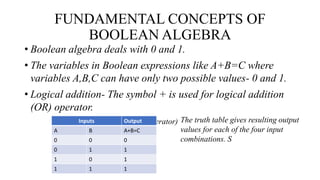
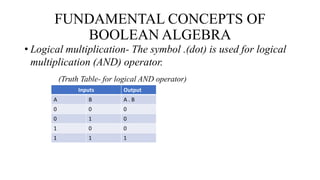
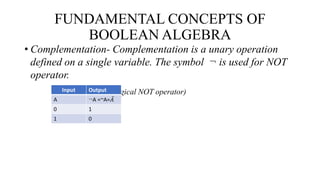
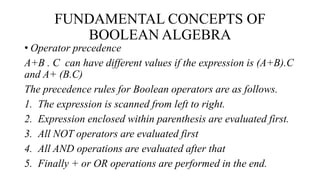
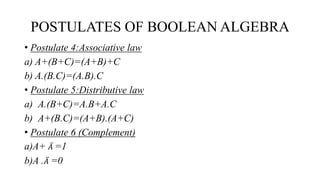
Boolean algebra uses the values true (1) and false (0) for variables. It defines three main operations: AND (.); OR (+); and NOT (¬). Boolean algebra was introduced by George Boole and is useful for designing computer logic circuits. It has fundamental concepts like logical addition, multiplication, and complementation defined by truth tables. Boolean algebra also defines postulates like identity, commutative, associative, distributive laws and the principle of duality.