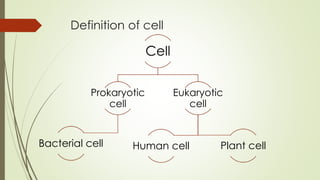
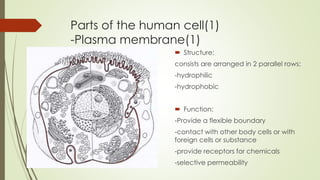
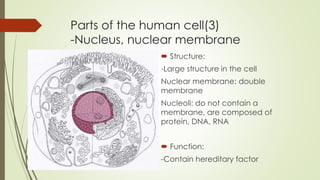
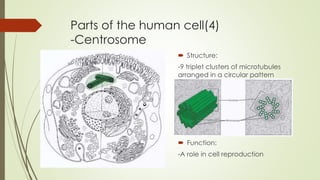
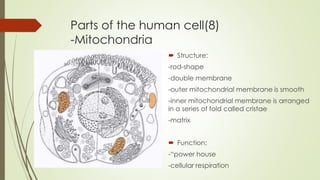
The document describes the key parts and functions of human, plant, and bacterial cells. It identifies 11 main parts of the human cell: plasma membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, centrosome, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi complex, mitochondria, lysosomes, peroxisomes, and vacuoles. Each part is described in terms of its structure and function, such as the plasma membrane providing a boundary and selective permeability, the nucleus containing genetic material, and mitochondria generating energy through cellular respiration. The objective is to understand the differences between human, plant, and bacterial cells and explain the roles of organelles within human cells.