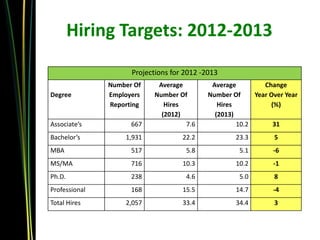
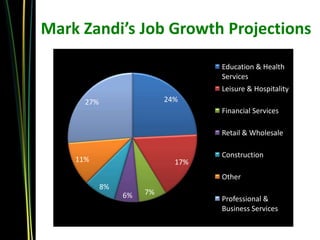
Dr. Philip Gardner gave a presentation on the college labor market and workforce readiness. He discussed trends over the past 3 years, noting strong growth in 2011-2012 but a more cautious outlook in 2012-2013 with only moderate hiring increases expected. He highlighted in-demand fields and obstacles employers face in hiring. Gardner also reviewed employers' perspectives on needed skills like problem-solving, communication, and managing priorities. Research from Boise State examined critical competencies and attitudes desired by employers.





















![Employers’ Takes on Attitude
There is an overinflated sense of self and abilities…
College students have an attitude of entitlement that they
are owed a job, and it should be at a specific dollar
amount, even though they do not have a basis for that
dollar amount.
Many candidates don’t project that they are
interested, optimistic, and want to help the company
succeed.
[We have] retention issues because candidates resign due
to business challenges being more than they expected or
are willing to try to accomplish.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/boisetrends2013-130225094537-phpapp02/85/Boise-trends-2013-25-320.jpg)












