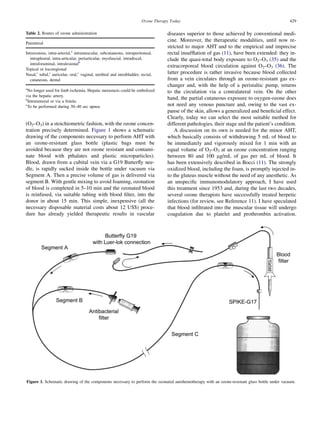
This document reviews the scientific and medical aspects of ozone therapy. It aims to dispel misconceptions about ozone therapy and clarify its biochemical mechanisms of action. When ozone comes into contact with biological fluids, it rapidly reacts to form reactive oxygen species (ROS) and lipid oxidation products (LOPs). In small, controlled doses, ROS and LOPs can trigger beneficial biological responses by inducing antioxidant defenses and oxidative stress proteins, without causing toxicity. The document discusses how ozone dosage is critical to eliciting a therapeutic effect through acute oxidative stress, while avoiding harm.