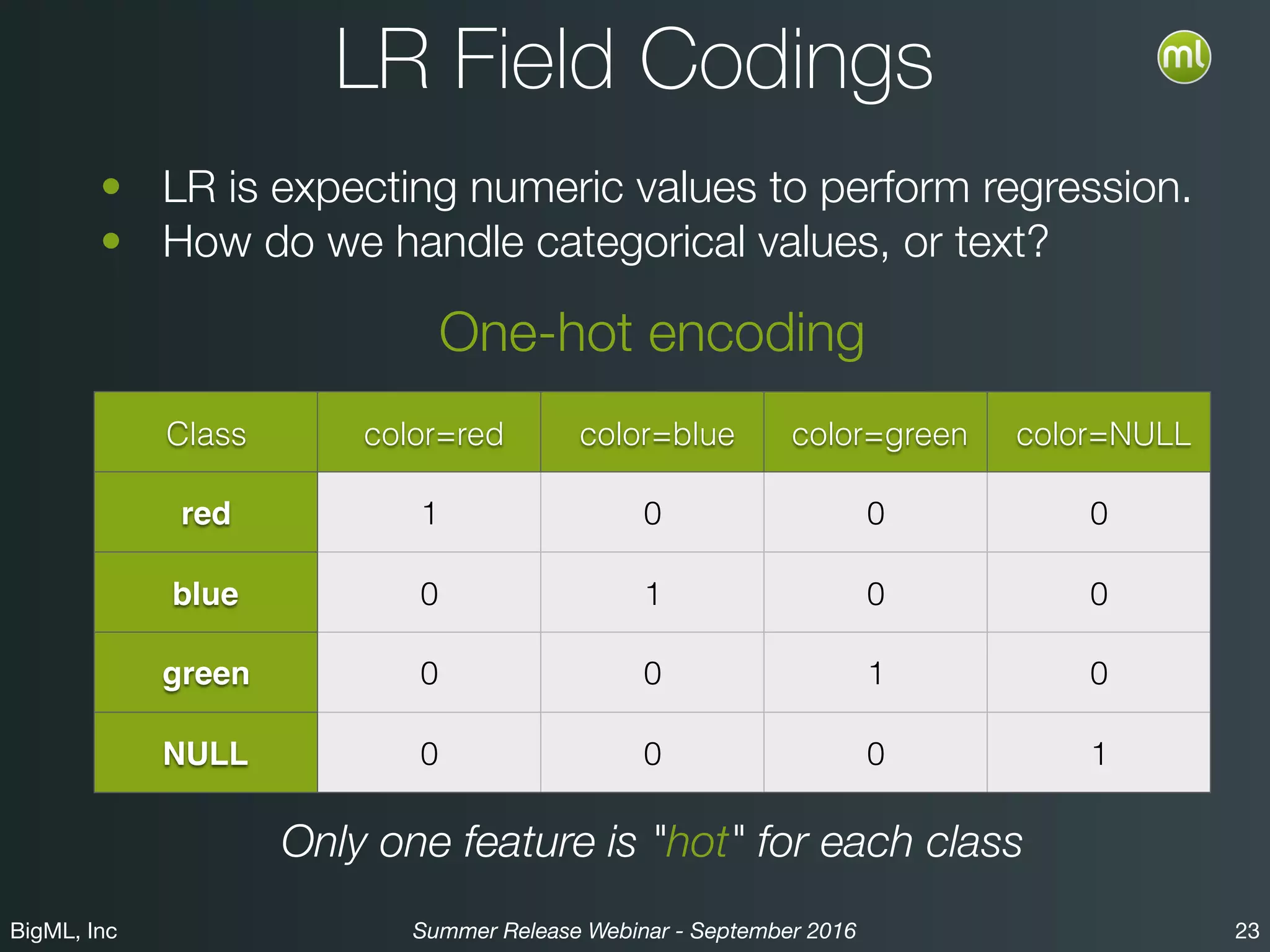
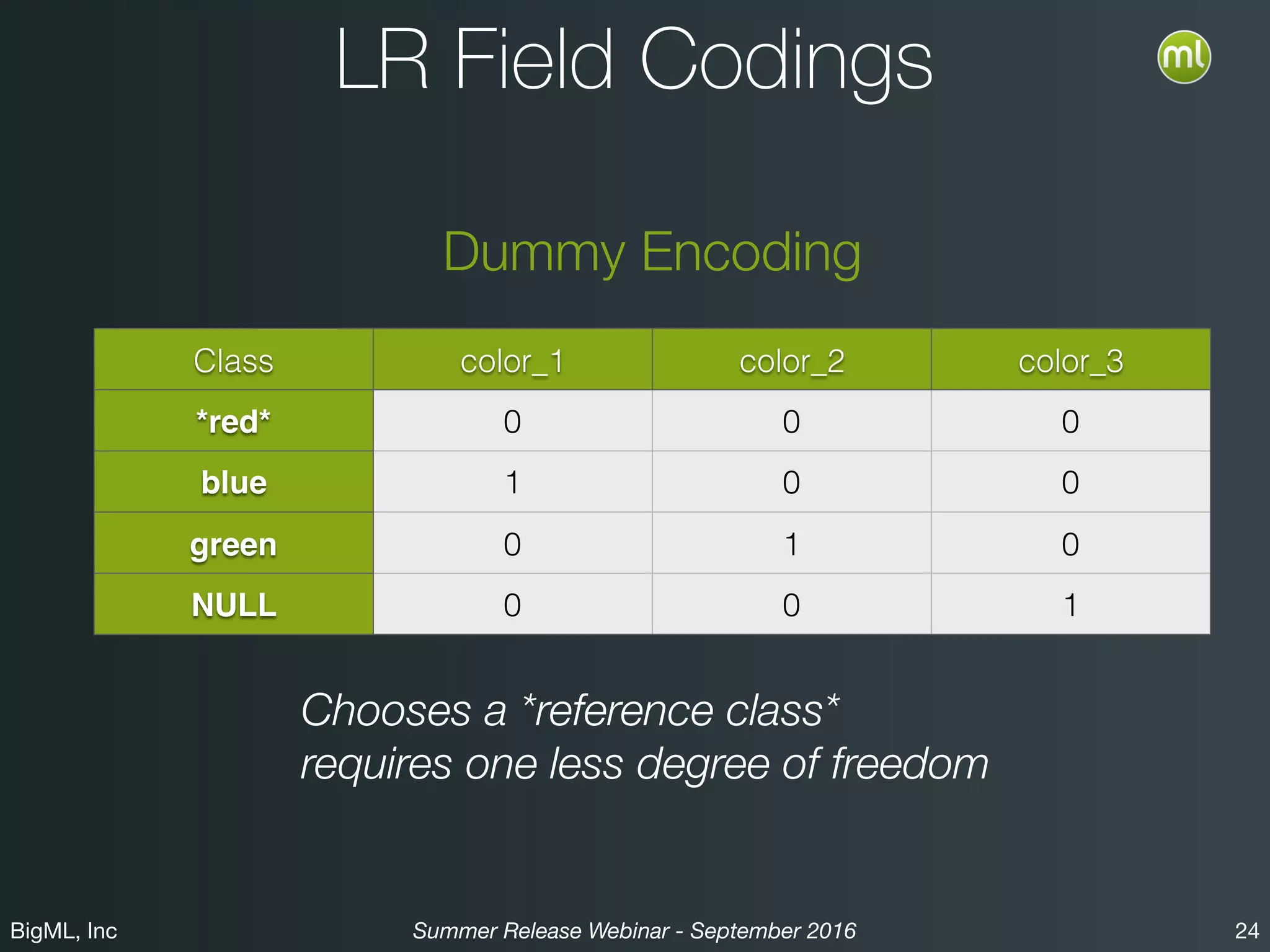
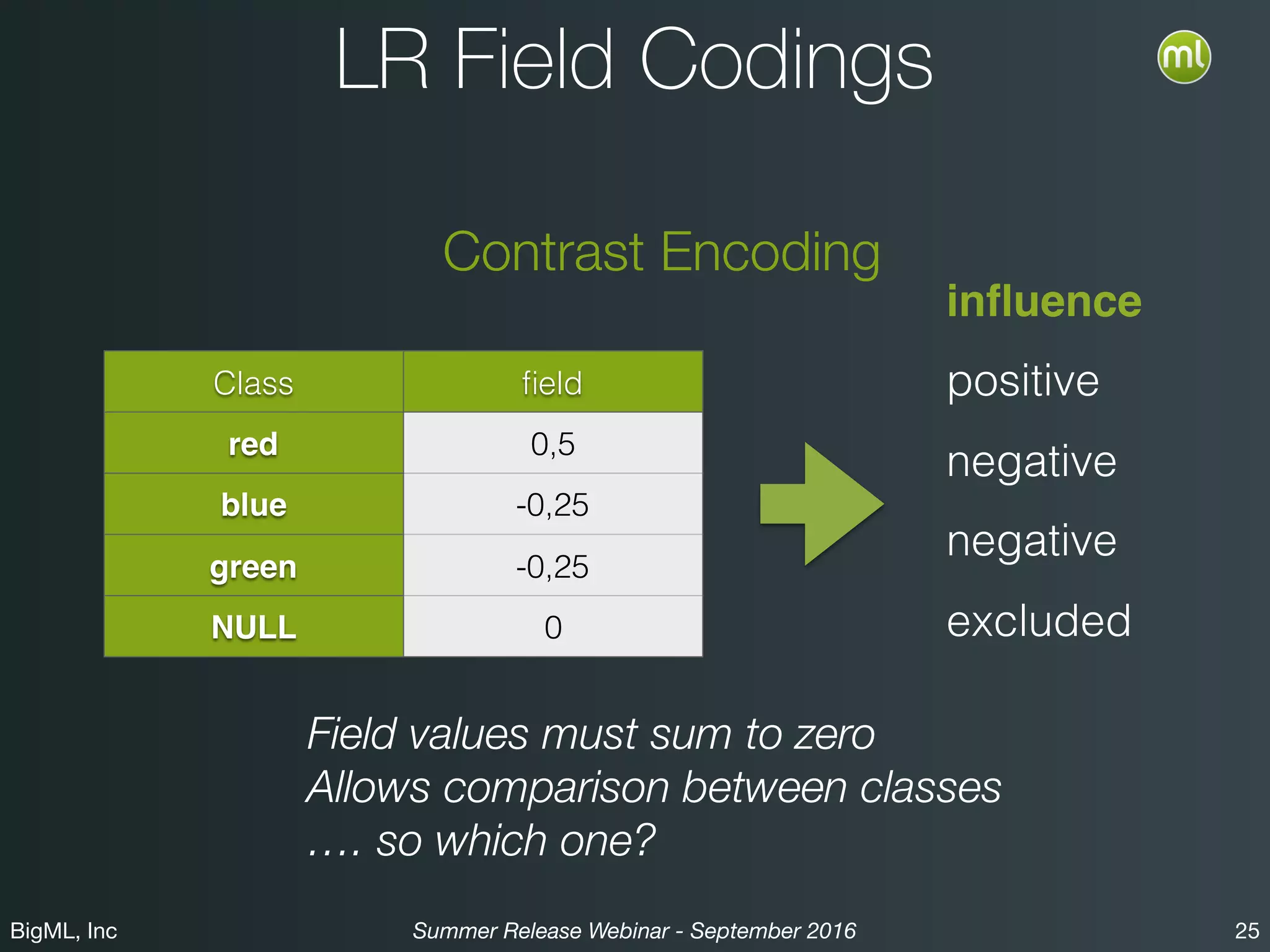
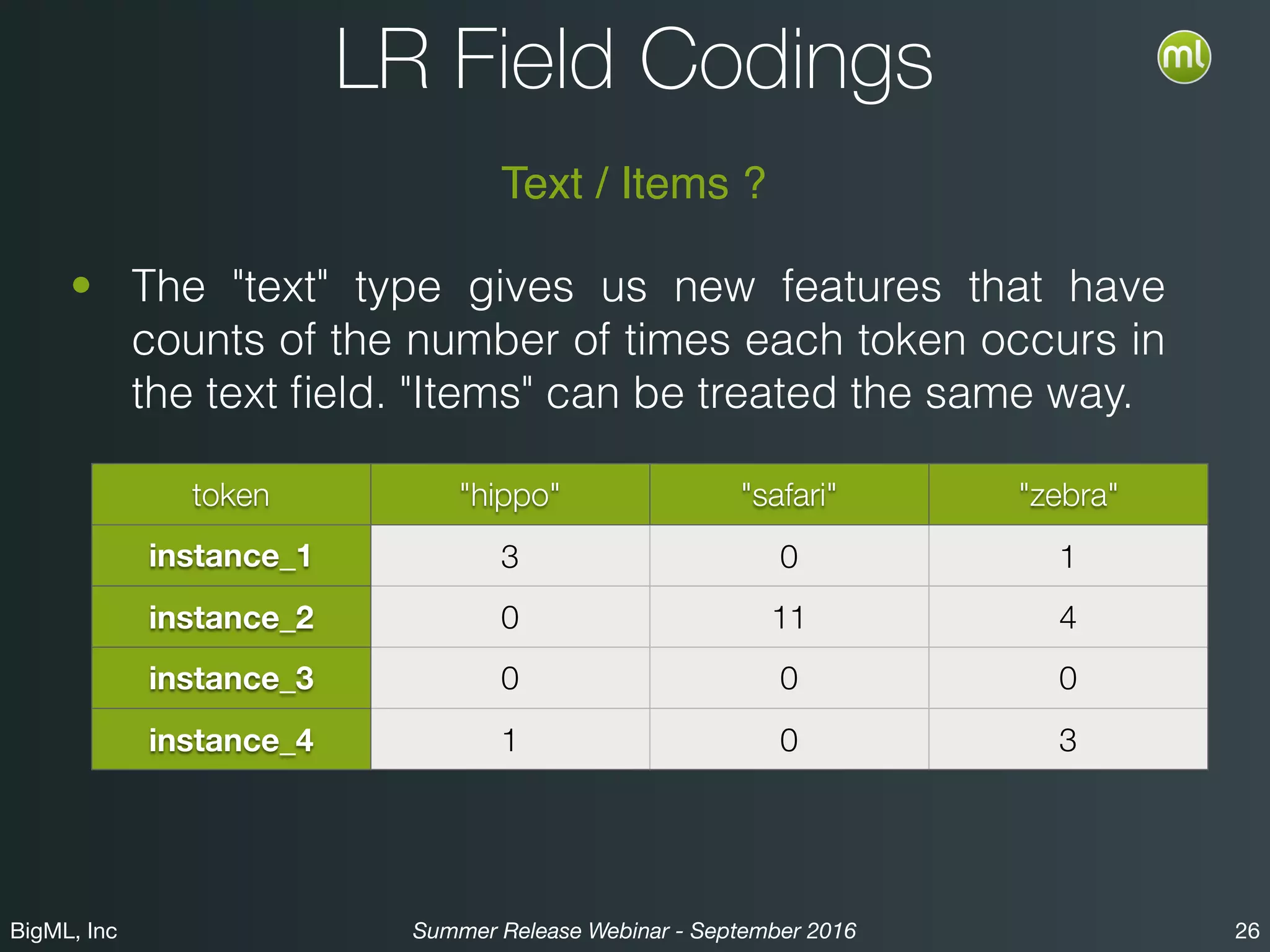
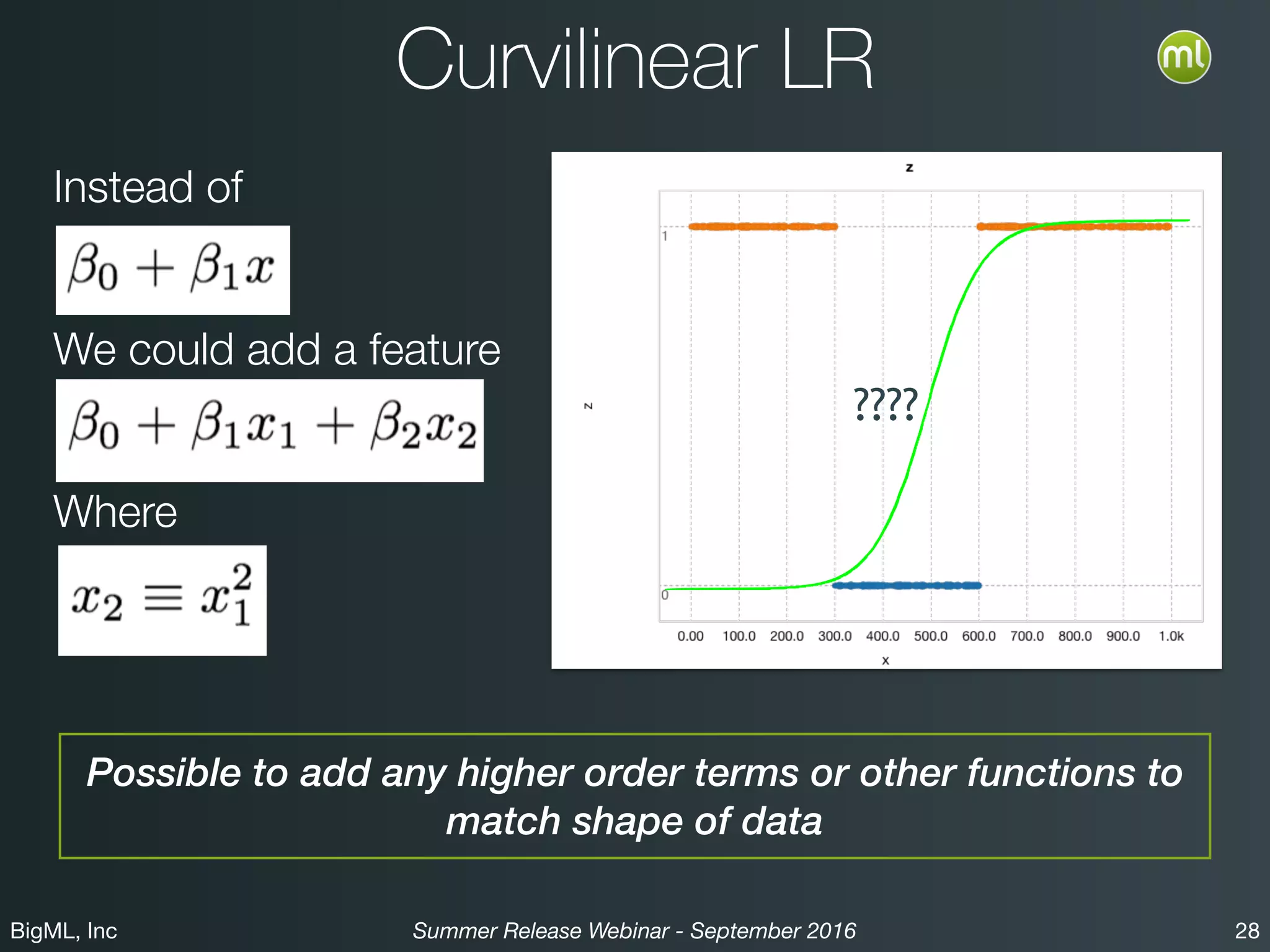
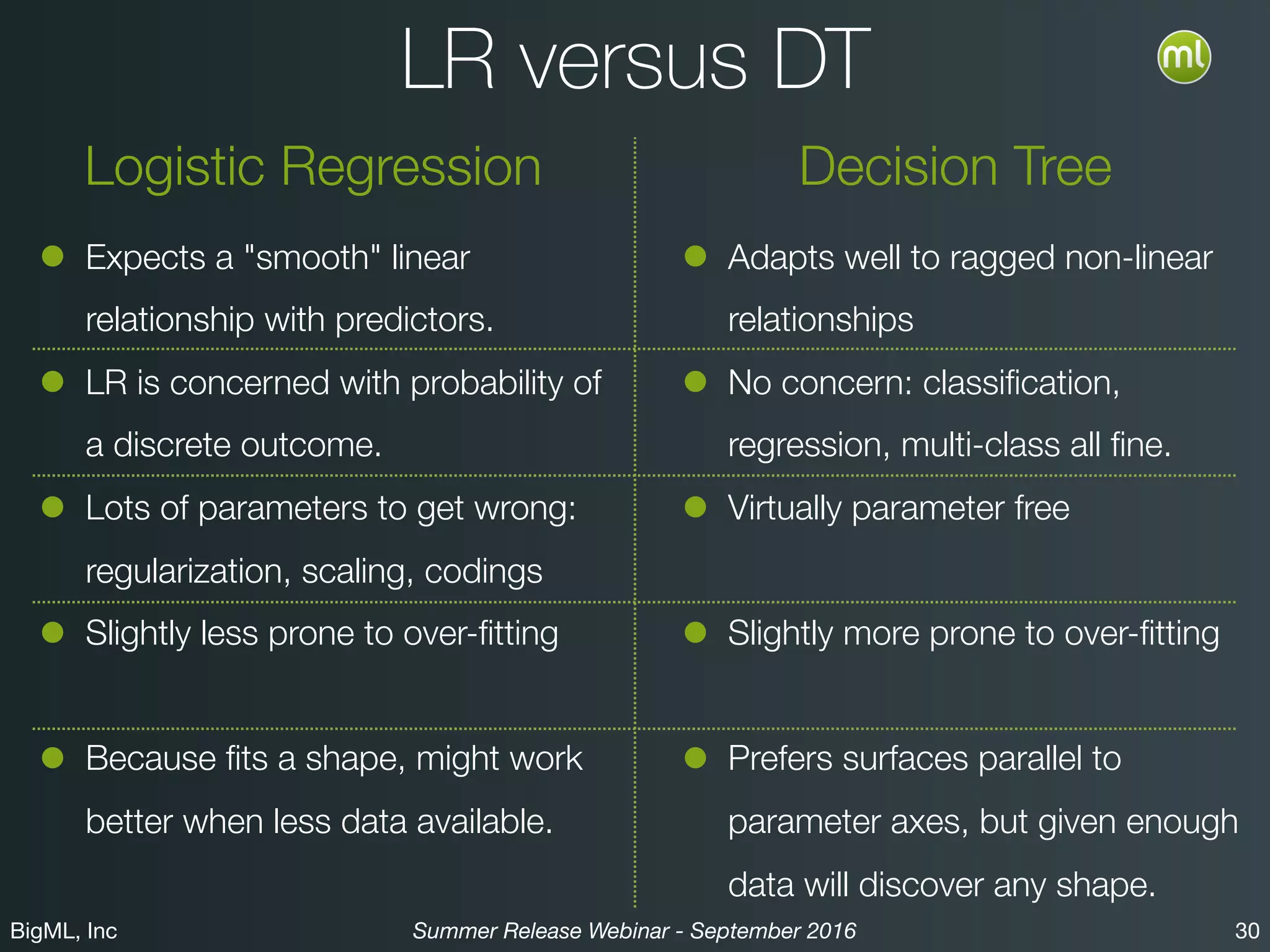
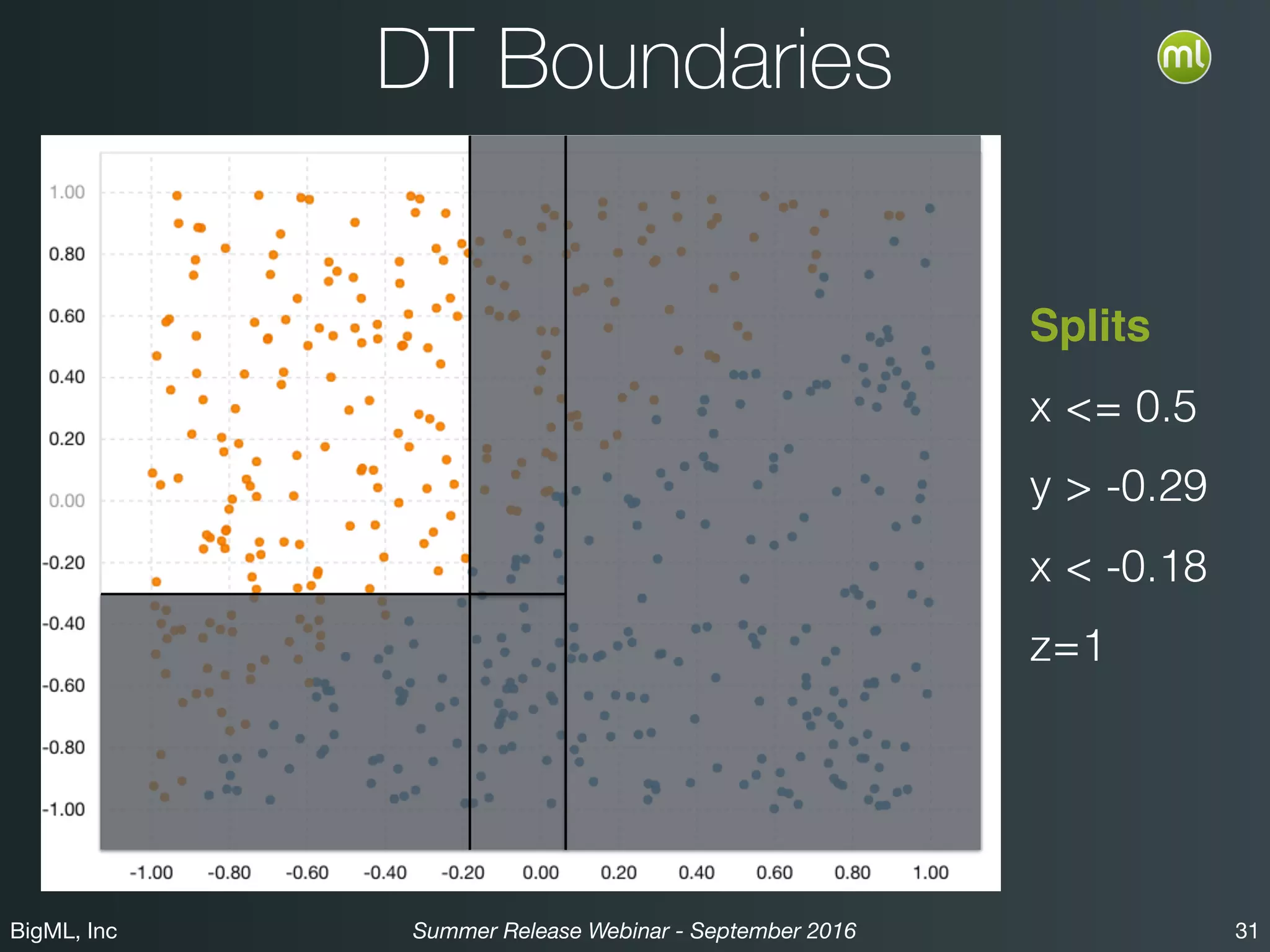
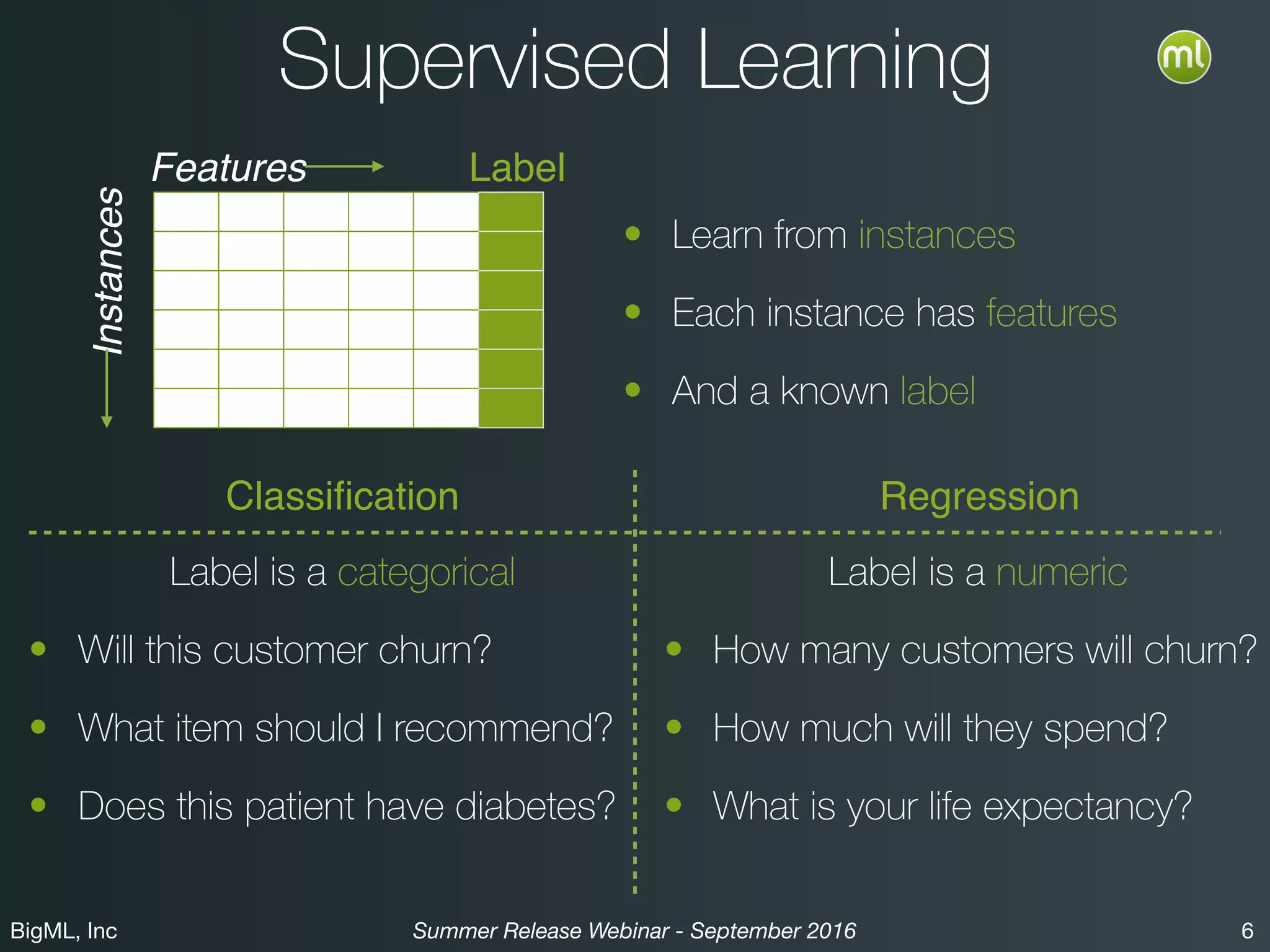
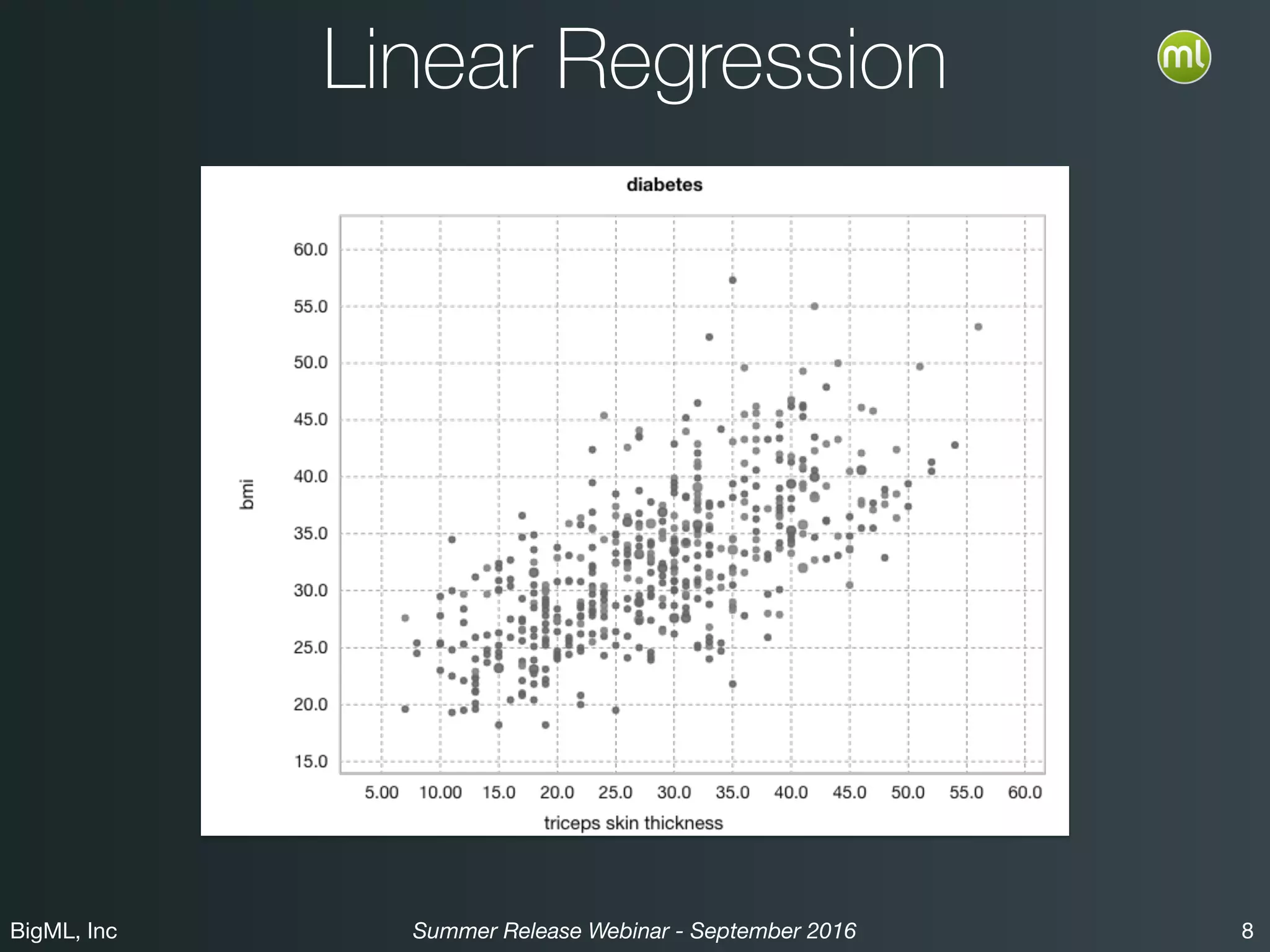
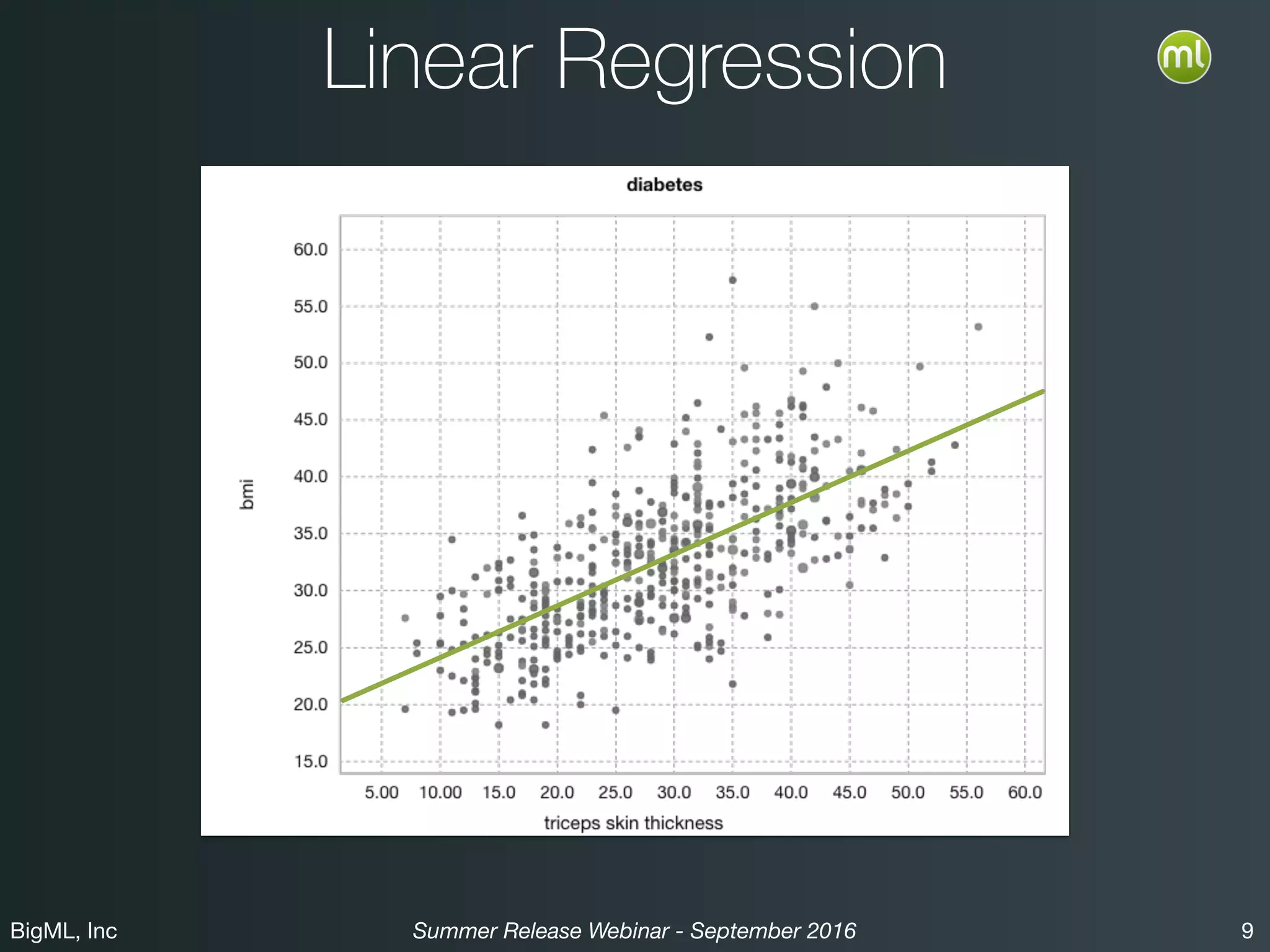
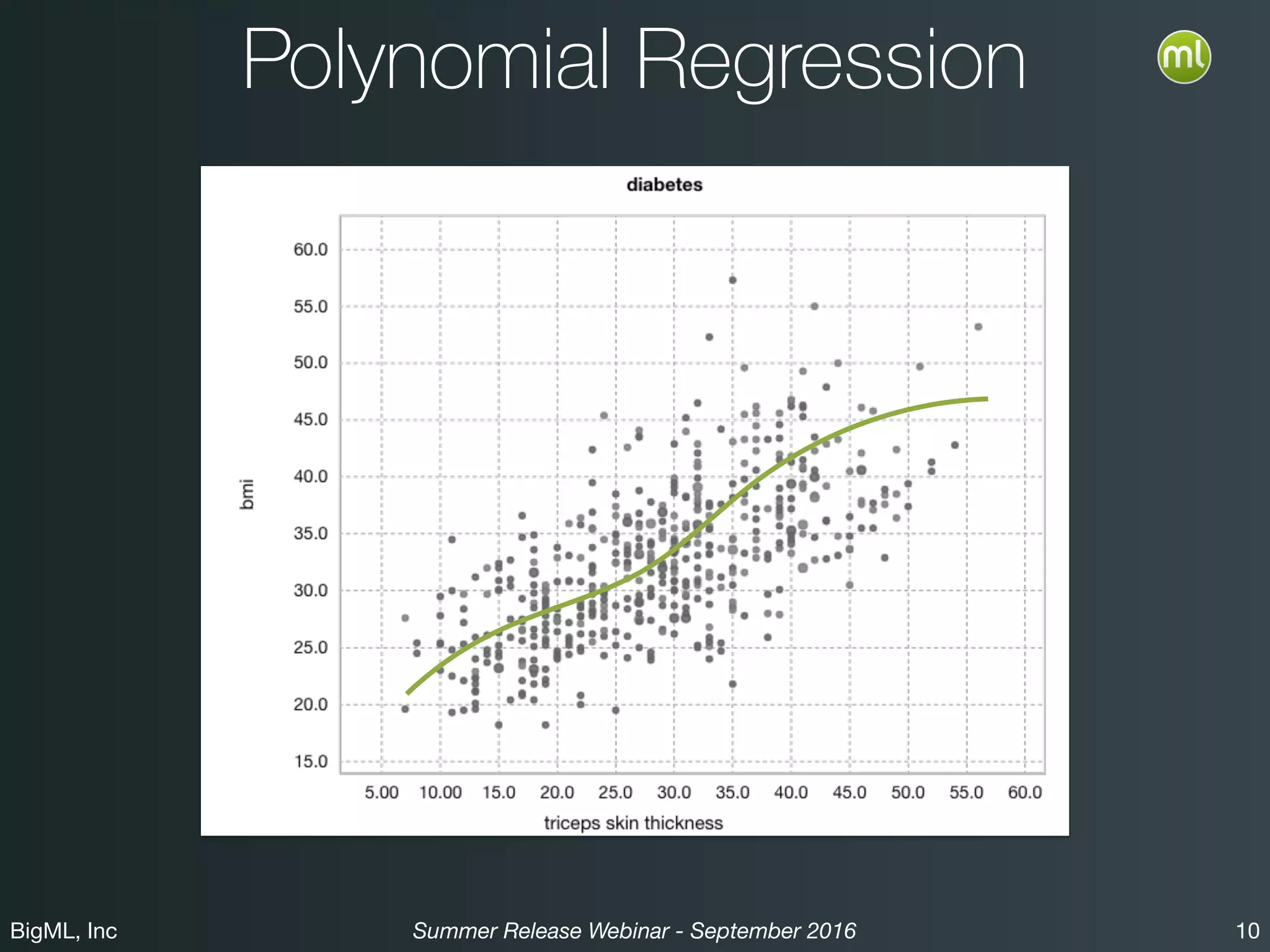
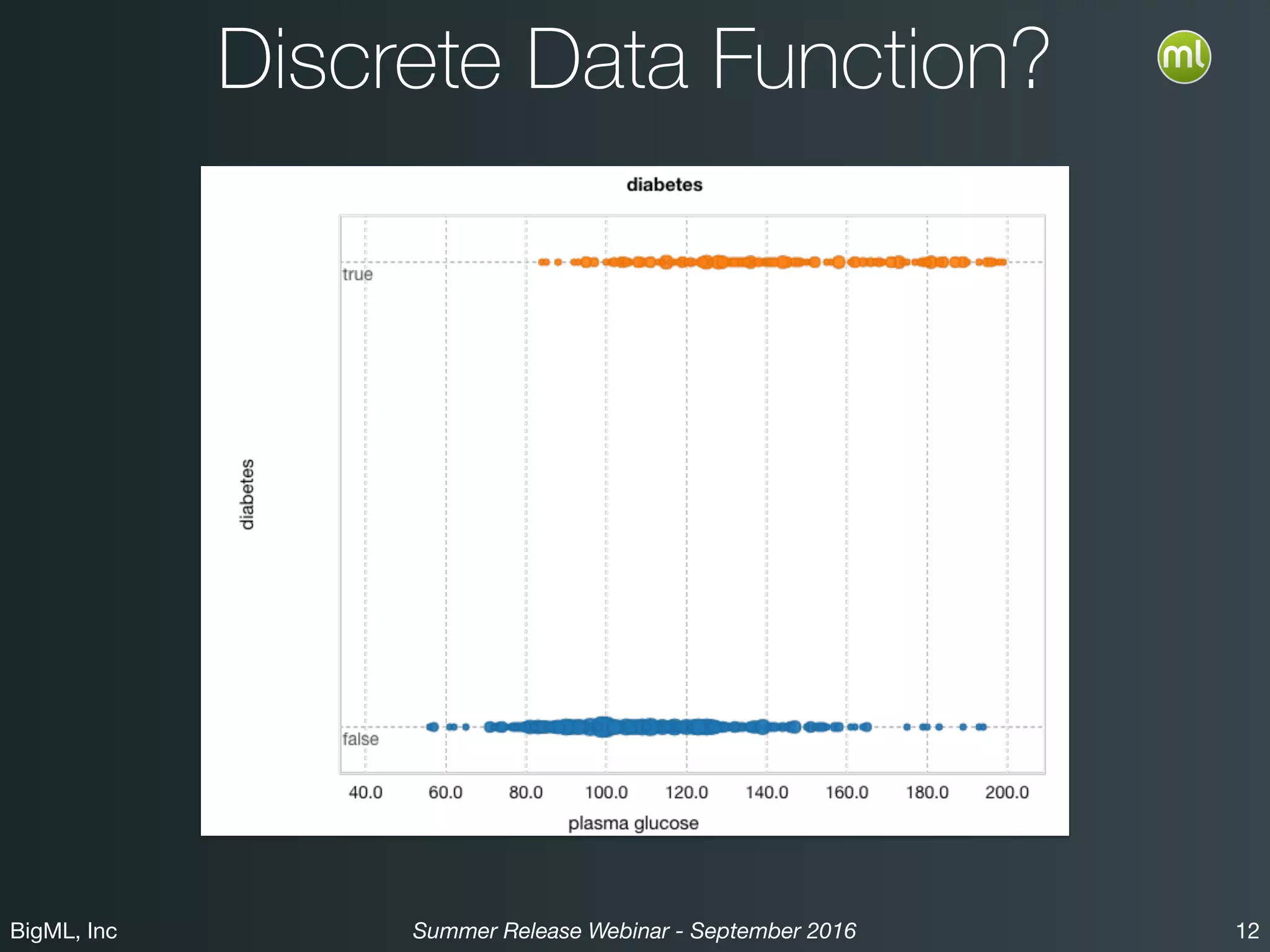
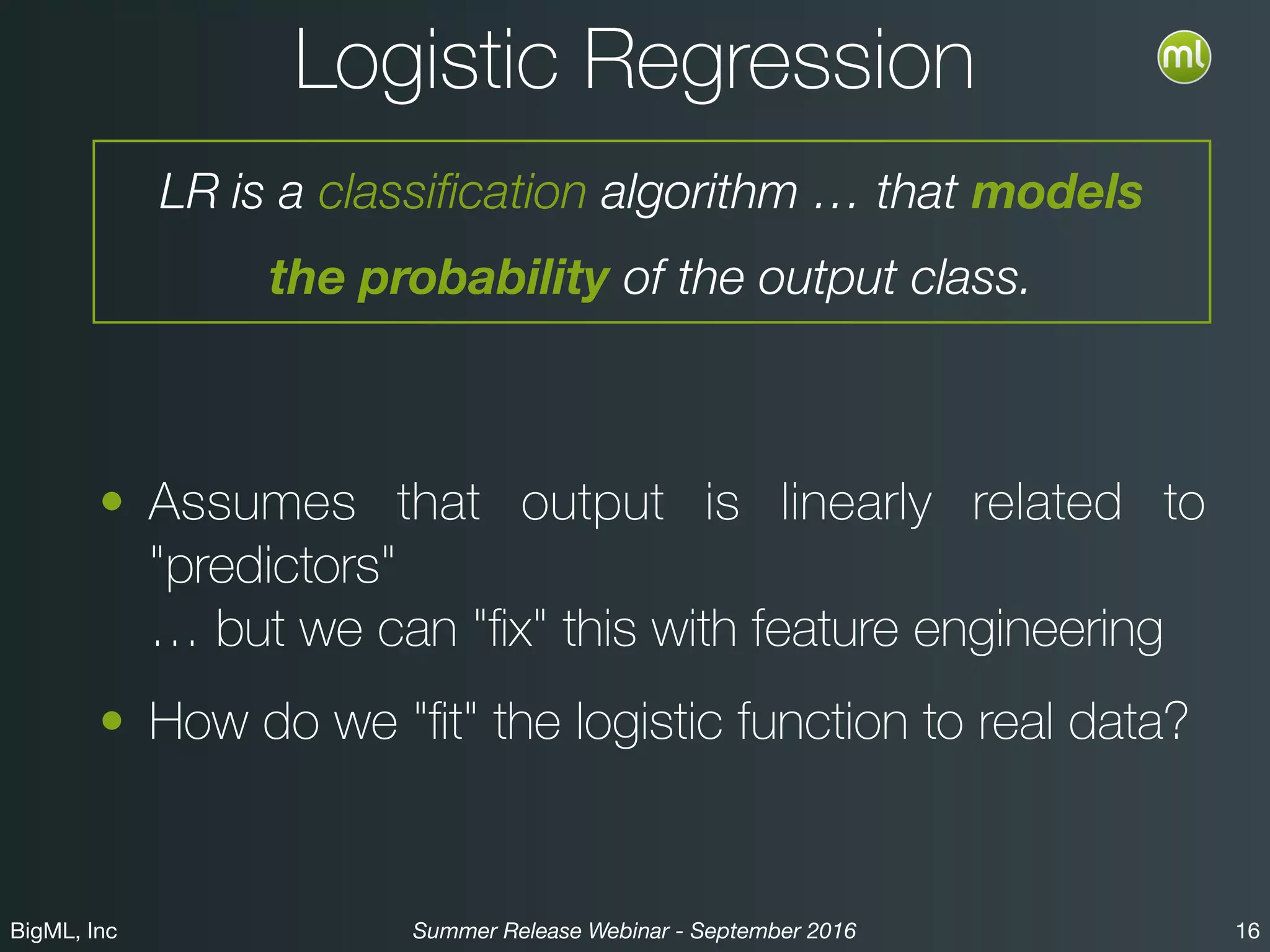
The BigML Summer 2016 release introduced Logistic Regression, expanding its capabilities as a classification algorithm that models the probability of an output class. The release includes details on handling multiple classes, categorical inputs through various encoding methods, and comparisons to decision tree algorithms. Additionally, BigML promotes its educational program, offering free resources and support to students and institutions interested in machine learning.










![BigML, Inc 22Summer Release Webinar - September 2016
LR Multi-Class
• Instead of a binary class ex: [ true, false ], we have multi-
class ex: [ red, green, blue, … ]
• consider “k” classes
• solve “k” one-vs-rest LRs
• Result: coefficients βᵢ for
each of the “k” classes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigml-summer-2016-release-160927185548/75/BigML-Summer-2016-Release-22-2048.jpg)