This document discusses the challenges of dentin bonding and the evolution of dentin bonding agents. It addresses the following key points:
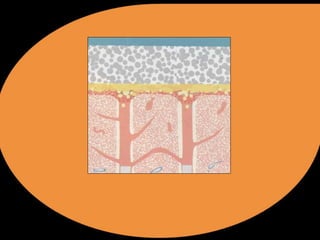
- Dentin is a highly permeable tissue with dentinal tubules that make bonding challenging.
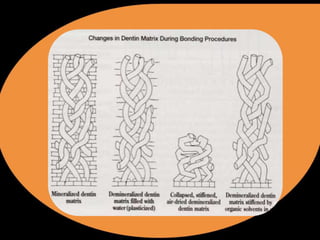
- Early bonding agents from generations I-III showed bond strengths from 2-15 MPa but bonding decreased over time as resin did not penetrate smear layers well.
- Generation IV agents introduced acid etching to open tubules followed by a primer and bonding agent, increasing bond strengths to 20-28 MPa.
- Current self-etching agents from generations V-VII are more user-friendly as a single bottle or step but may compromise enamel margins. Hybrid layer formation