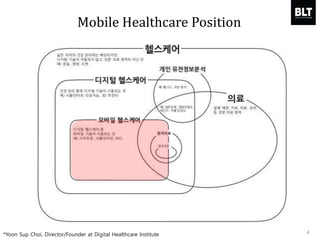
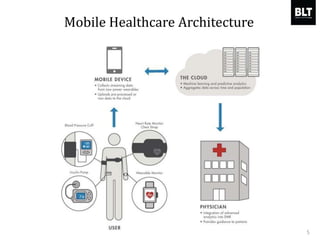
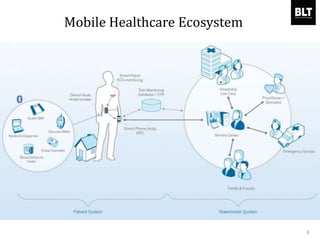
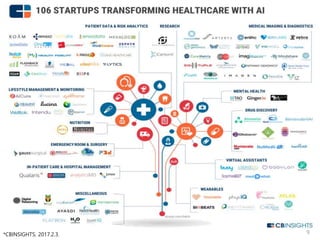
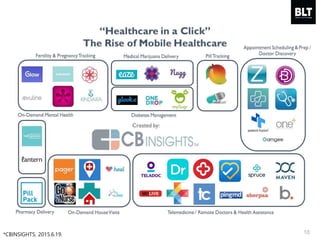
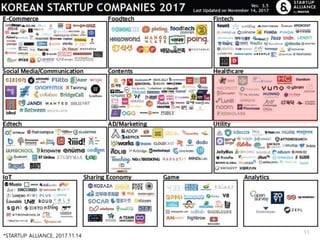
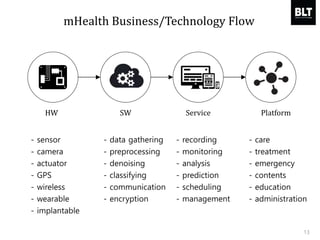
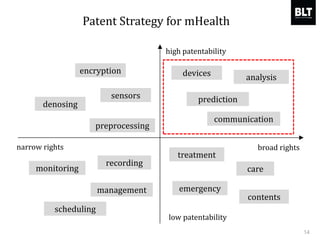
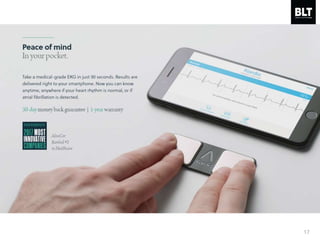
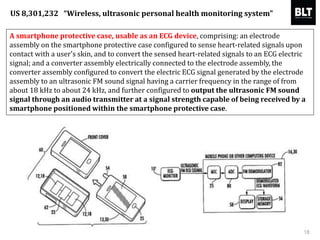
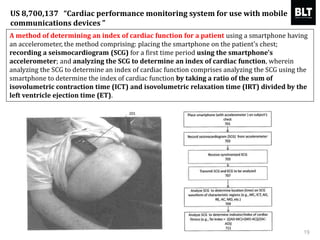
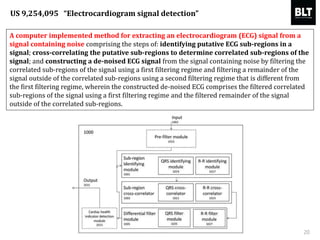
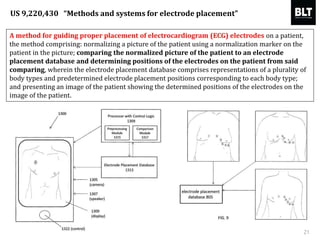
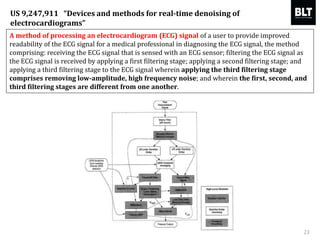
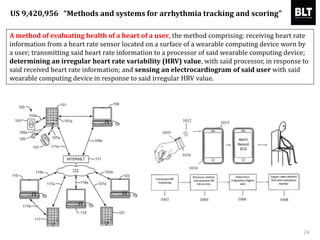
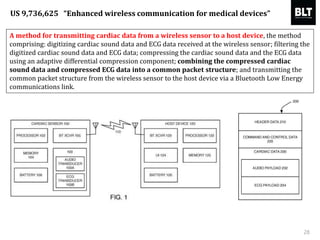
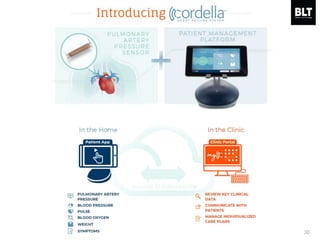
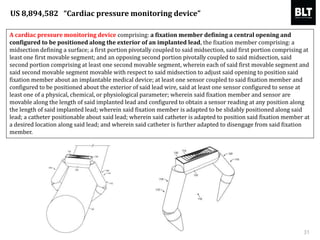
This document summarizes a presentation given by Kim Sung-hyun, a Korean patent attorney, on mobile healthcare patent trends and strategies. The presentation covered the growth of the mobile health market and examples of patented mobile health technologies, including technologies from companies like AliveCor, Eko Devices, and Endotronix. Key mobile health areas that were discussed in terms of patentability included sensors, monitoring, communication devices, and treatment.