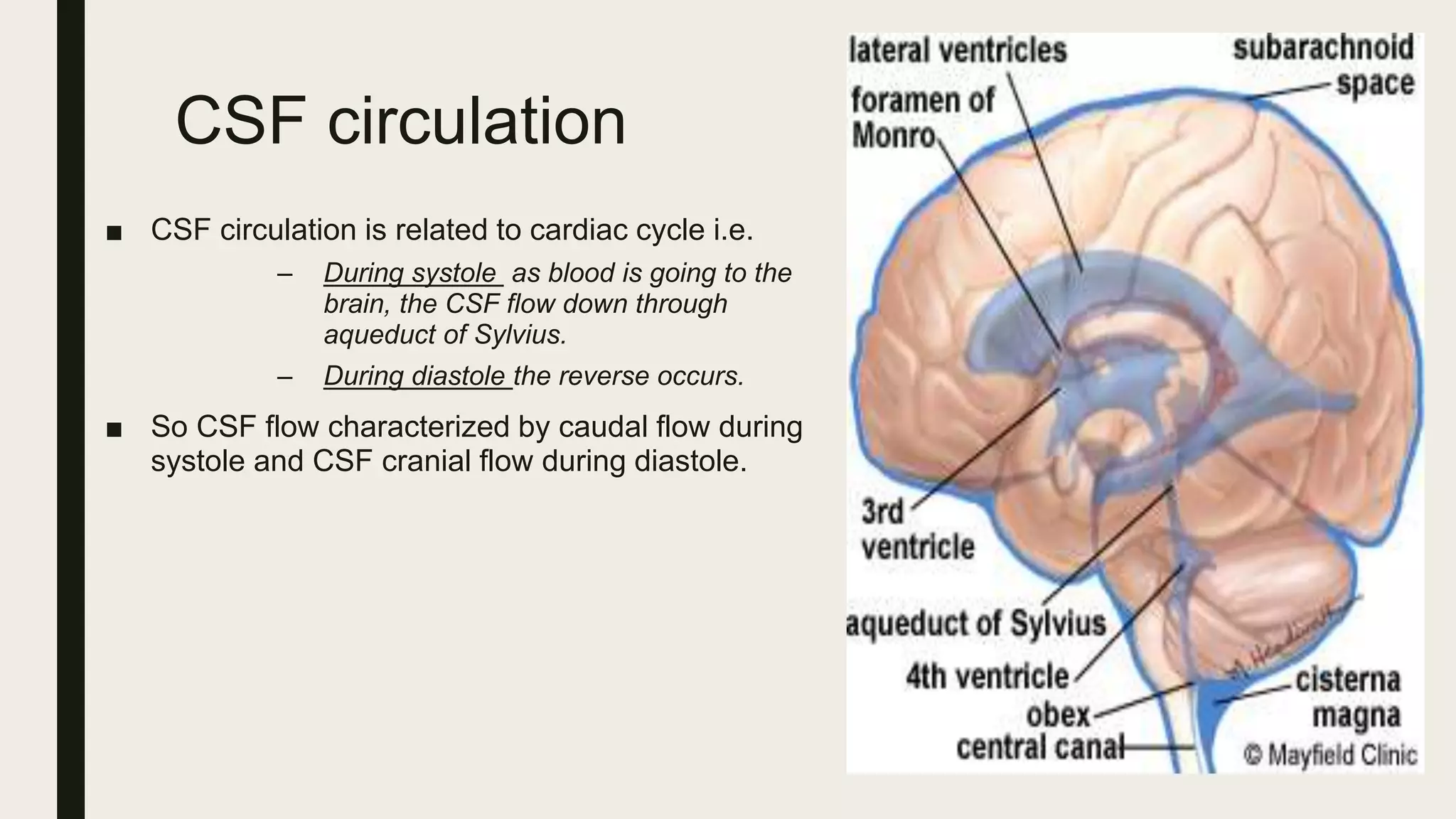
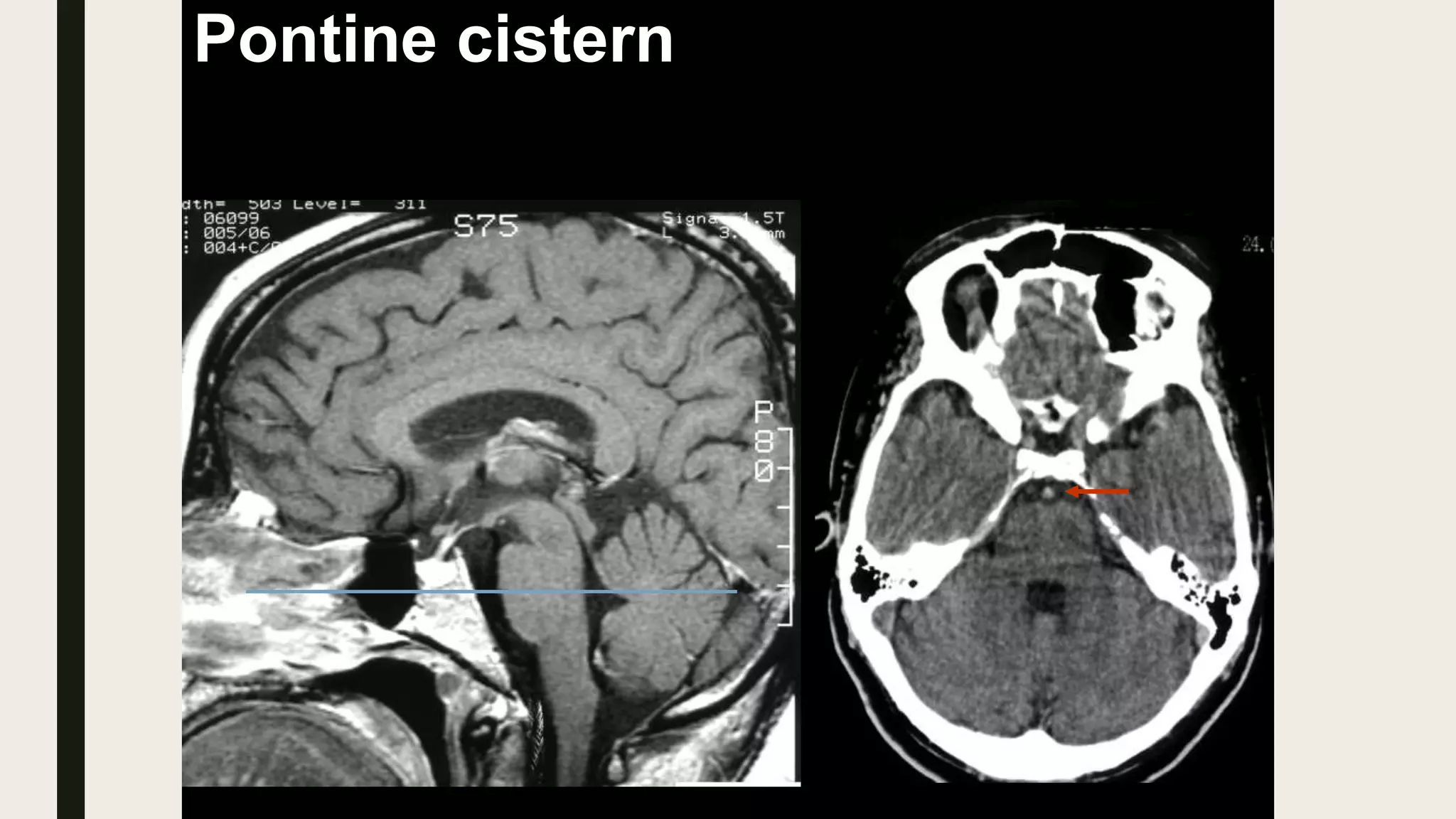
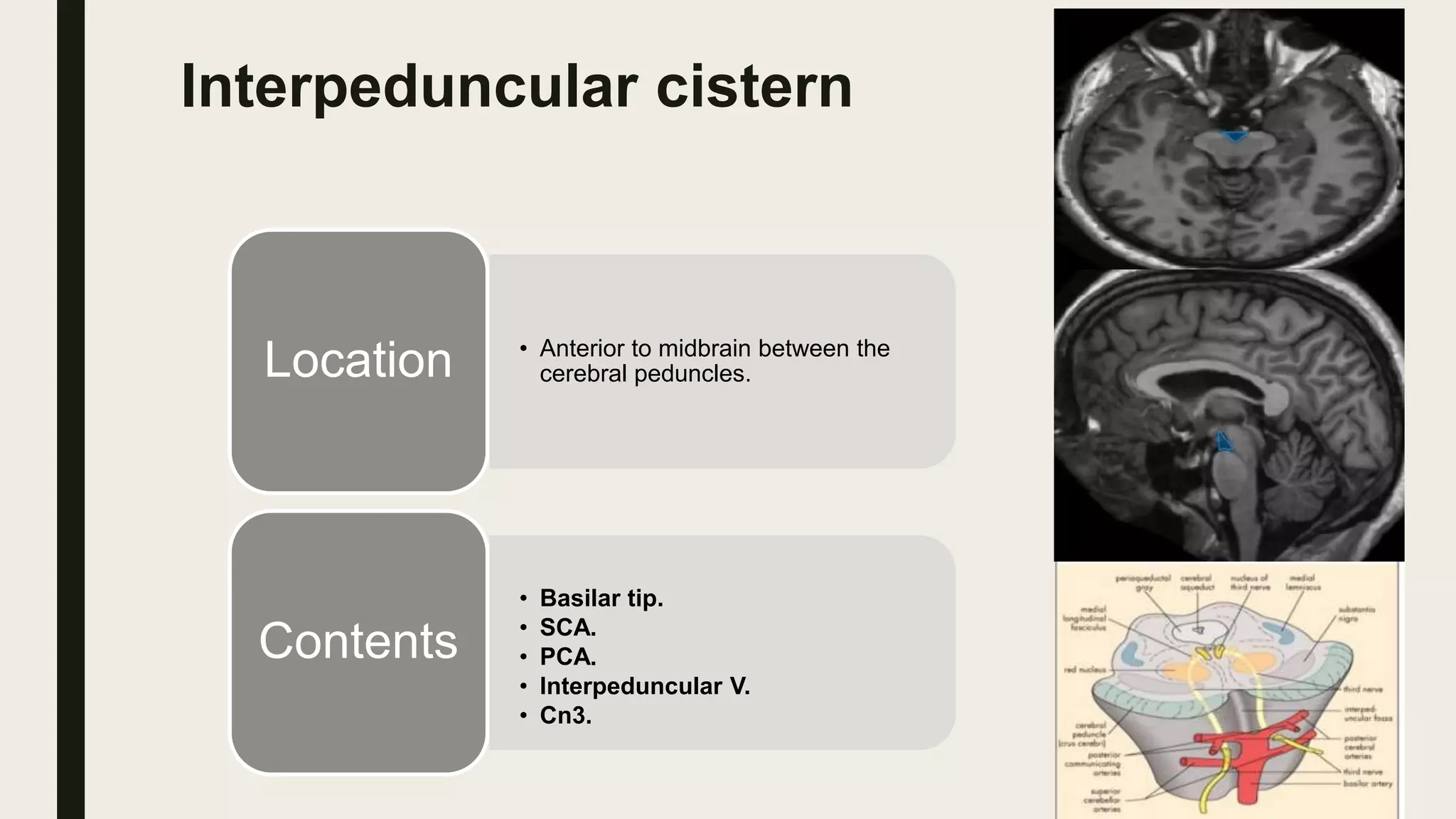
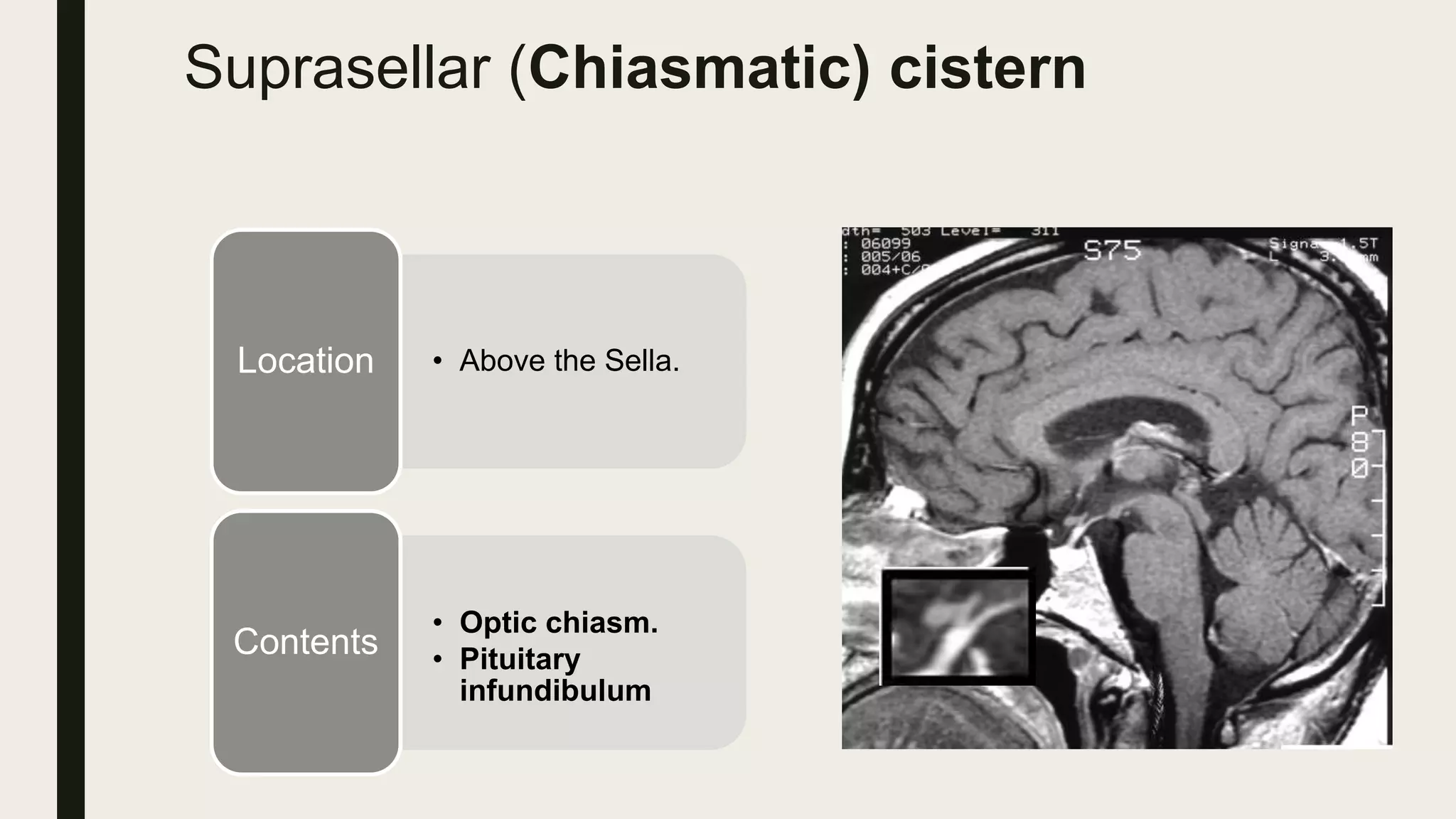
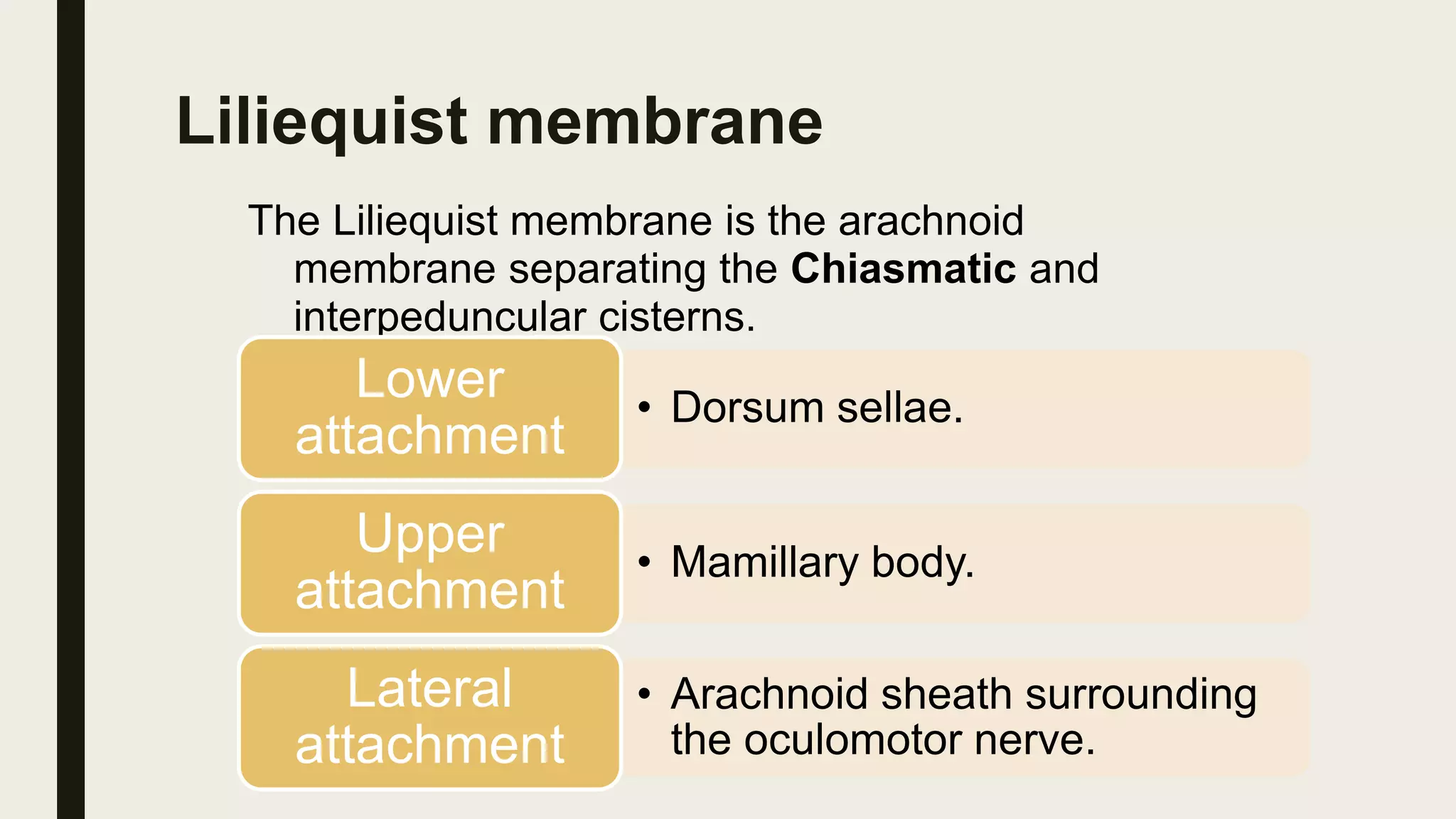
This document contains Islamic greetings and supplications. It begins with the Islamic greeting "Bismillah ar-Rahman ar-Rahim" which means "In the name of God, the Most Gracious, the Most Merciful." It then praises God and sends prayers upon the Prophet Muhammad. The document concludes by bearing witness that there is no God but Allah and asking Allah for forgiveness and guidance.