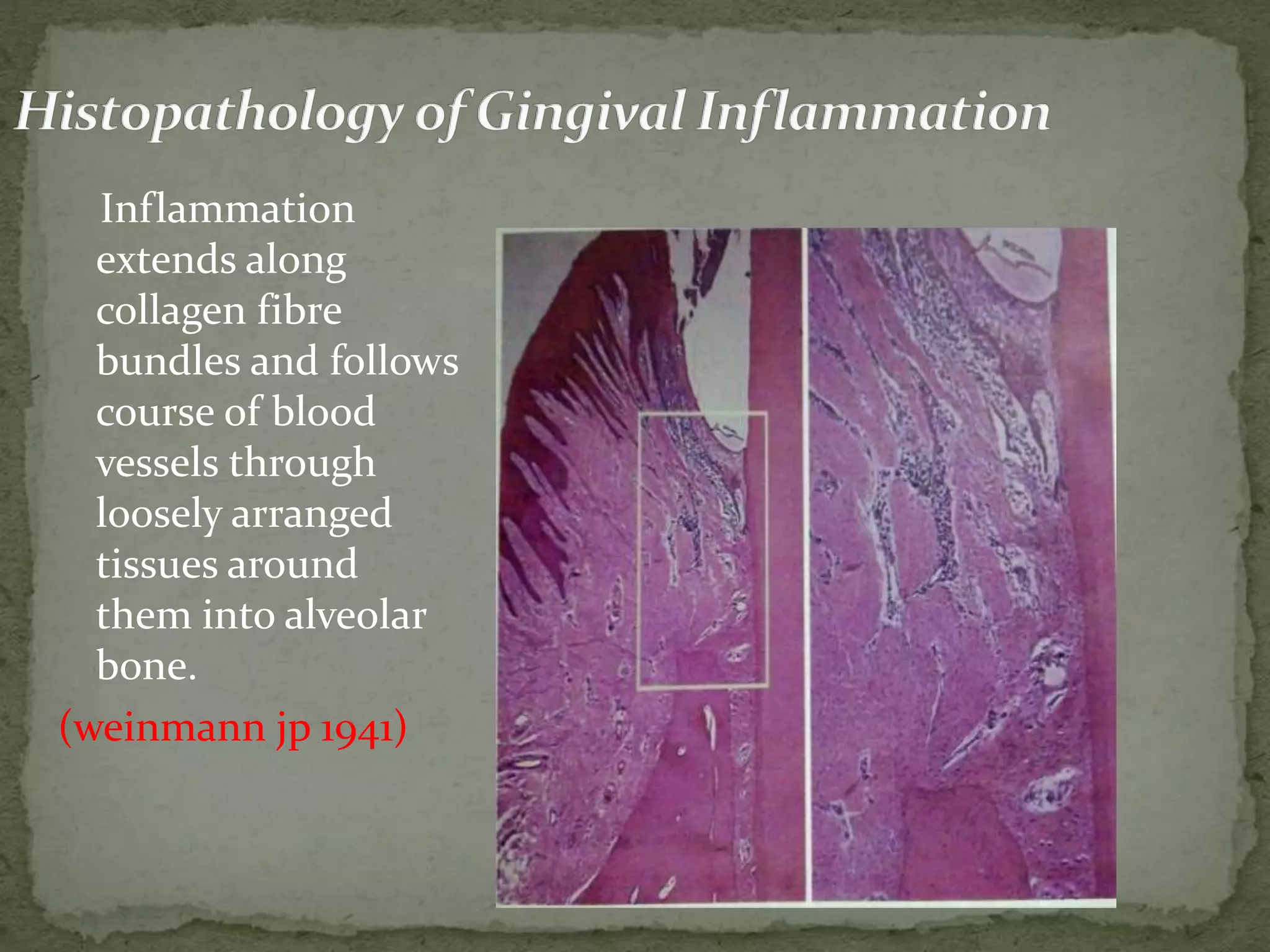
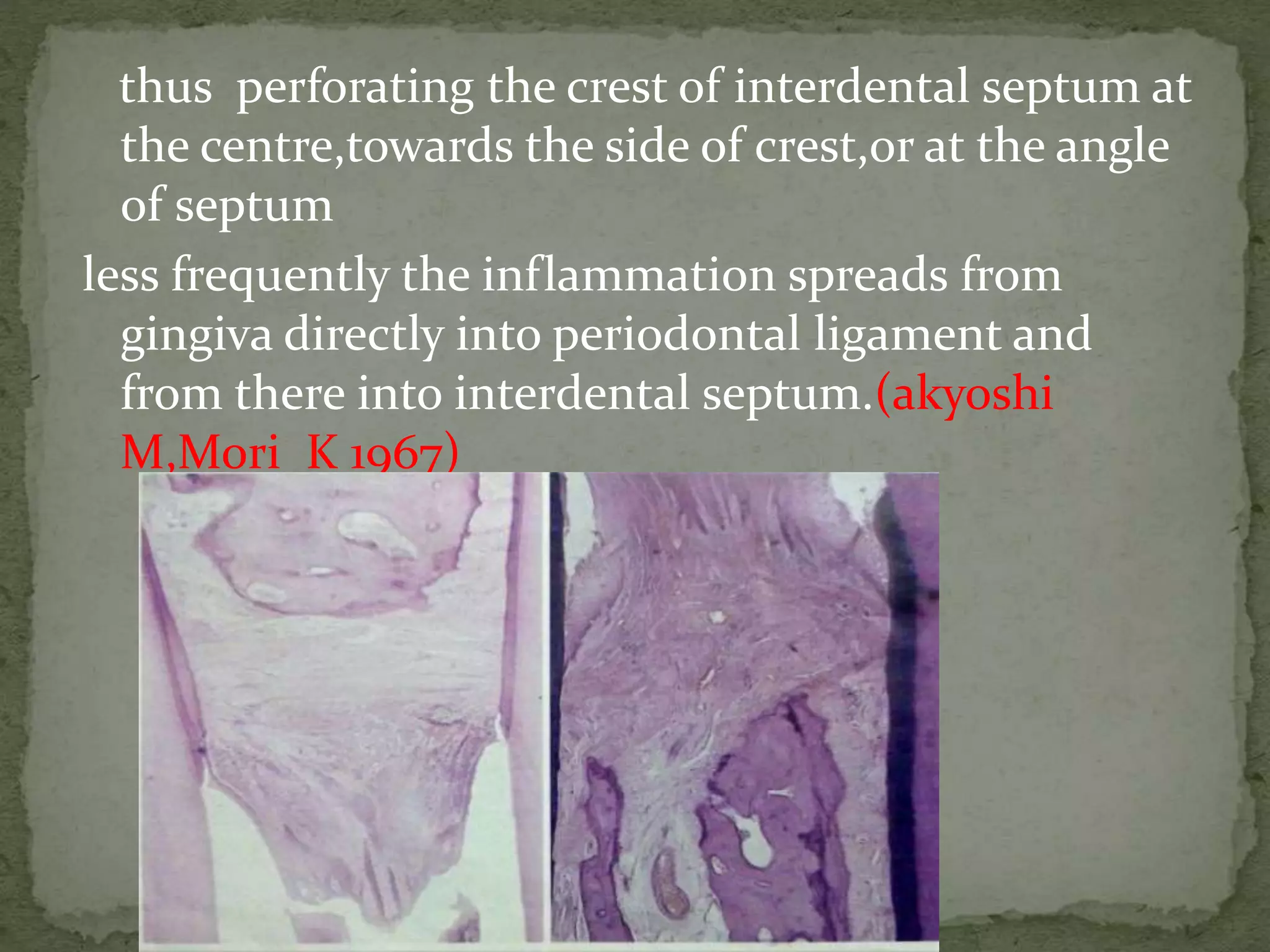
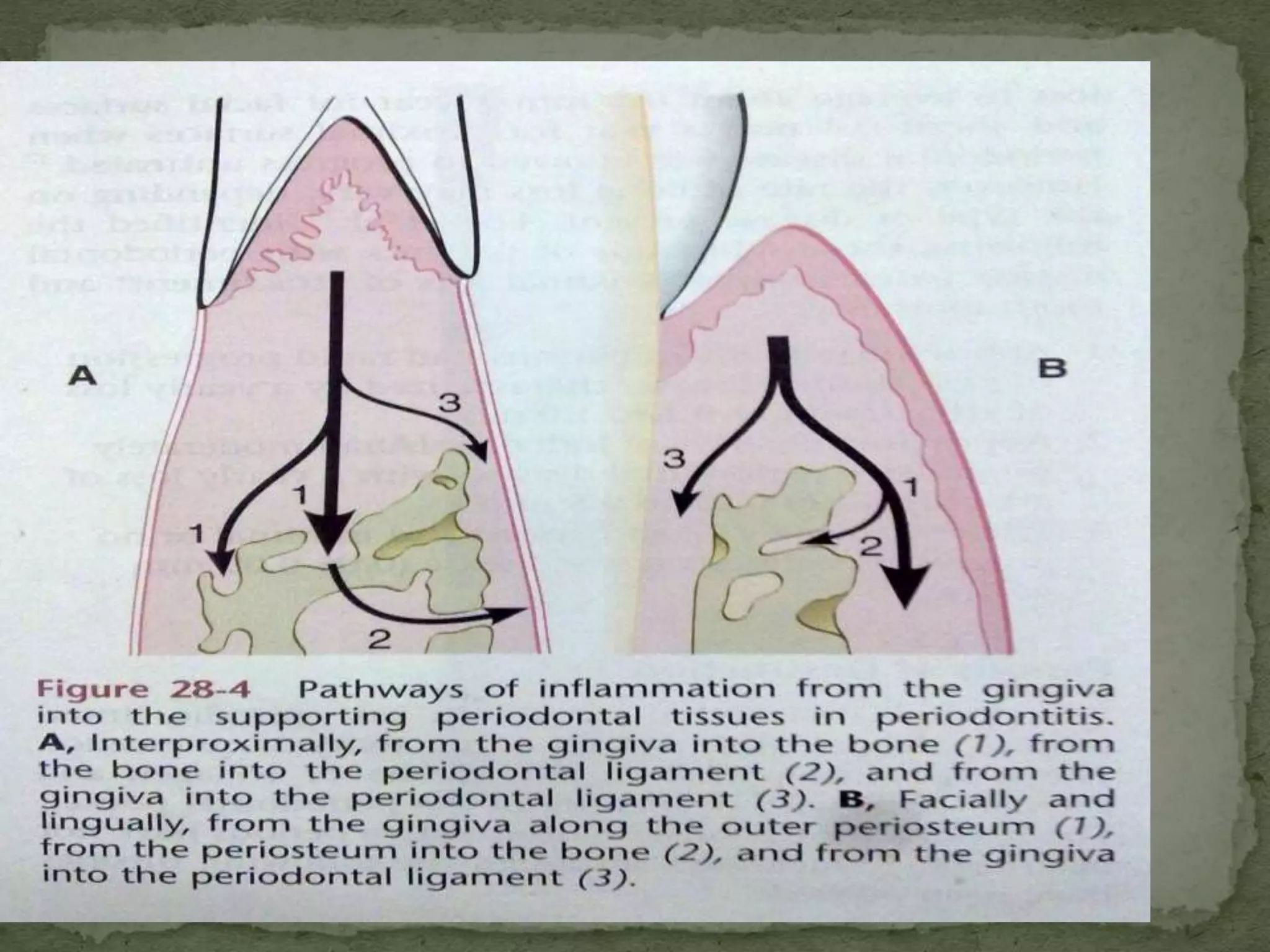
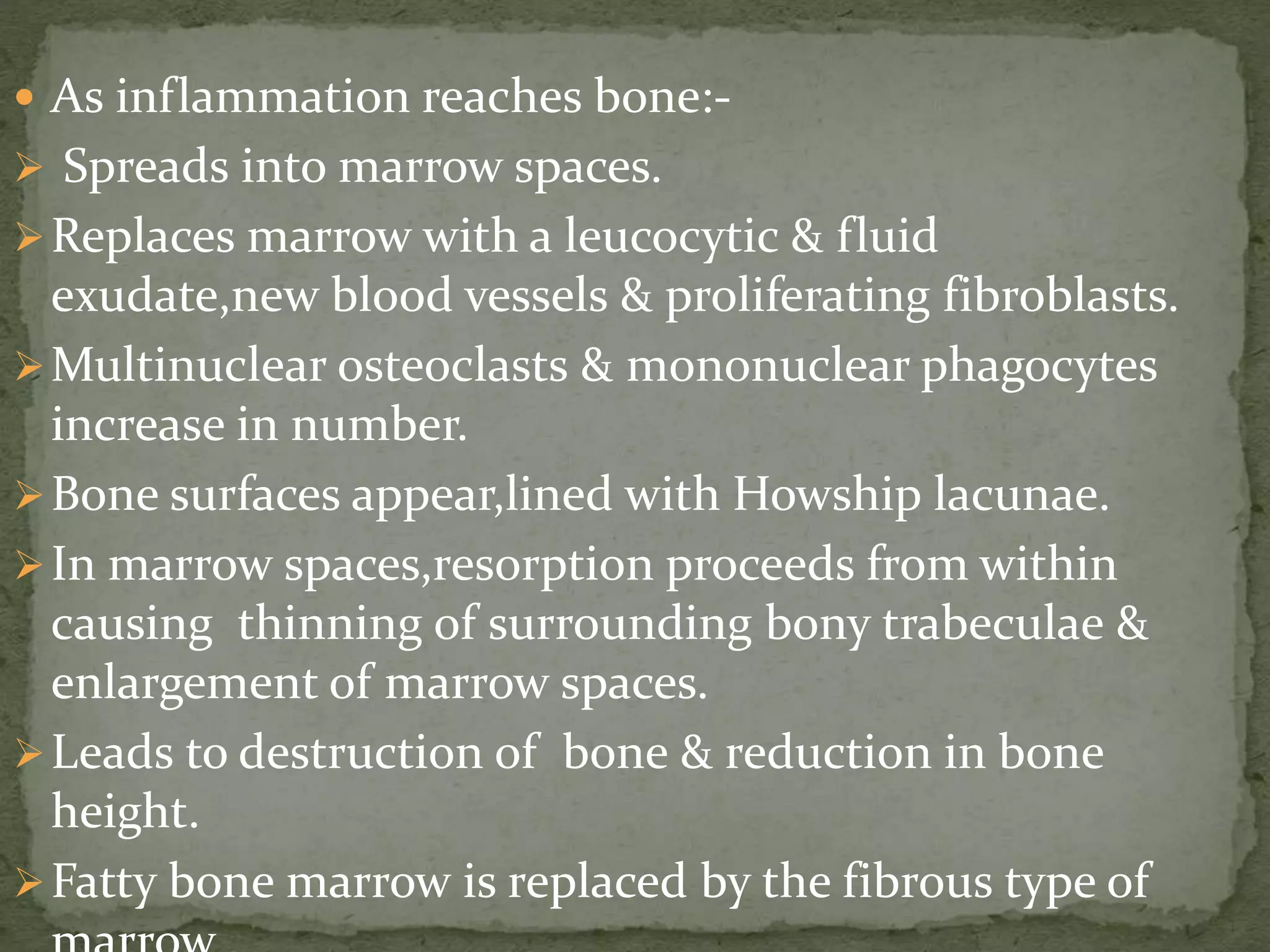
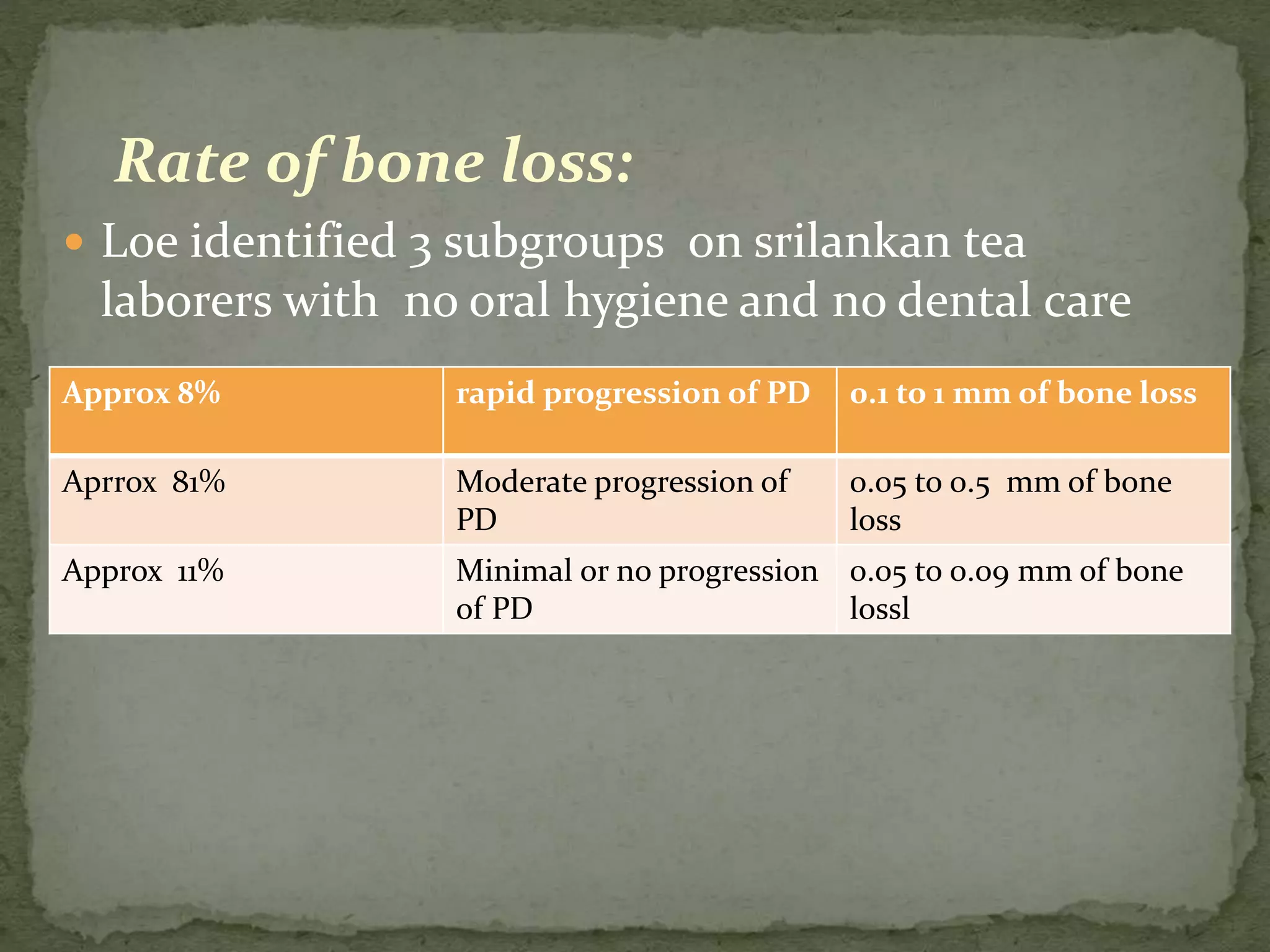
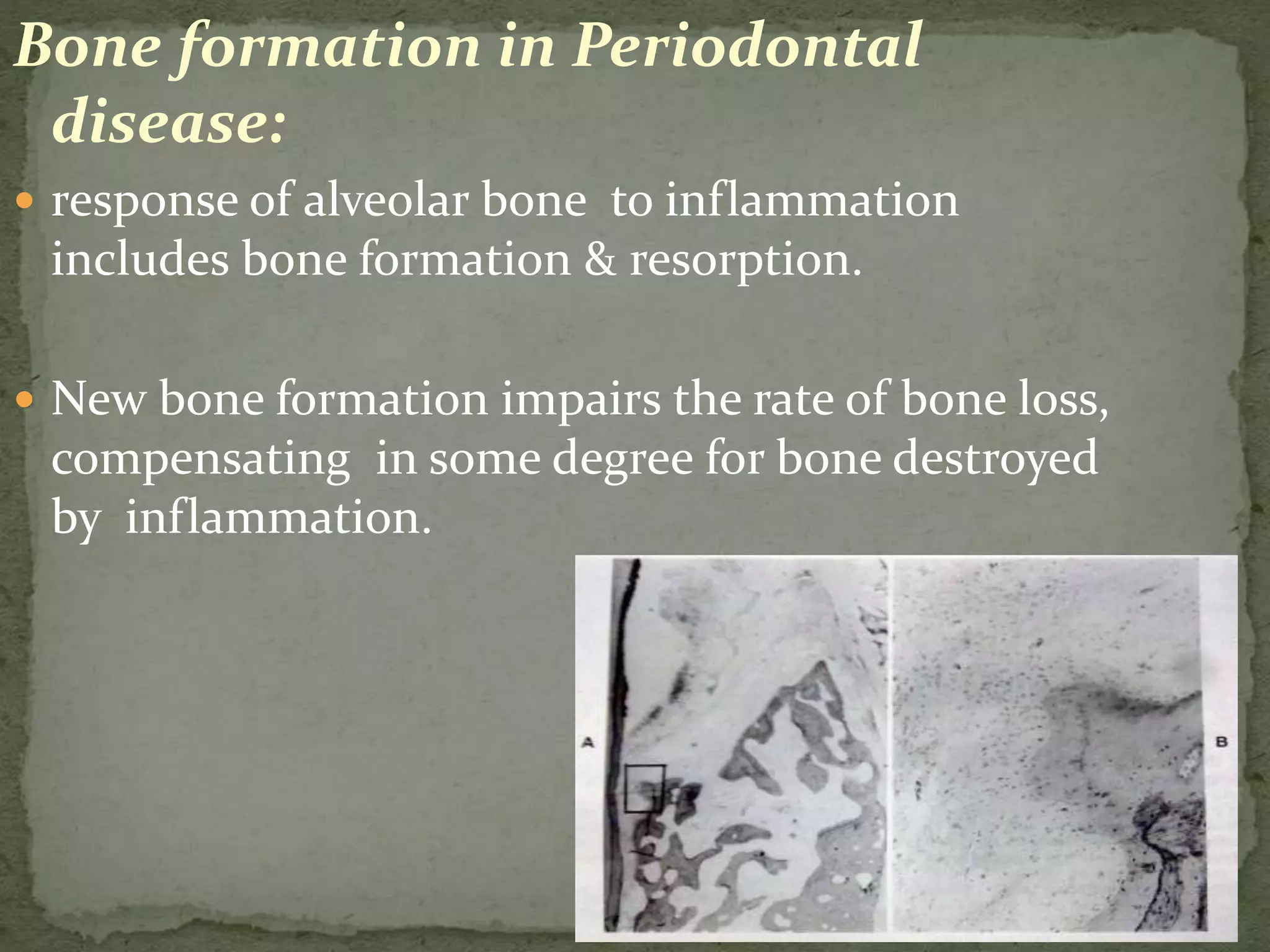
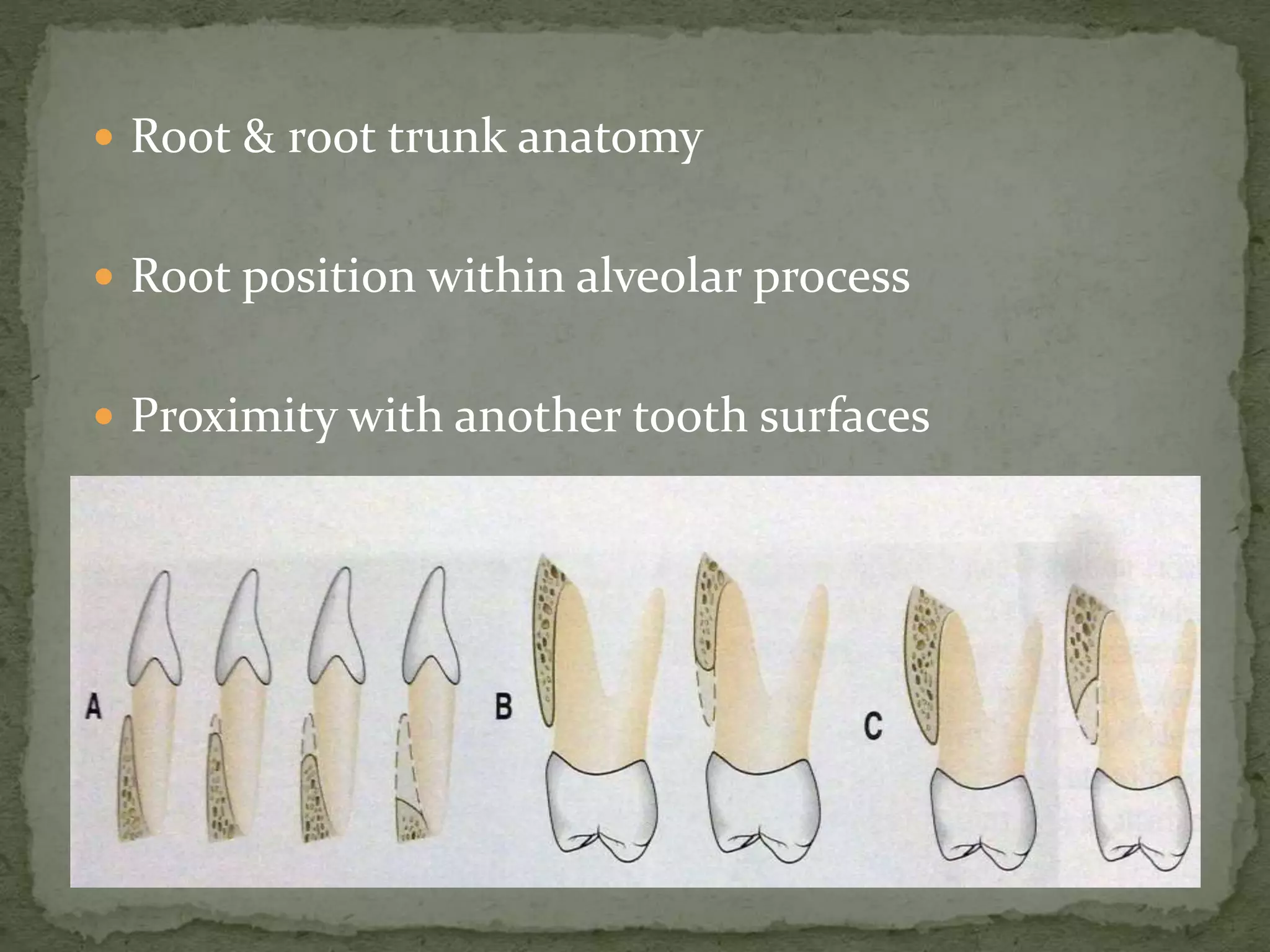
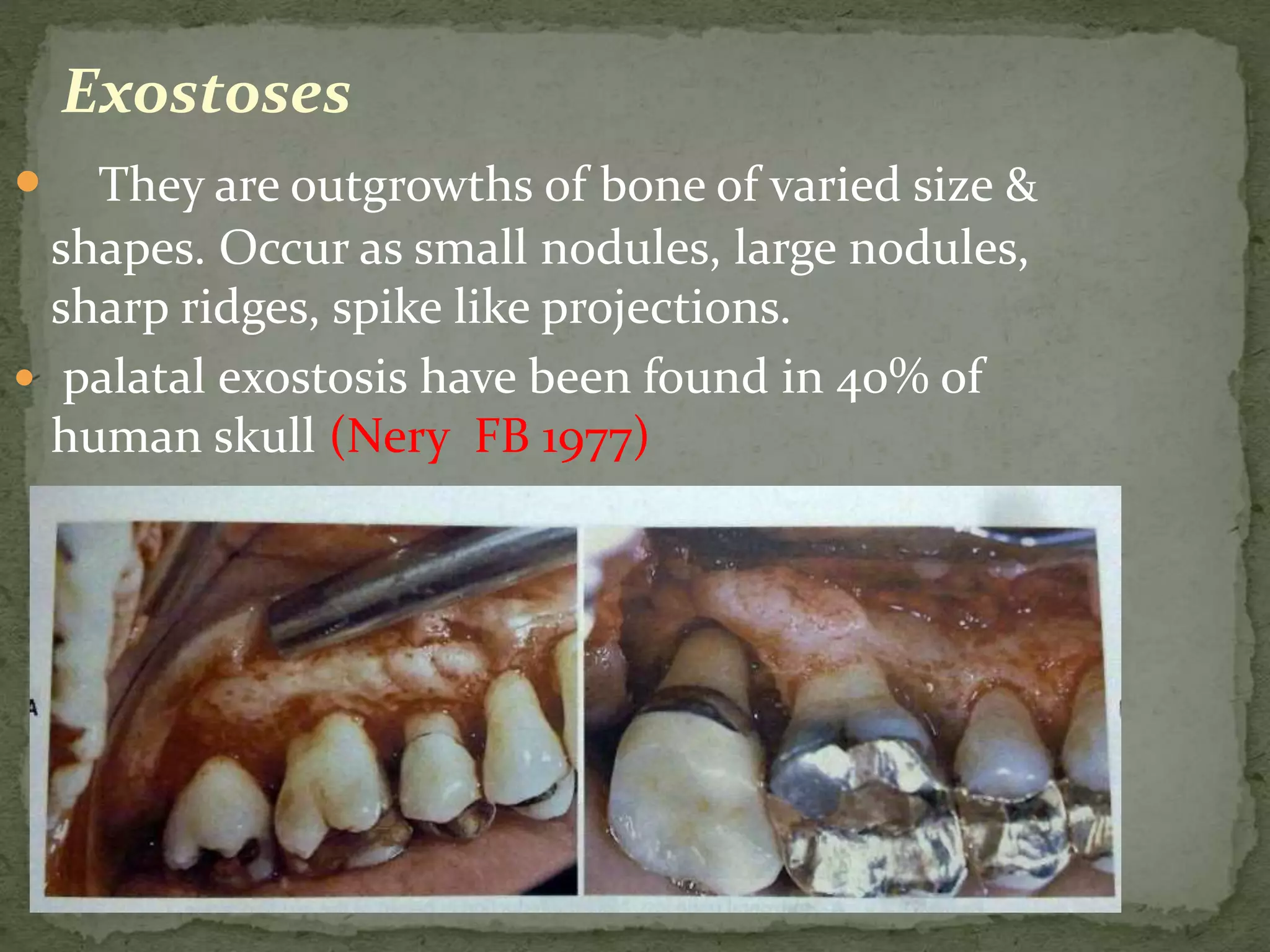
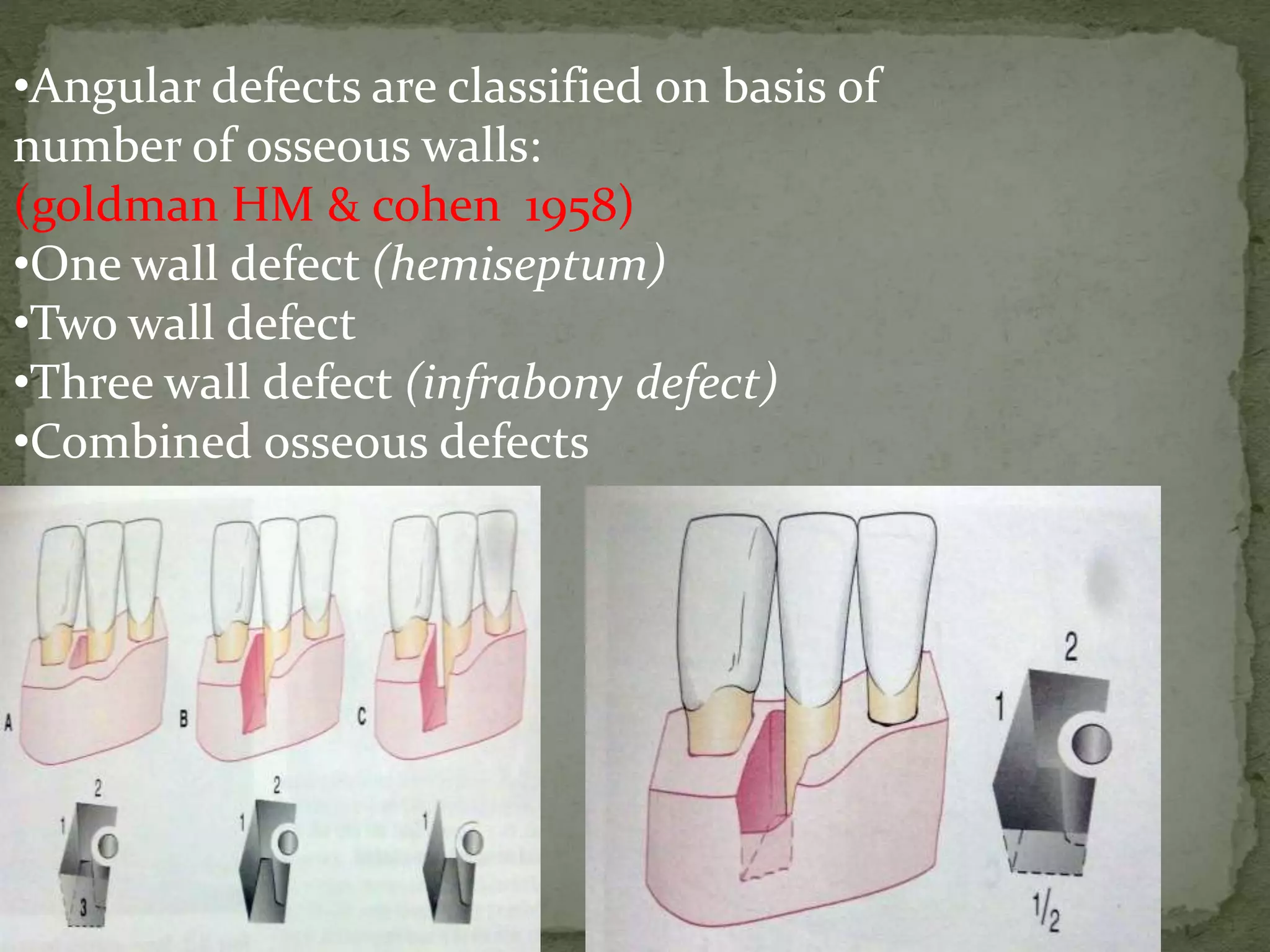
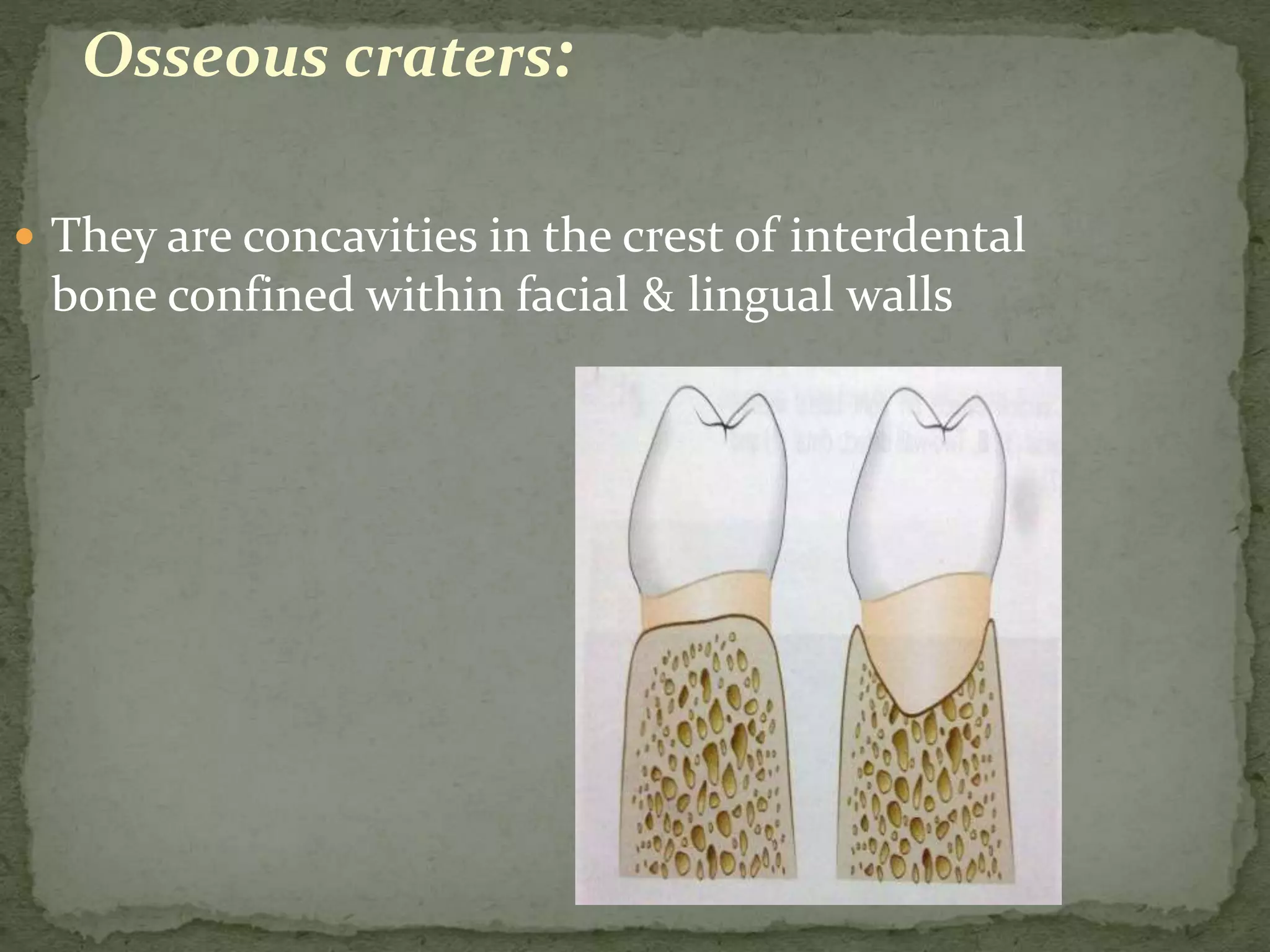
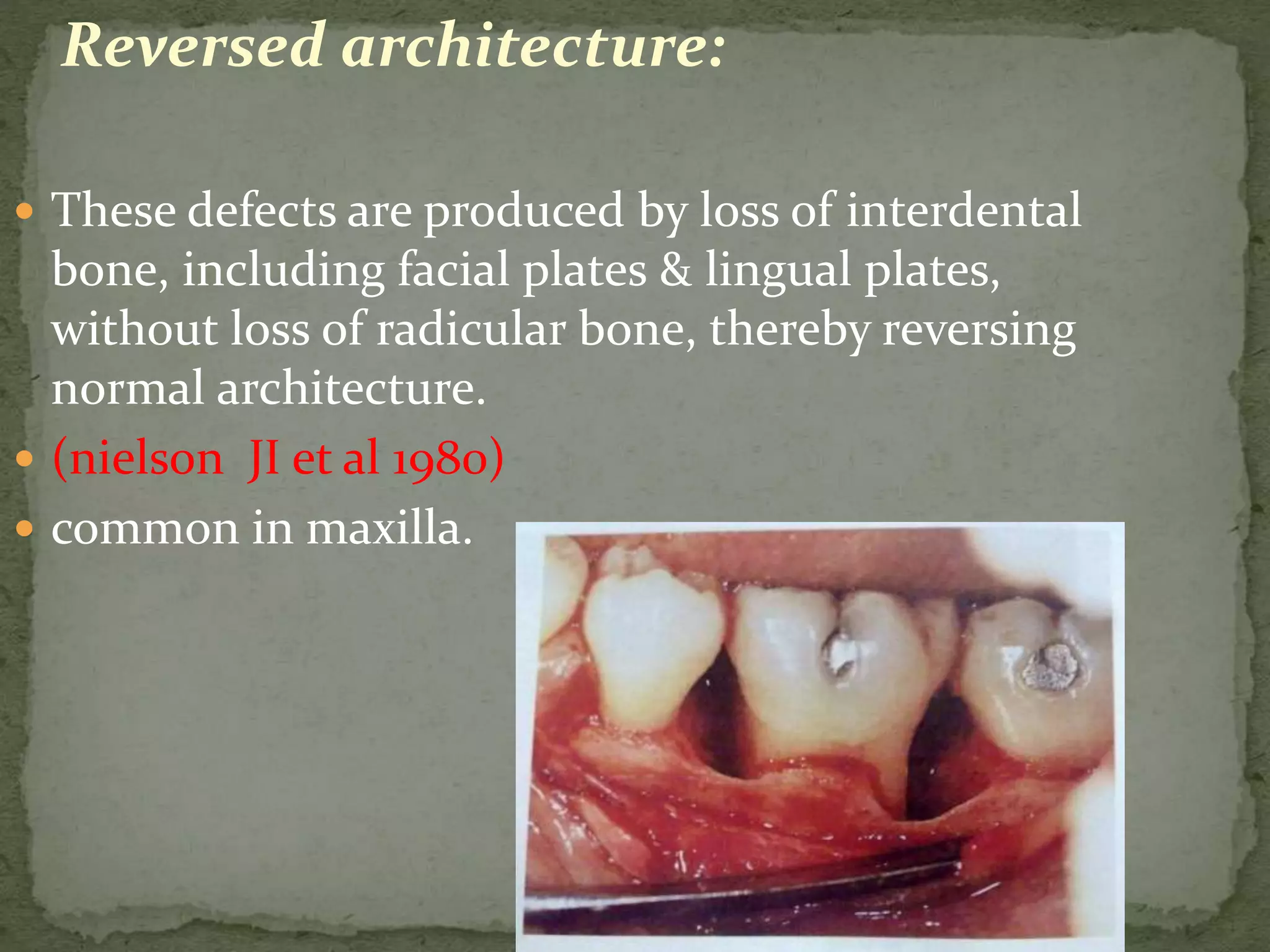
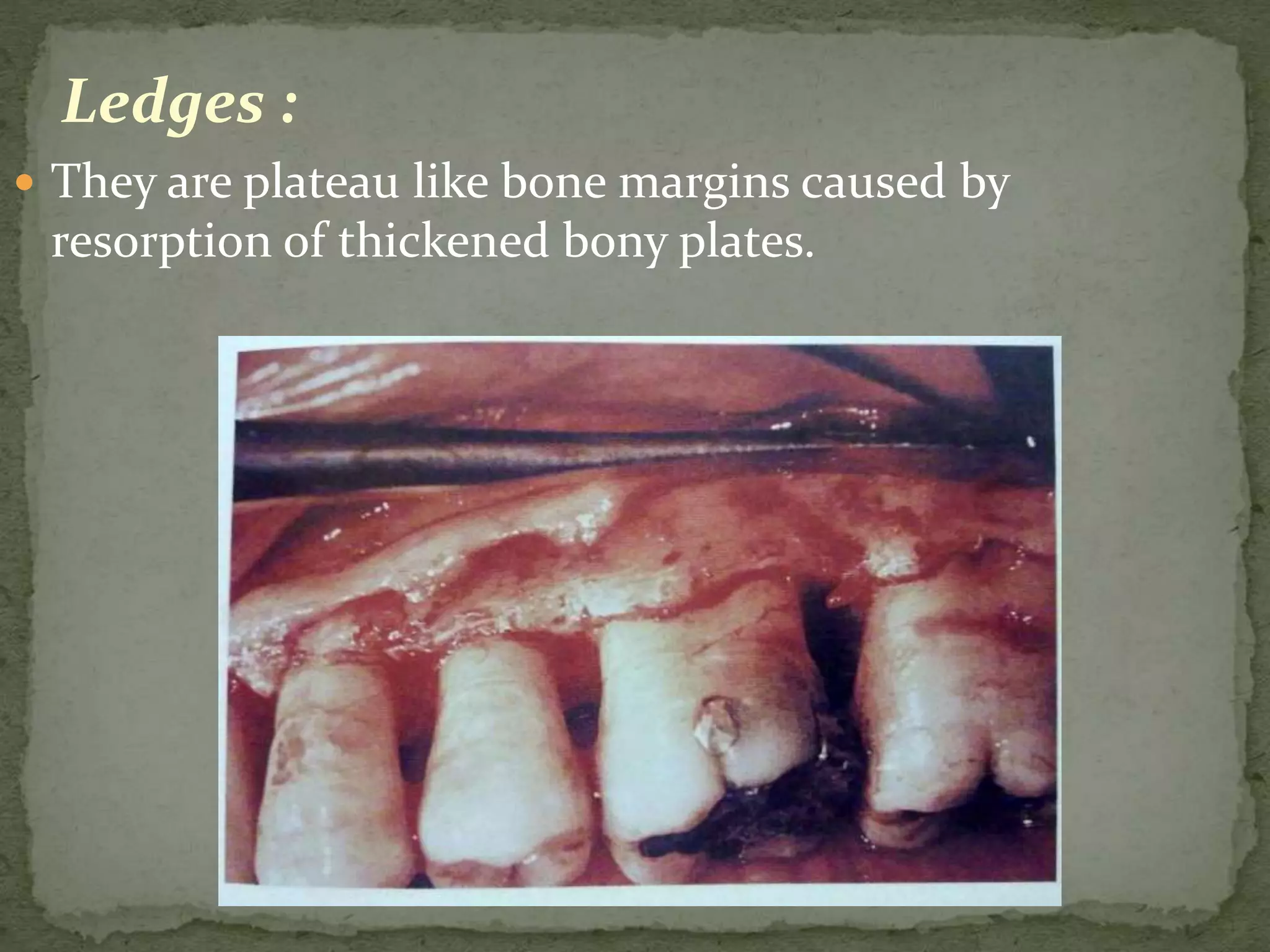
The document discusses bone morphology and destruction patterns in periodontal disease. It covers several key points:
1) Periodontitis involves an inflammatory process that drives the destruction of connective tissue and alveolar bone. Inflammation spreads from the gingiva along collagen fibers and blood vessels.
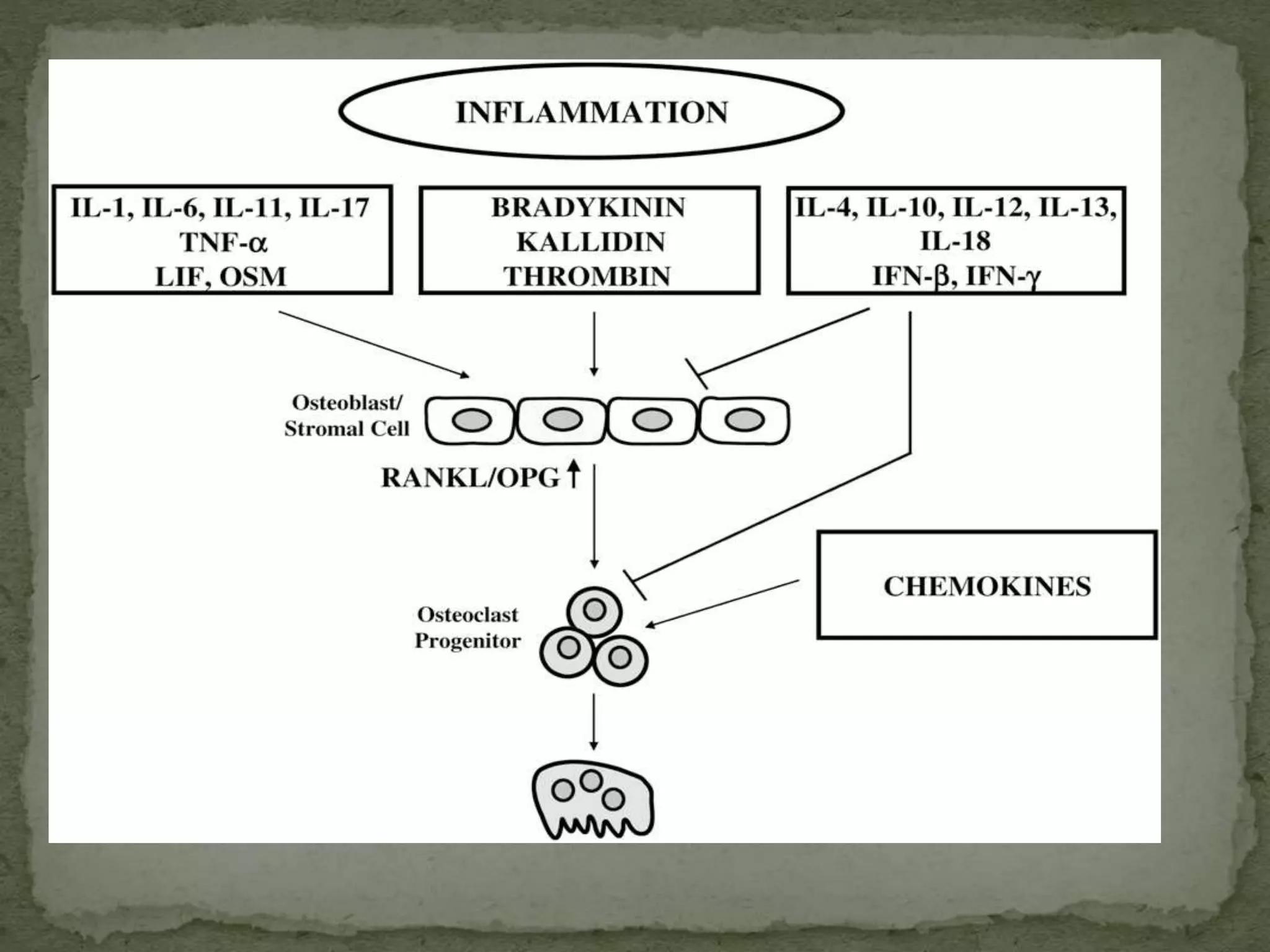
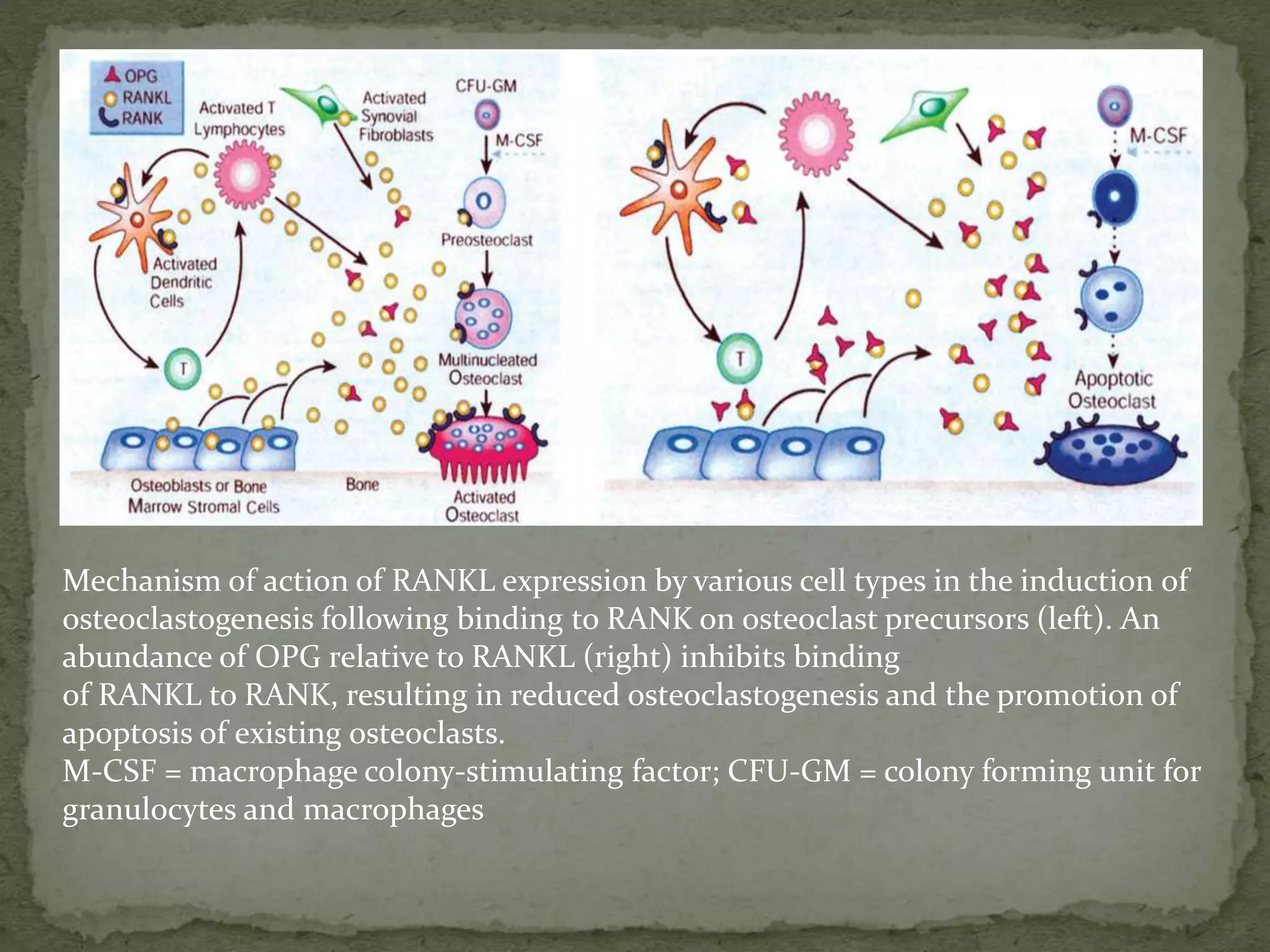
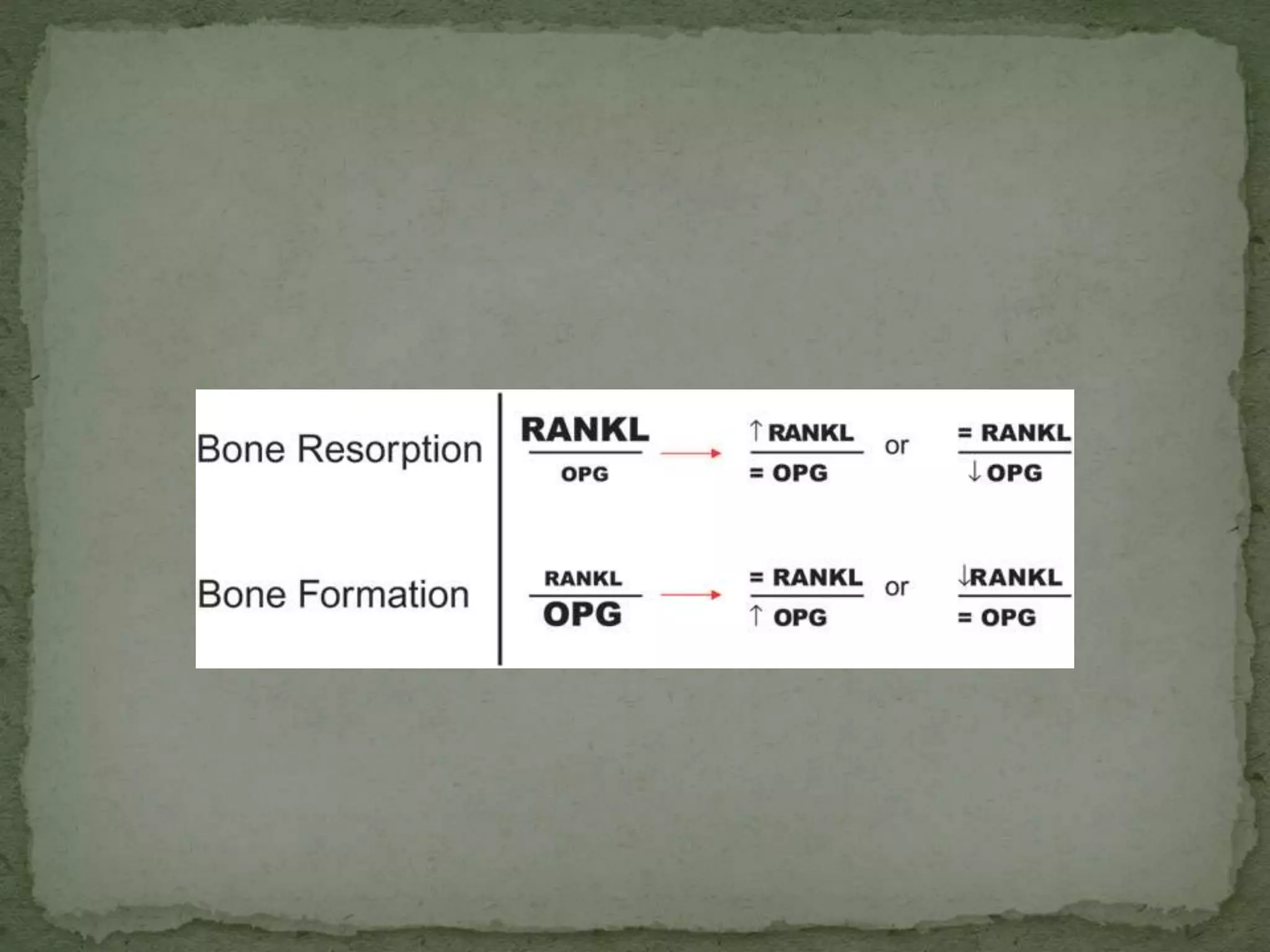
2) Several host-derived factors like prostaglandins, interleukin-1, and tumor necrosis factor can stimulate bone resorption. The RANKL-RANK-OPG pathway also regulates osteoclastogenesis.
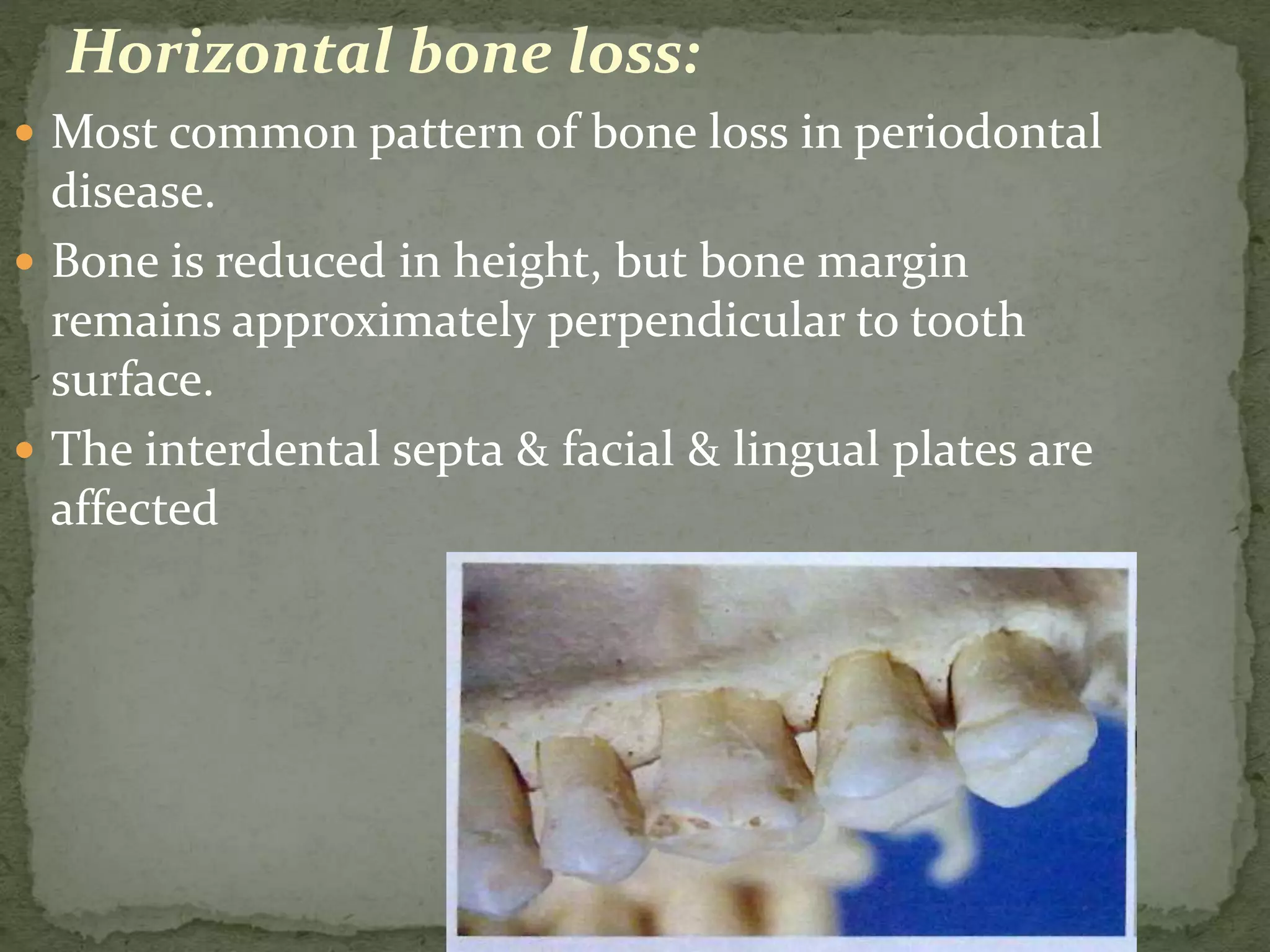
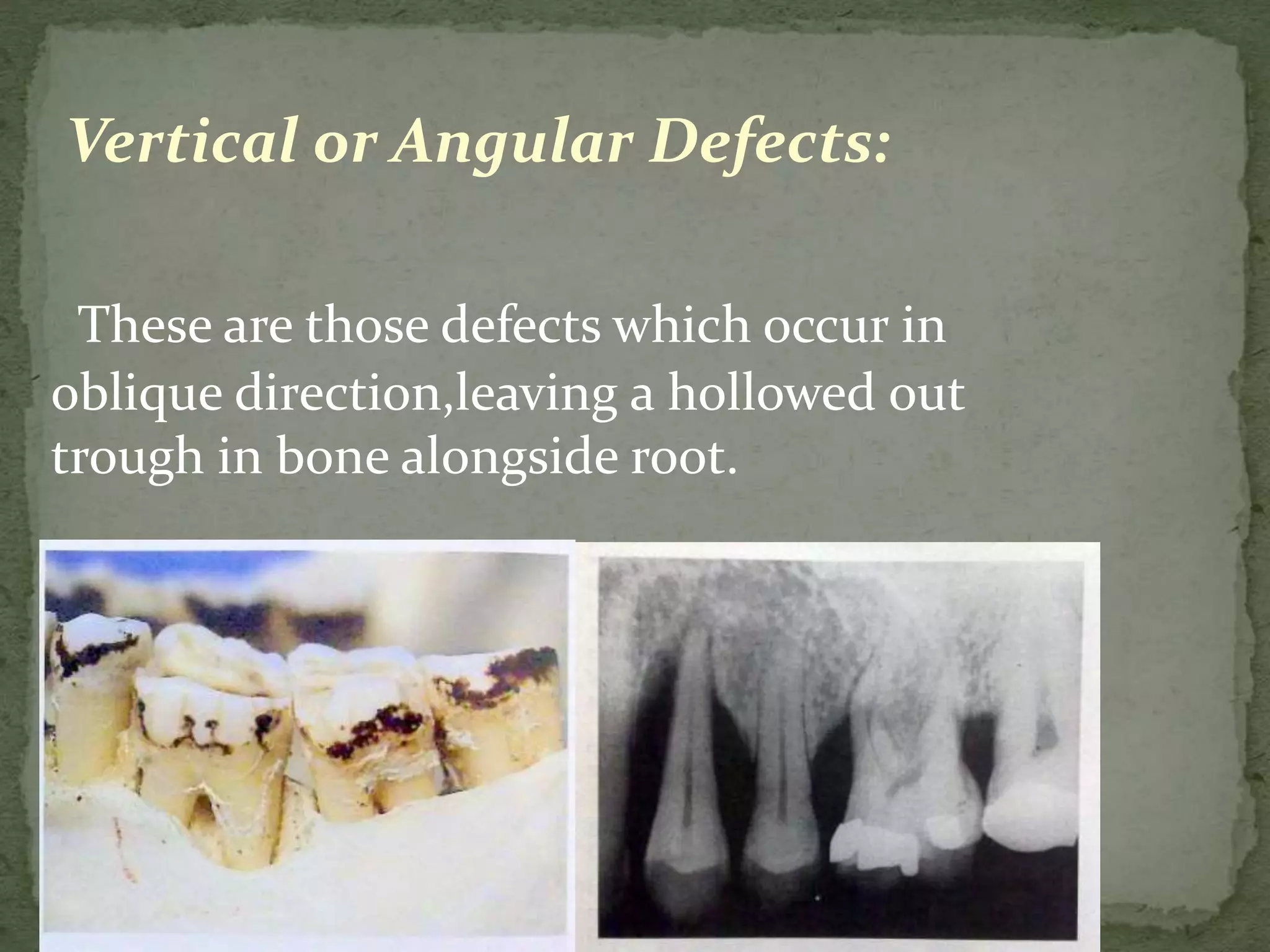
3) Normal anatomic variations, trauma from occlusion, and systemic disorders can influence bone loss patterns, which may be horizontal, vertical, or result in defects like osseous cr