The document is a table of contents for a book on Excel VBA macros. It lists over 50 chapter titles that cover topics like creating your first macro, working with ranges, worksheets, variables, loops, arrays, sorting, file handling, email, charts and more. Each chapter title is accompanied by a brief 1-2 sentence description of what will be covered in that chapter.












































































![VBA Application.StatusBar to Mark Progress
More Info
Page 77 of 176 wellsr.com
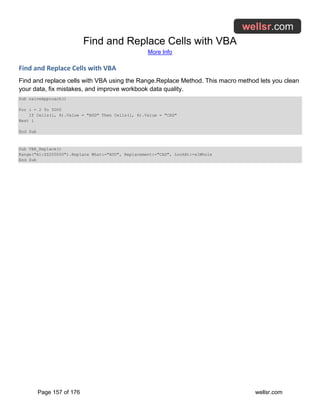
VBA Application.StatusBar to Mark Progress
Use the VBA Application.StatusBar Property to display progress updates when your macro is running.
The StatusBar progress updater is easy to implement.
Sub StatusBar_Updater()
Dim CurrentStatus As Integer
Dim NumberOfBars As Integer
Dim pctDone As Integer
Dim lastrow As Long, i As Long
lastrow = Range("a" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row
'(Step 1) Display your Status Bar
NumberOfBars = 40
Application.StatusBar = "[" & Space(NumberOfBars) & "]"
For i = 1 To lastrow
'(Step 2) Periodically update your Status Bar
CurrentStatus = Int((i / lastrow) * NumberOfBars)
pctDone = Round(CurrentStatus / NumberOfBars * 100, 0)
Application.StatusBar = "[" & String(CurrentStatus, "|") & _
Space(NumberOfBars - CurrentStatus) & "]" & _
" " & pctDone & "% Complete"
DoEvents
'--------------------------------------
'the rest of your macro goes below here
'
'
'--------------------------------------
'(Step 3) Clear the Status Bar when you're done
If i = lastrow Then Application.StatusBar = ""
Next i
End Sub](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigbookofexcelvbamacros-231030172814-5d6c29de/85/big_book_of_excel_vba_macros-pdf-77-320.jpg)




























![VBA Regex Regular Expressions Guide
More Info
Page 106 of 176 wellsr.com
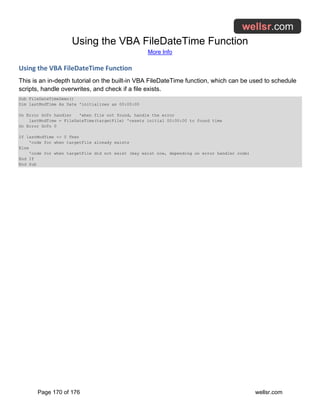
VBA Regex Regular Expressions Guide
VBA RegEx, or Regular Expressions, are special character sequences that define search patterns
and are used to identify specific patterns of characters in a string. This tutorial will explain VBA RegEx
pattern examples so you can create your own regular expressions.
Sub CallRegEx()
'Must add reference (Tools > References) to the
' "Microsoft VBScript Regular Expressions 5.5" Object Library
Dim r As Match
Dim mcolResults As MatchCollection
Dim strInput As String, strPattern As String
strInput = "The email address,'Mary-Jo.T.Williamson_01+test@test-site.com', is contained within this string"
strPattern = "[a-z0-9-.+_]+@[a-z-]+.[a-z]+"
Set mcolResults = RegEx(strInput, strPattern, , , True)
'print the returned results to the immediate window
If Not mcolResults Is Nothing Then
For Each r In mcolResults
'***********************************
'Insert your code here
'***********************************
Debug.Print r ' remove in production
Next r
End If
End Sub
Function RegEx(strInput As String, strPattern As String, _
Optional GlobalSearch As Boolean, Optional MultiLine As Boolean, _
Optional IgnoreCase As Boolean) As MatchCollection
Dim mcolResults As MatchCollection
Dim objRegEx As New RegExp
If strPattern <> vbNullString Then
With objRegEx
.Global = GlobalSearch
.MultiLine = MultiLine
.IgnoreCase = IgnoreCase
.Pattern = strPattern
End With
If objRegEx.Test(strInput) Then
Set mcolResults = objRegEx.Execute(strInput)
Set RegEx = mcolResults
End If
End If
End Function](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigbookofexcelvbamacros-231030172814-5d6c29de/85/big_book_of_excel_vba_macros-pdf-106-320.jpg)











![Format Numbers with VBA NumberFormat
More Info
Page 118 of 176 wellsr.com
Format Numbers with VBA NumberFormat
This tutorial teaches you how to format numbers in Excel using the VBA NumberFormat property. The
VBA NumberFormat property can control the appearance of decimals, commas and can even format
text.
Sub assigning_numberformats()
Dim cell_to_format As Range
Dim vector_to_format As Range
Dim matrix_to_format As Range
Set cell_to_format = Range("A1")
Set vector_to_format = Range("B1:B100")
Set matrix_to_format = Range("C1:D50")
range_to_format.NumberFormat = "YOUR FORMAT CODE HERE" 'replace range and format code
End Sub
Sub text_formatter()
Range("A1:A4").NumberFormat = "[Magenta] ""[TEXT:]"" @"
End Sub
Sub conditional_number_formats()
Range("A1:A4").NumberFormat = "[>=10][Green]$0.00;[<10][Red]$0.00"
End Sub
Sub fraction_non_base_ten()
Range("A1:A4").NumberFormat = "00 "" and "" 0/8 ""inches"""
End Sub](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigbookofexcelvbamacros-231030172814-5d6c29de/85/big_book_of_excel_vba_macros-pdf-118-320.jpg)