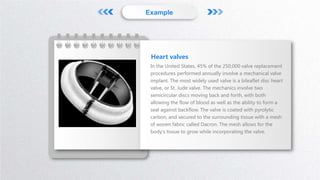
Biomaterials are advanced materials utilized for diagnosing, repairing, or enhancing human tissues and organs, categorized into metals, inorganic compounds, and organic polymers. These materials must possess biological functionality, biocompatibility, chemical stability, and machinability for applications in artificial joints and cardiovascular systems. Specific examples include medical-grade metals for implants and bioceramics that bond with bone tissue, contributing significantly to medical procedures like valve replacements.