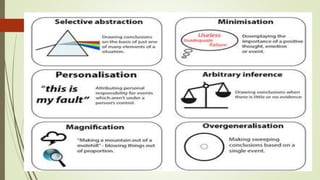
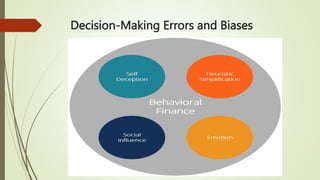
Behavioral finance is the study of how psychology affects the behavior of investors and financial markets. Traditional finance assumes investors are rational, but behavioral finance recognizes that investors are normal humans subject to cognitive biases. Some of the key concepts of behavioral finance include that investors have limits to self-control and are influenced by biases like overconfidence, confirmation bias, and narrative deception when processing information.