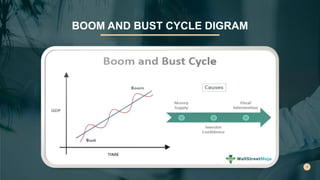
The boom and bust cycle describes alternating phases of economic growth (boom) and decline (bust) that occur in capitalist economies. During a boom, the economy grows strongly with high employment and returns for investors. This is followed by a bust, where the economy contracts and jobs and investment returns decline. While driven by economic fundamentals, boom and bust cycles are also influenced by investor and consumer psychology. Behavioral indicators provide insight into how cognitive biases, social factors, and other behaviors can influence investor decision making and exacerbate boom and bust patterns.