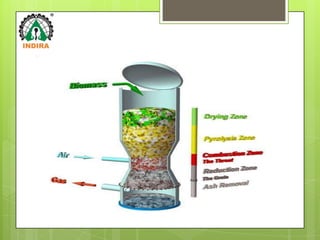
Dr. Sudhir Puloria invented a biomass gasifier that converts solid biomass fuels like wood and agricultural waste into a combustible gas. There are two types - a simple natural gasifier priced at Rs. 8000 and a forced draft model priced at Rs. 15000. The gasifier provides a sustainable energy source for rural areas by utilizing agricultural waste and has benefits such as reducing firewood consumption and smoke. Challenges include adequate land and waste collection, but opportunities exist in powering atta chakkis and replacing diesel generators. The gasifier offers environmental and cost benefits over fossil fuels.