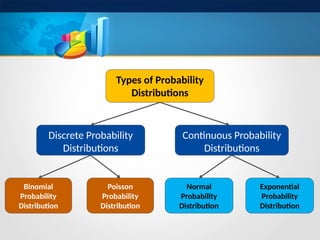
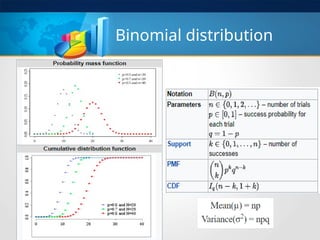
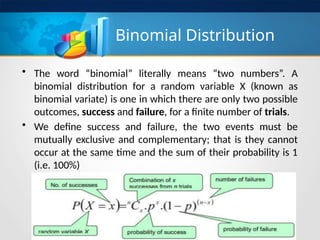
The document discusses the mathematical foundations of computer science with a focus on random variables and their types, specifically distinguishing between discrete and continuous random variables. It explains various probability distributions, including the binomial distribution discovered by James Bernoulli, which describes scenarios with two possible outcomes across a finite number of trials. Examples of binomial distribution applications are provided, such as lottery outcomes and election polls.