Embed presentation
Downloaded 12 times
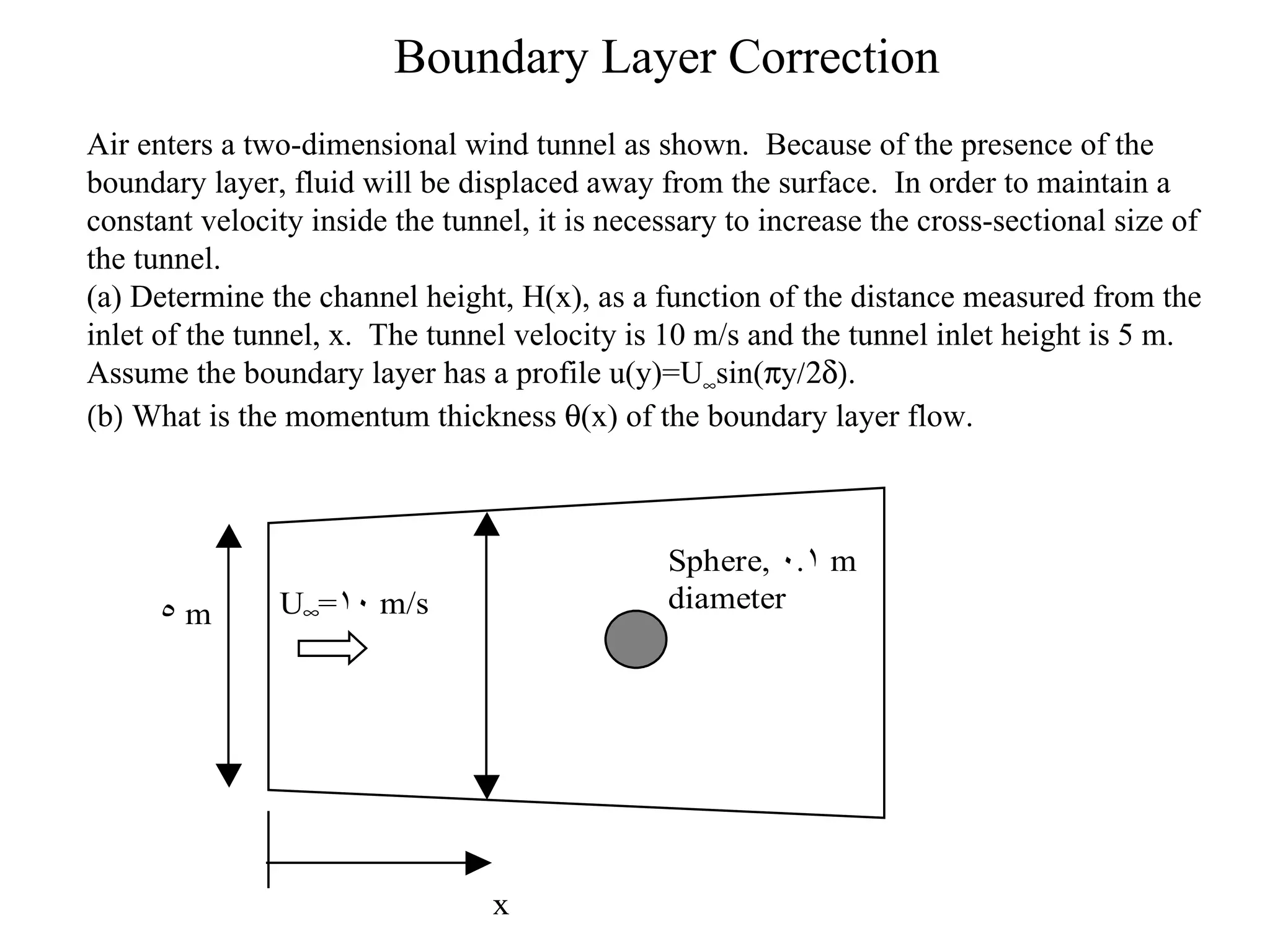
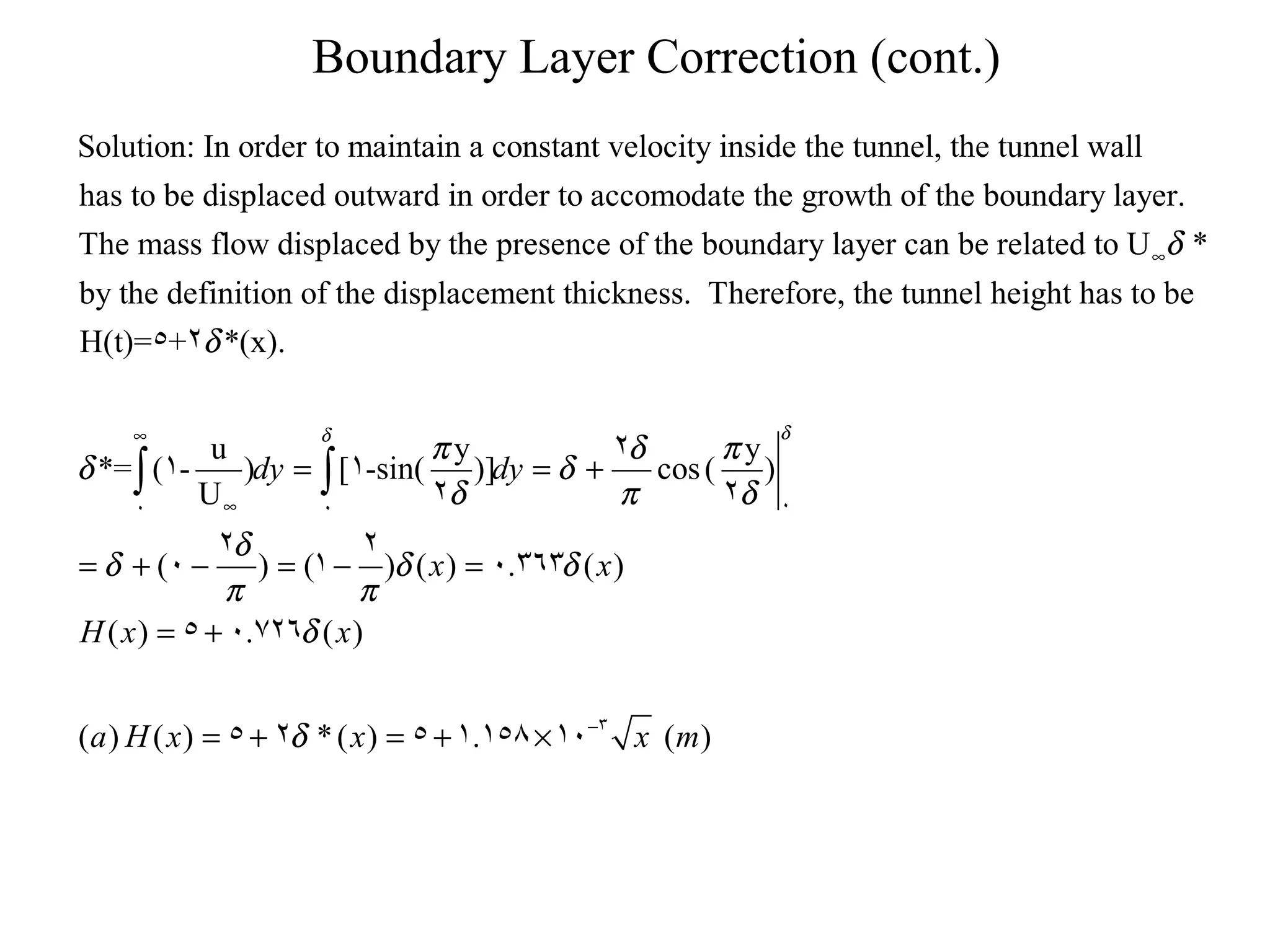
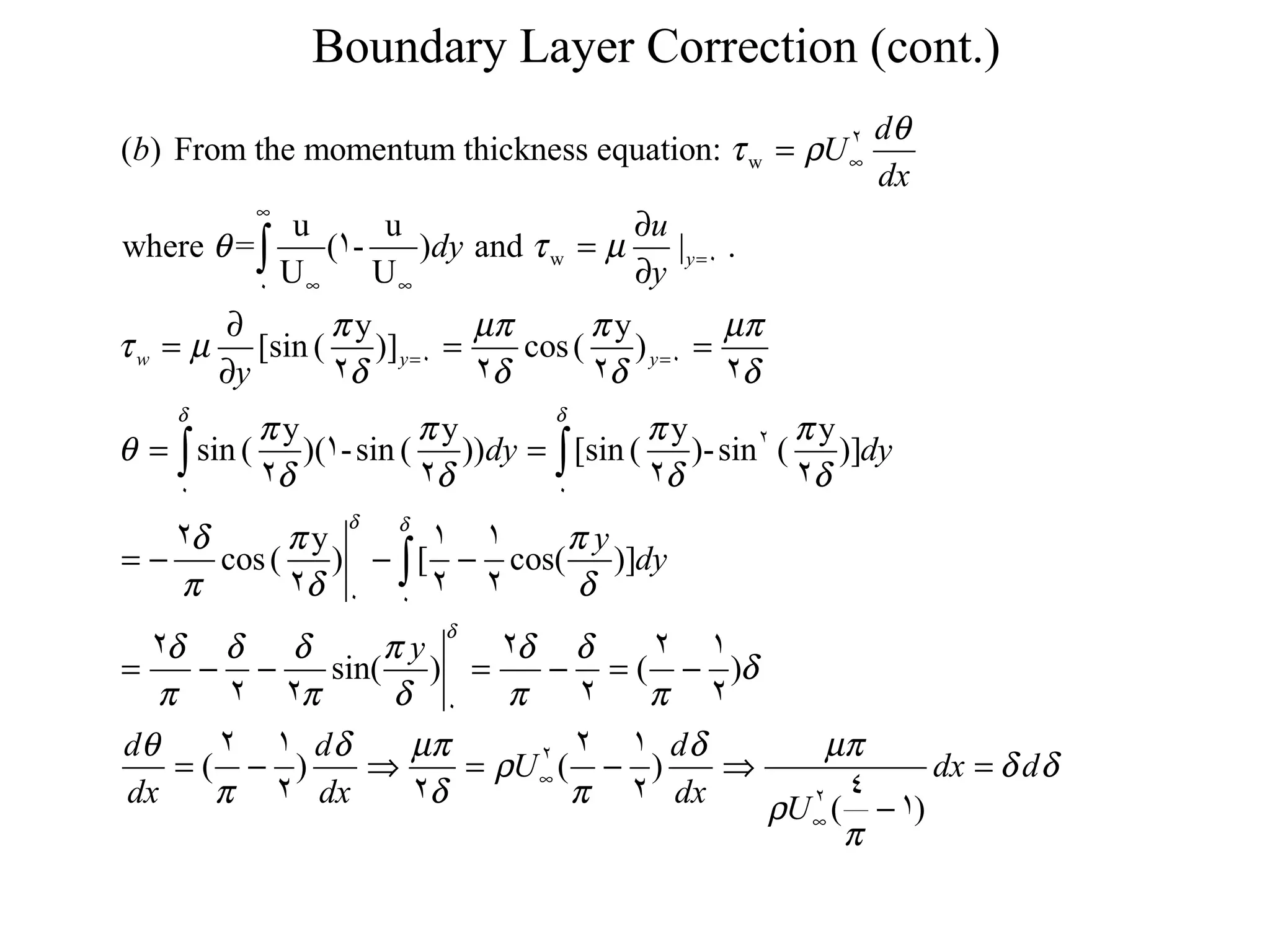
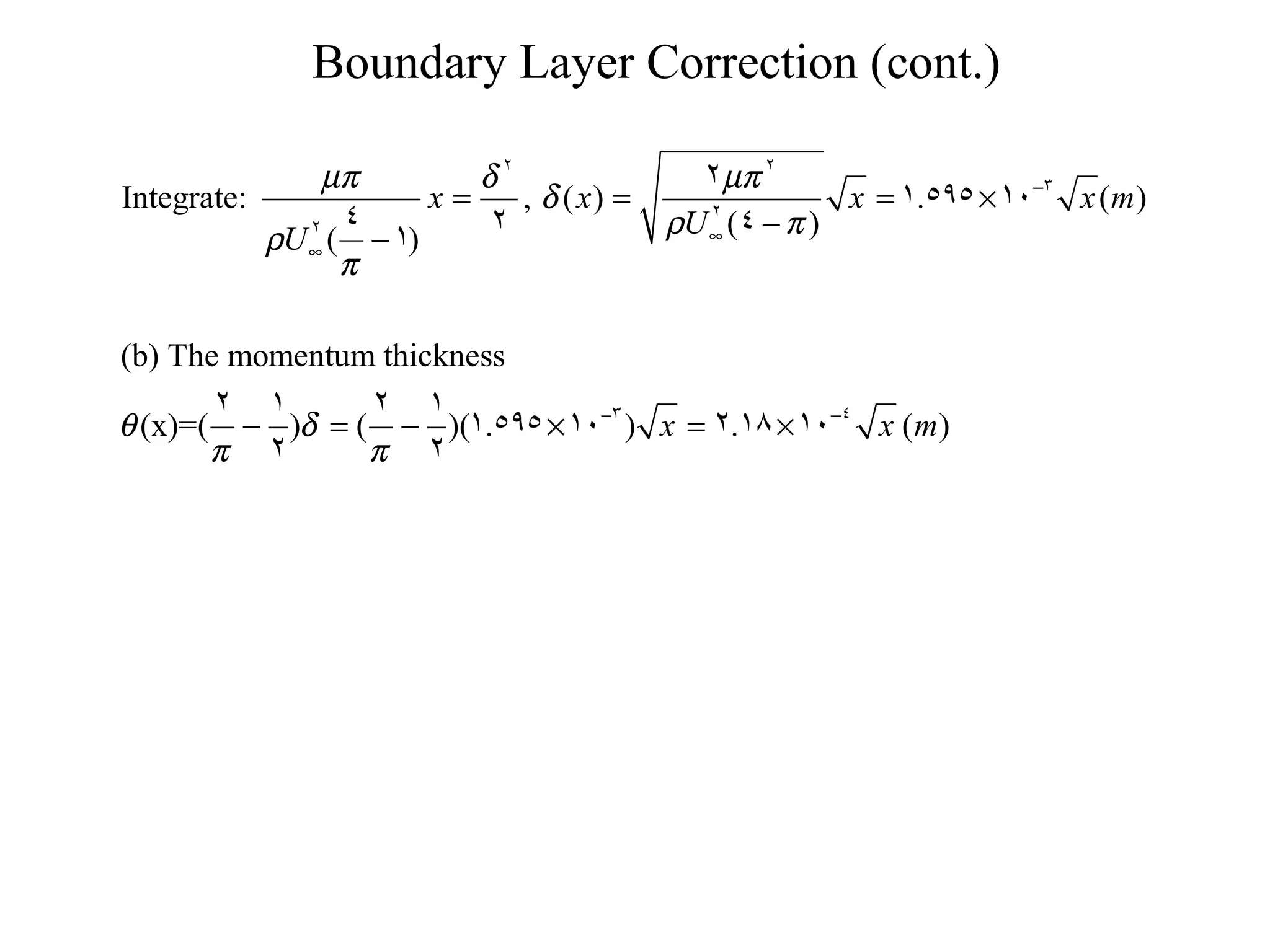
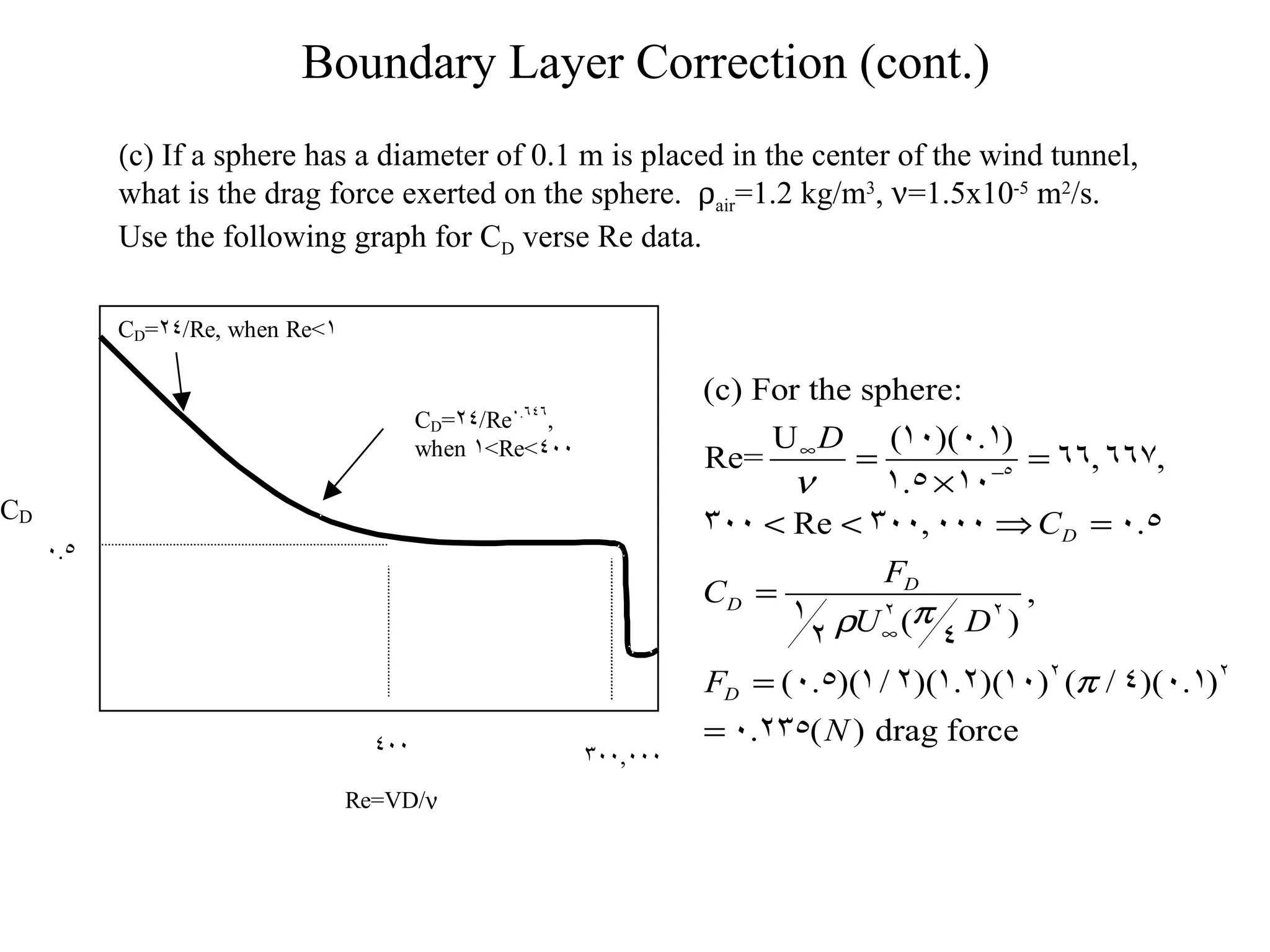
This document discusses boundary layer correction in a two-dimensional wind tunnel. The boundary layer causes fluid to be displaced away from the tunnel surface, requiring the tunnel cross-section to increase downstream to maintain a constant velocity. The document asks to determine the tunnel height as a function of distance from the inlet, calculate the boundary layer momentum thickness, and estimate the drag force on a sphere placed in the tunnel center.




