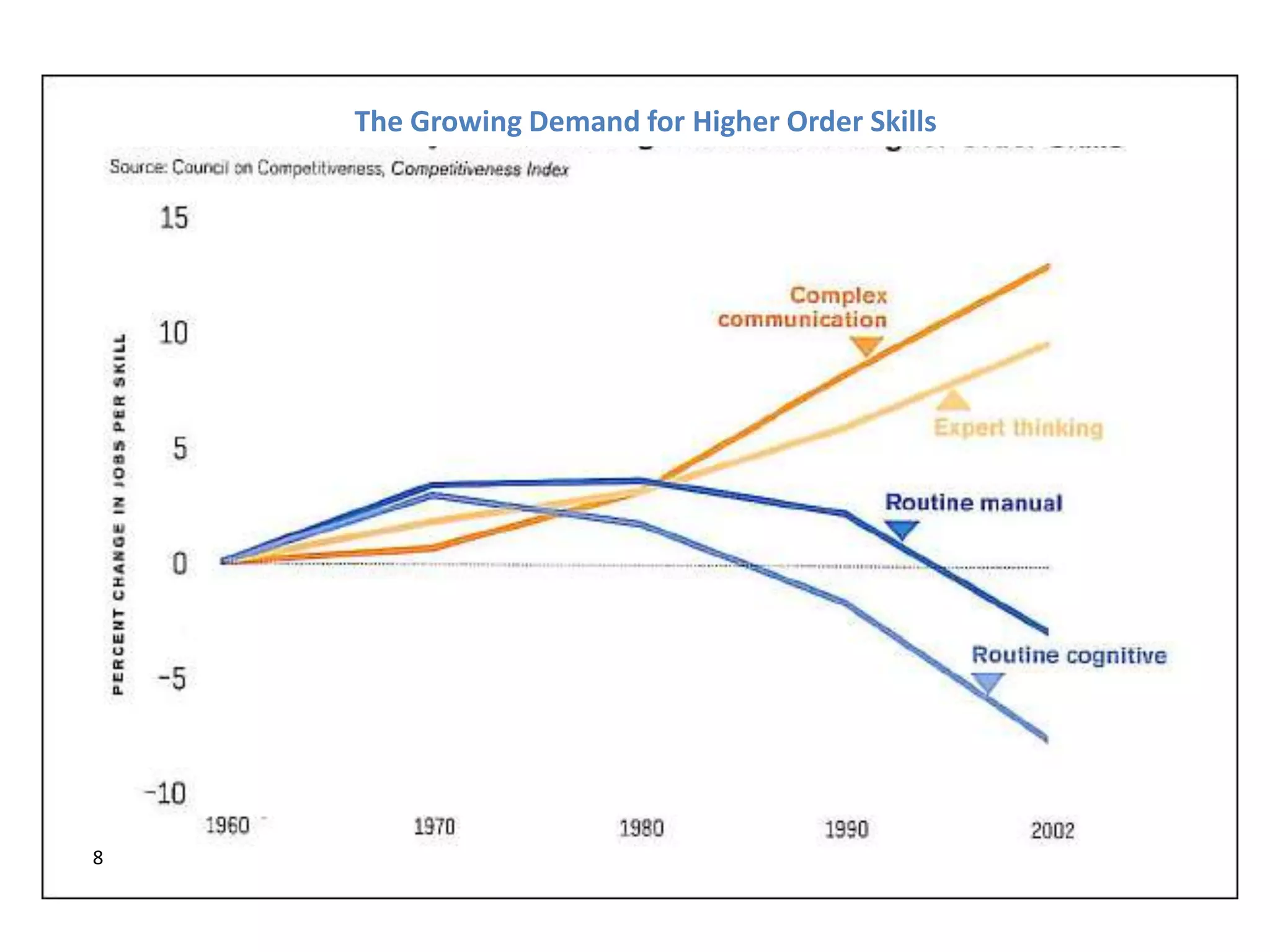
The Global Citizenship Program at Webster University aims to ensure that all undergraduate students develop the core competencies required for responsible global citizenship in the 21st century. The program is guided by the university's mission and aligns with employer needs, student needs, and national research on skills development. It focuses on providing students with knowledge in various areas as well as skills like critical thinking, communication, cultural competence, collaboration, and ethical reasoning. A key part of the program is integrative learning experiences like first-year seminars and a global keystone seminar in the third year that combine knowledge and skill development.