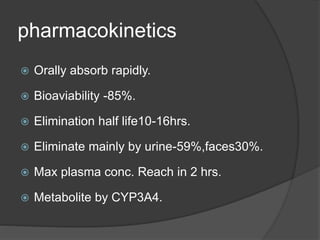
This document discusses Blonanserin, a novel antipsychotic drug approved in Japan and Korea for treating schizophrenia. It has high affinity for dopamine D2 and D3 receptors and serotonin 5-HT2A receptors. Blonanserin is orally absorbed, metabolized by CYP3A4 enzymes, and can interact with other drugs that induce or inhibit these enzymes. It is used to treat schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and other psychotic or mood disorders. Blonanserin is generally well tolerated with mild to moderate adverse effects like parkinsonism and akathisia. Studies found it to be as effective as haloperidol and risperidone for schizophrenia symptoms but with a better