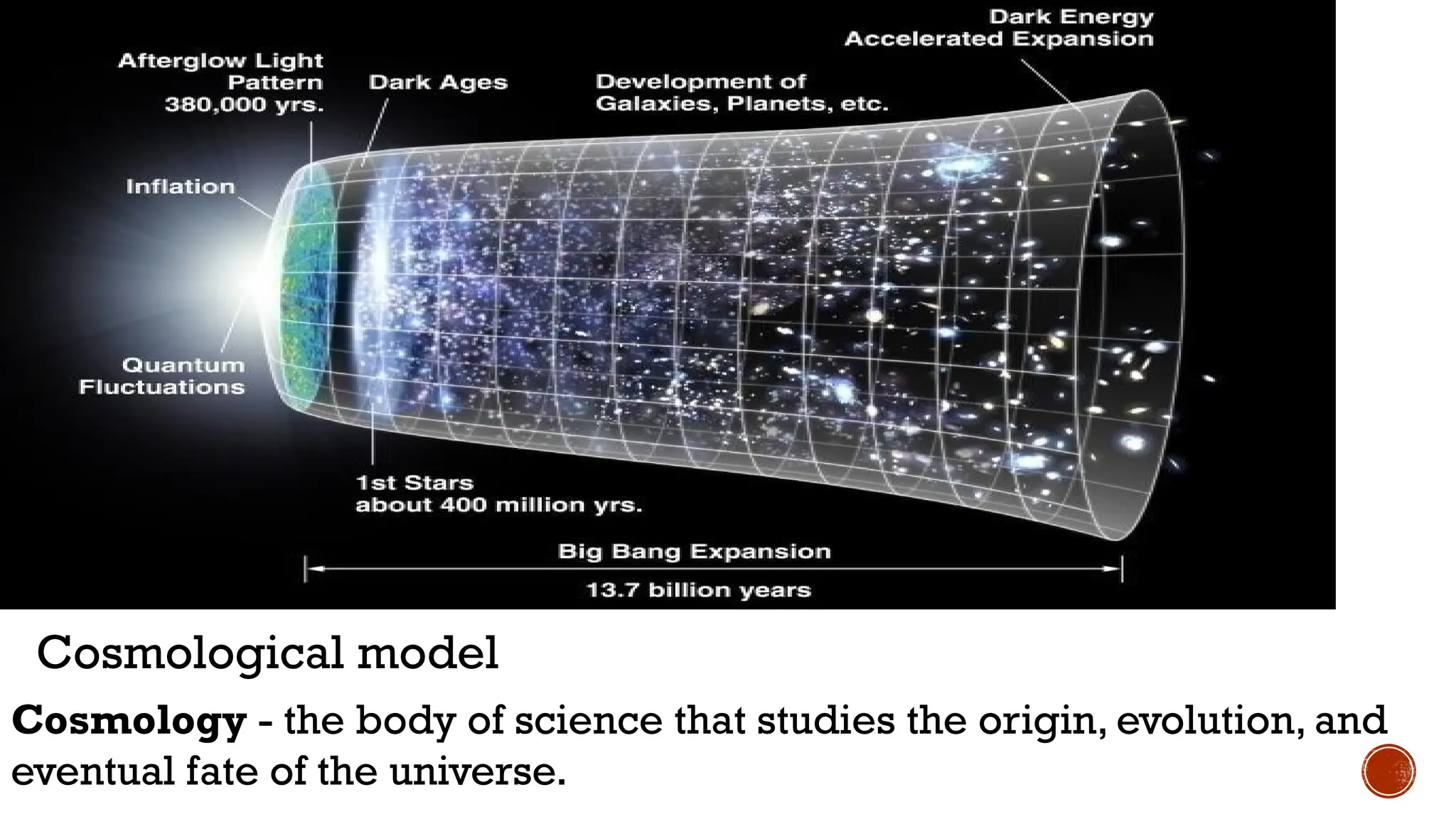
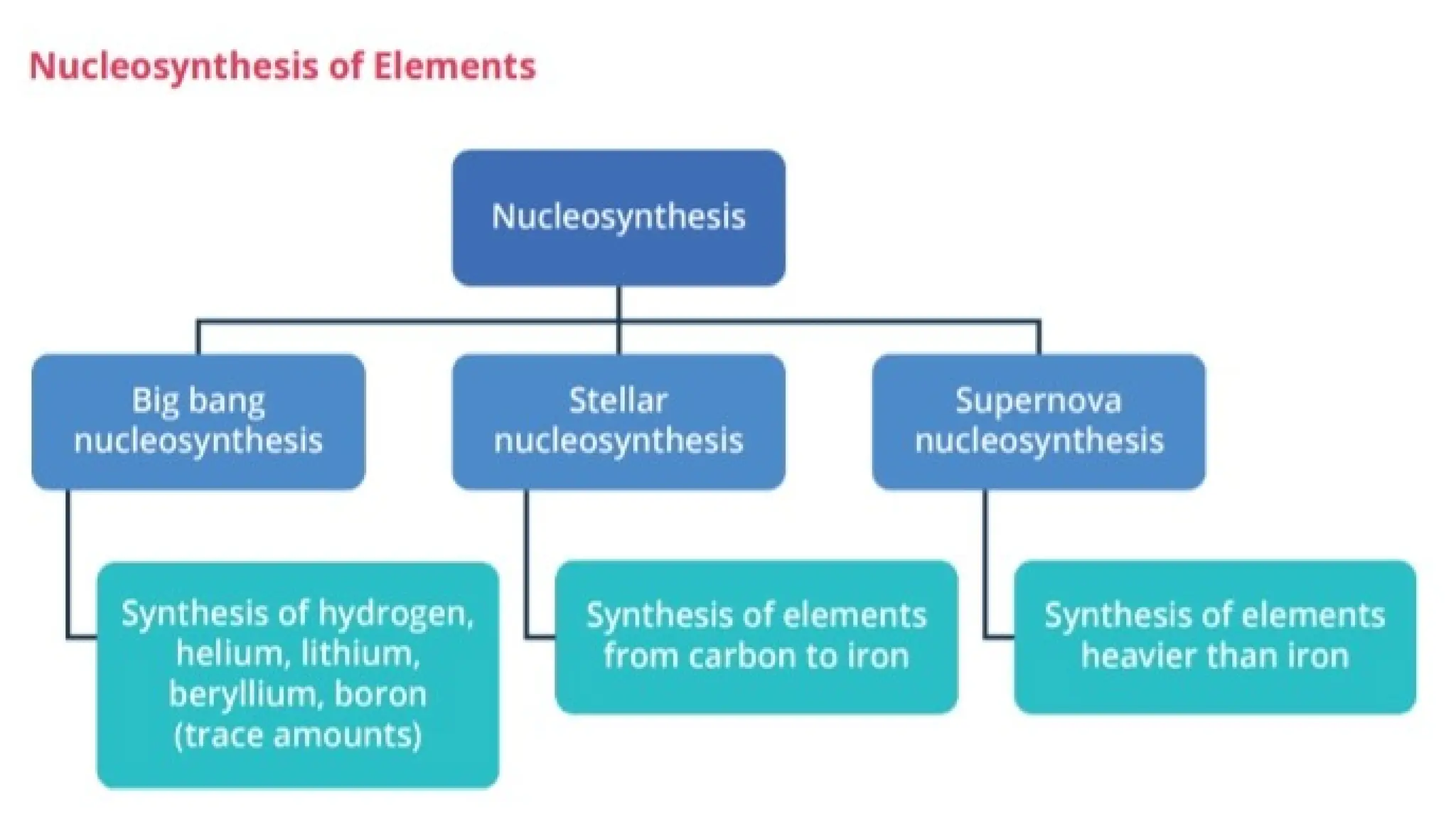
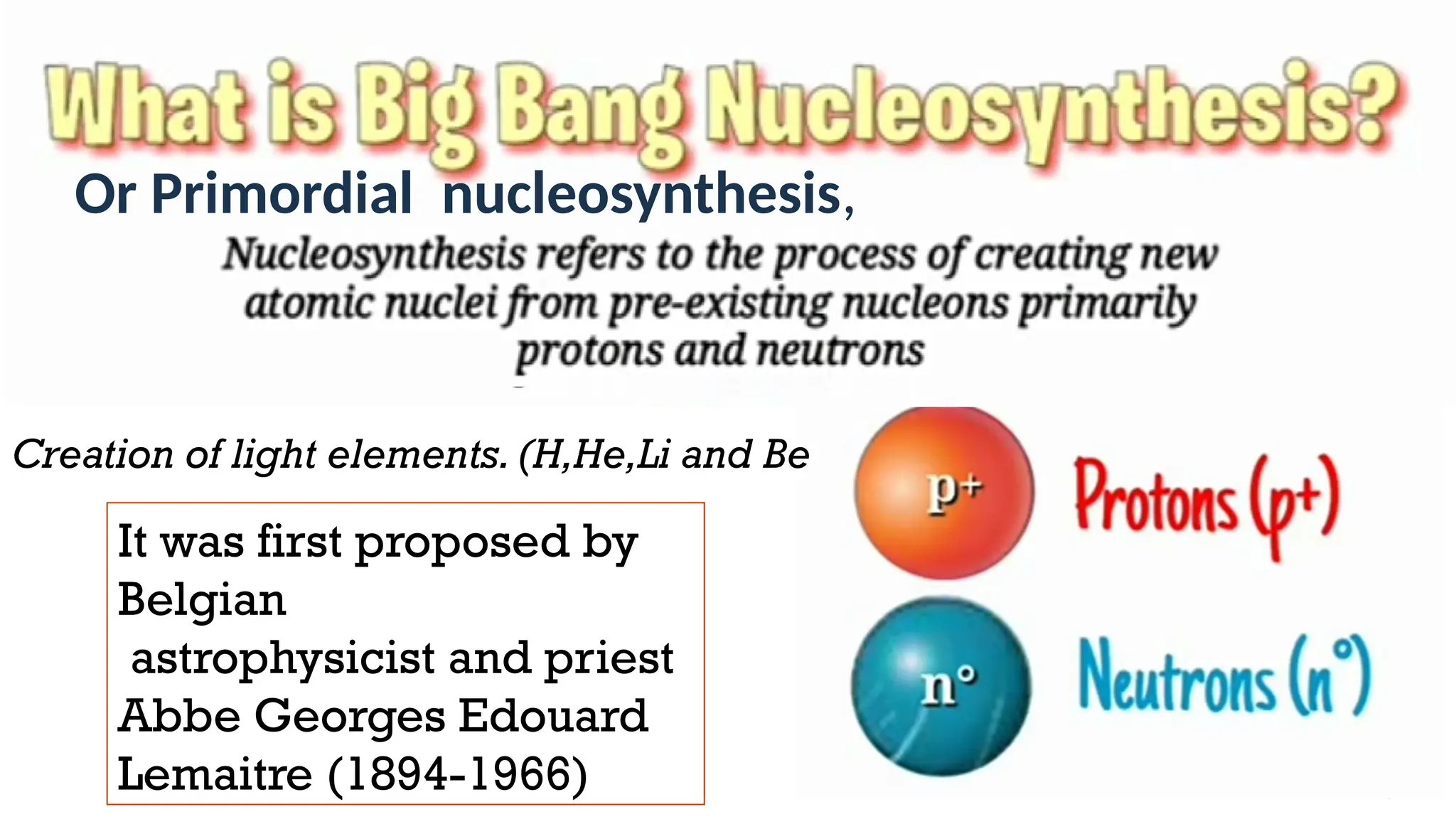
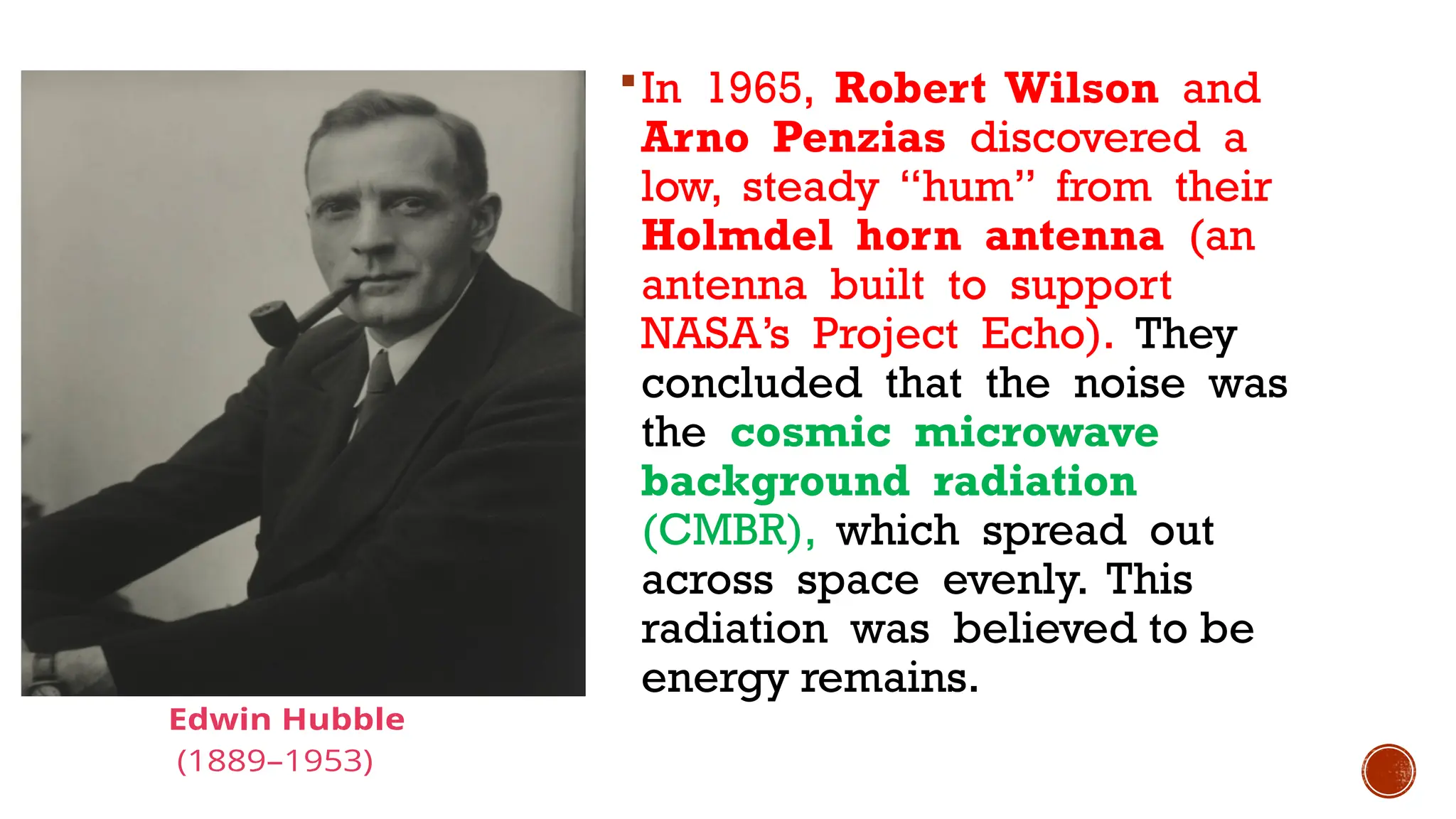
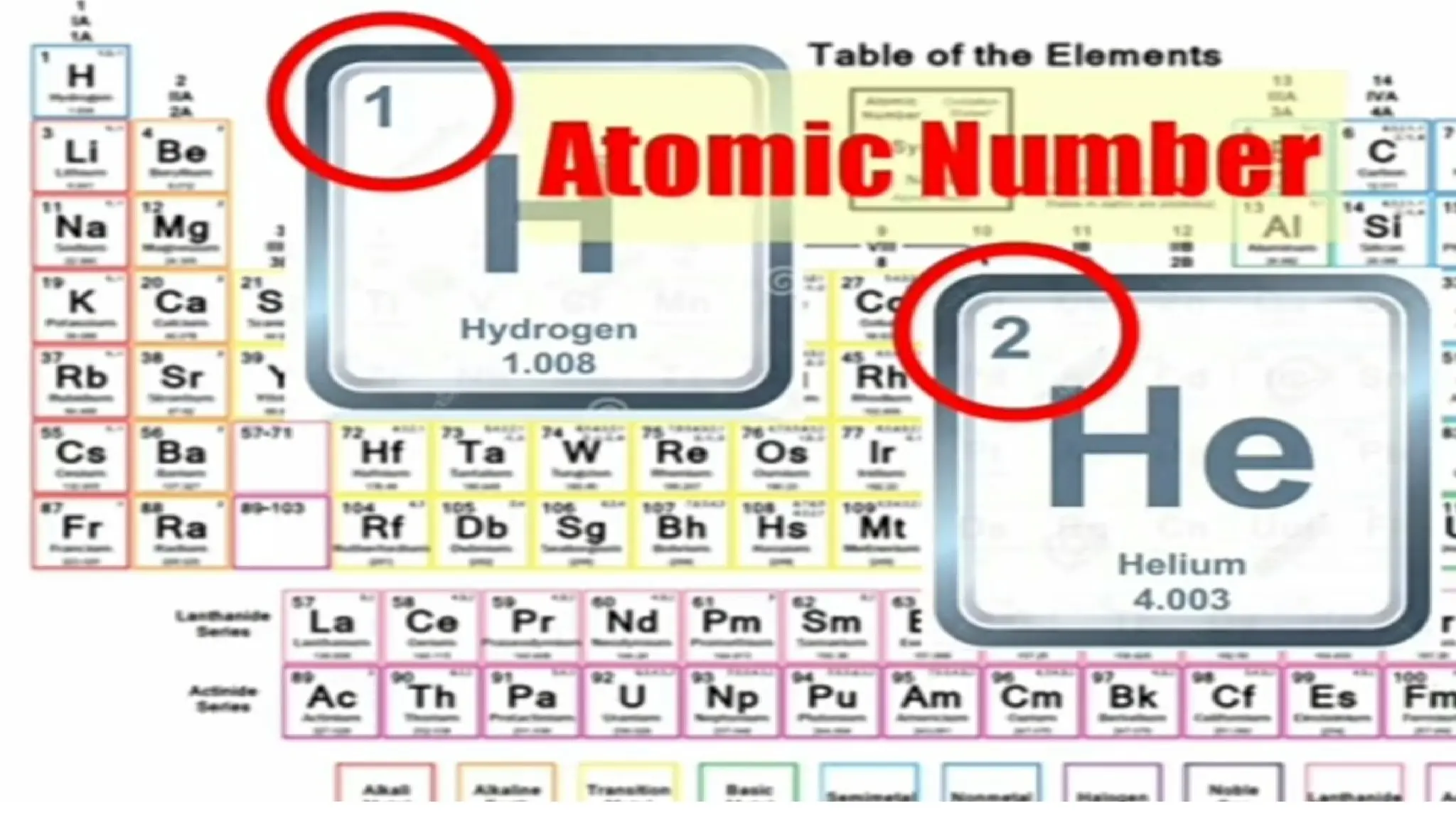
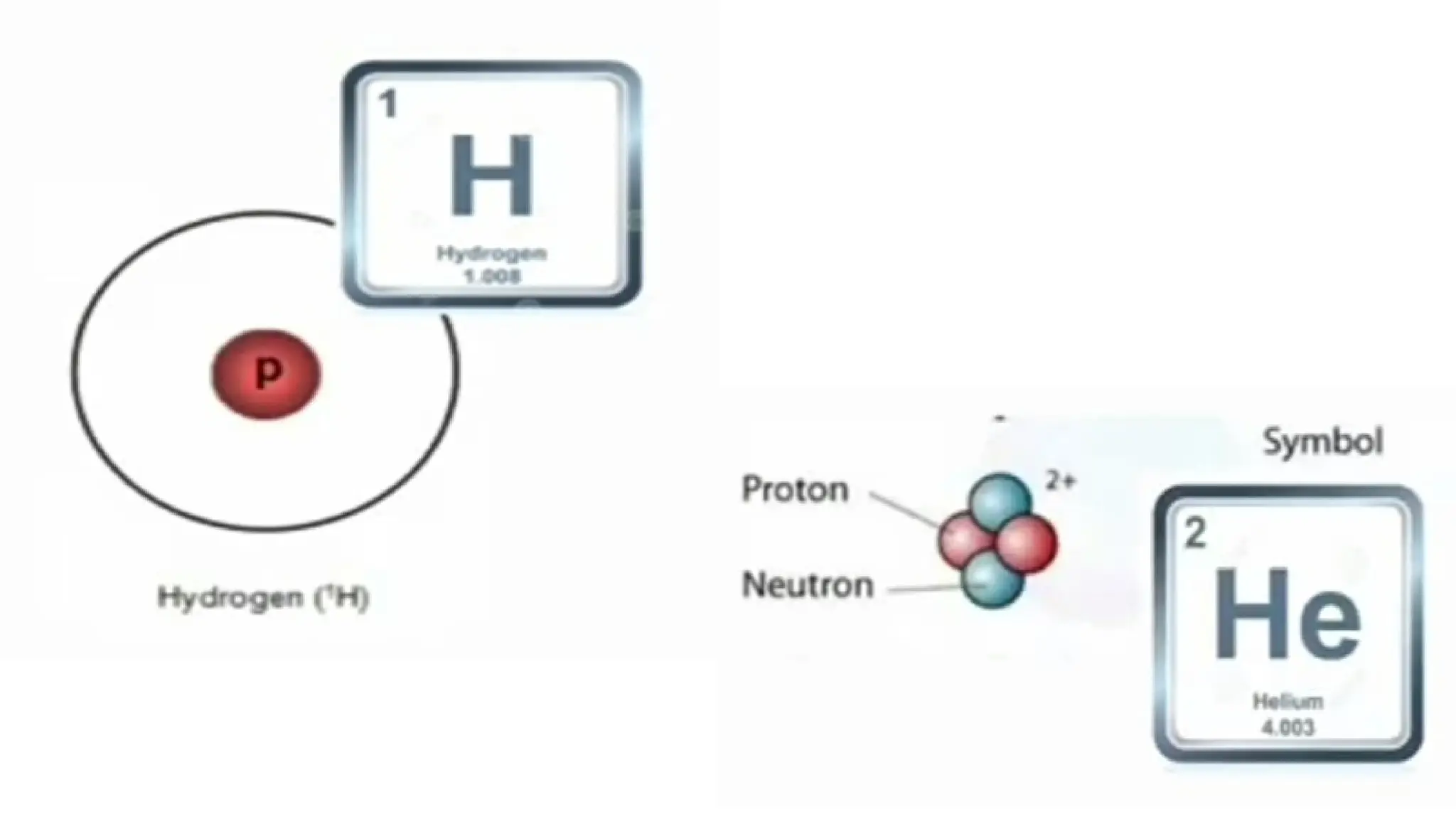
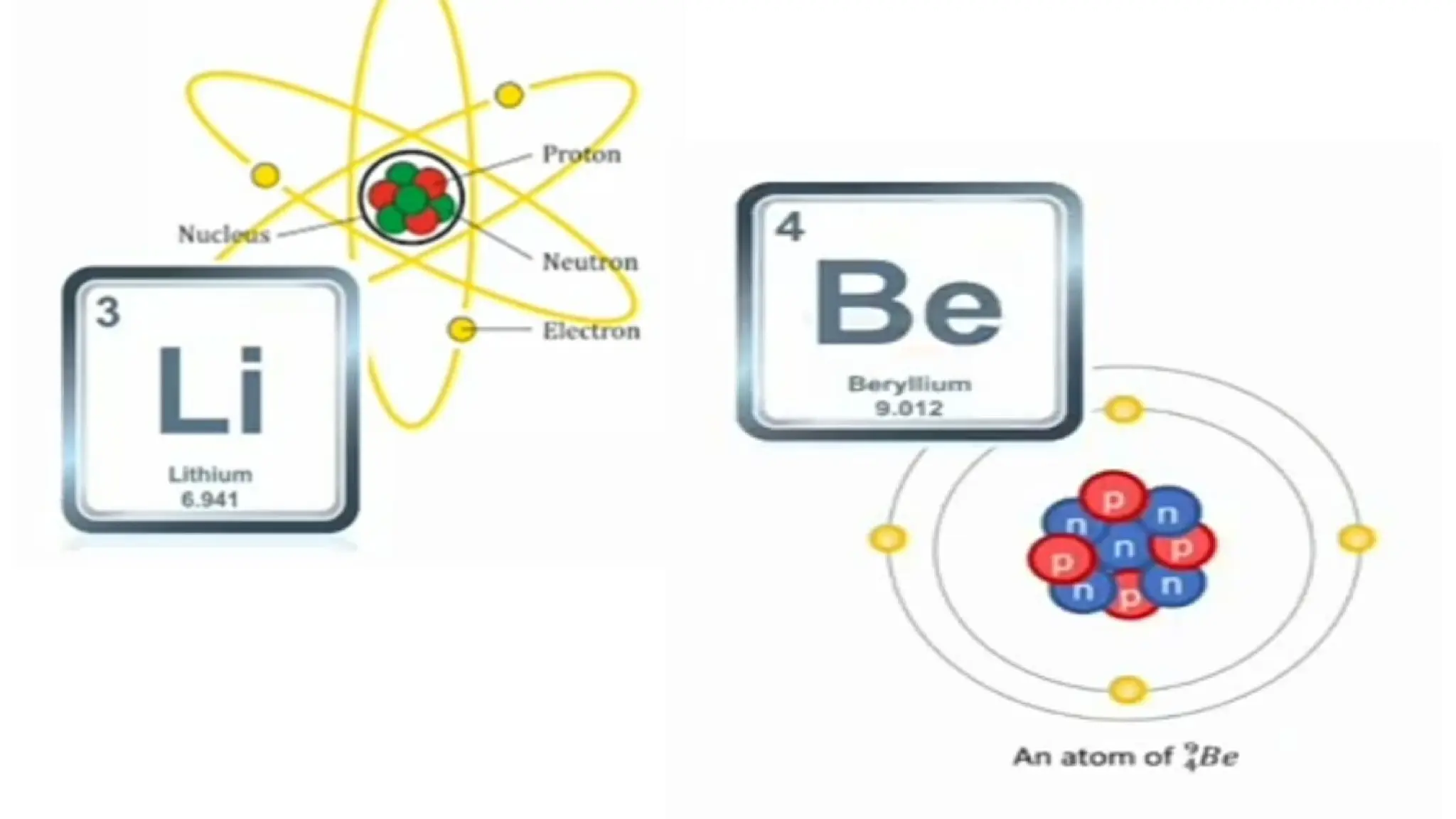
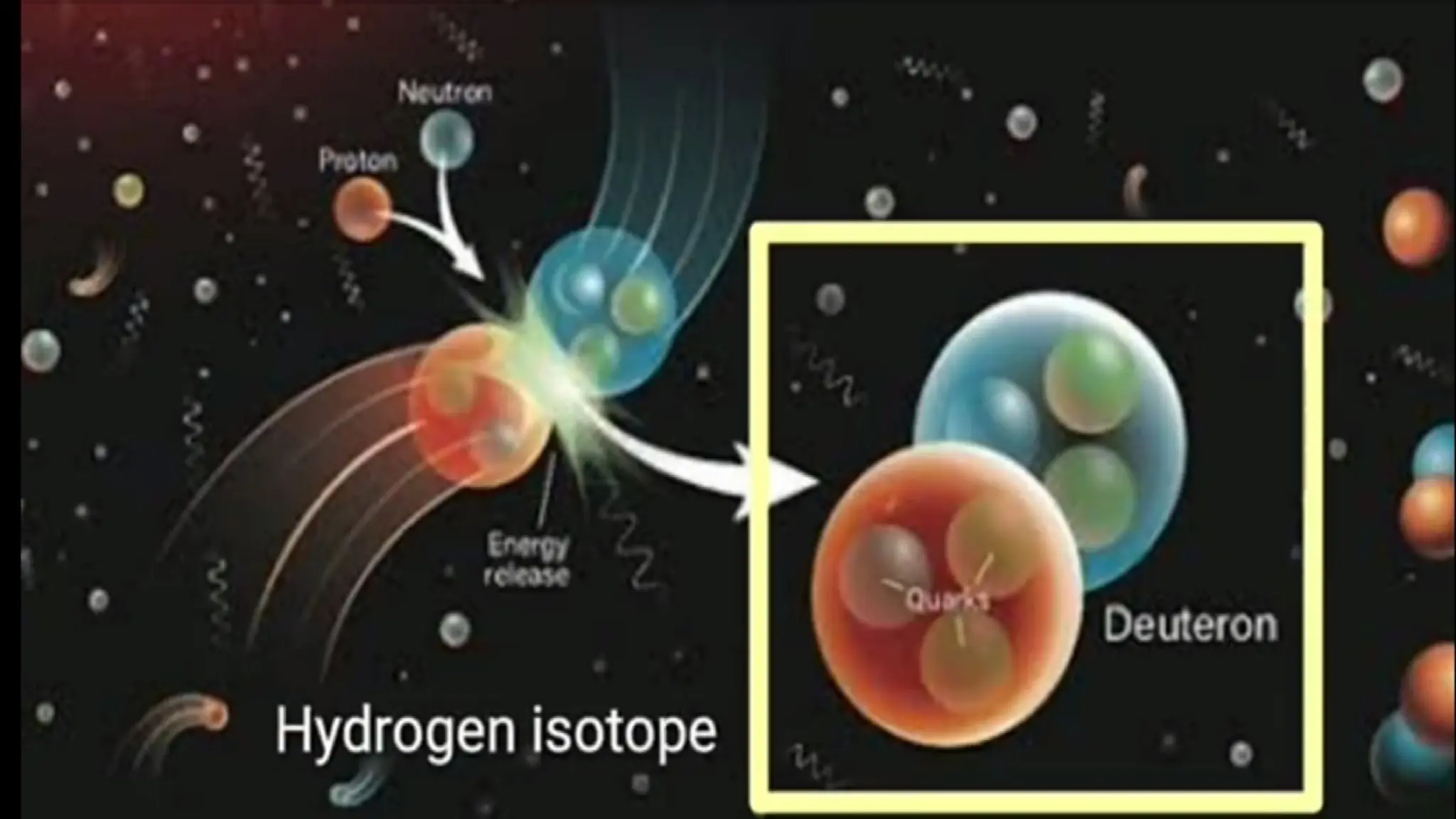
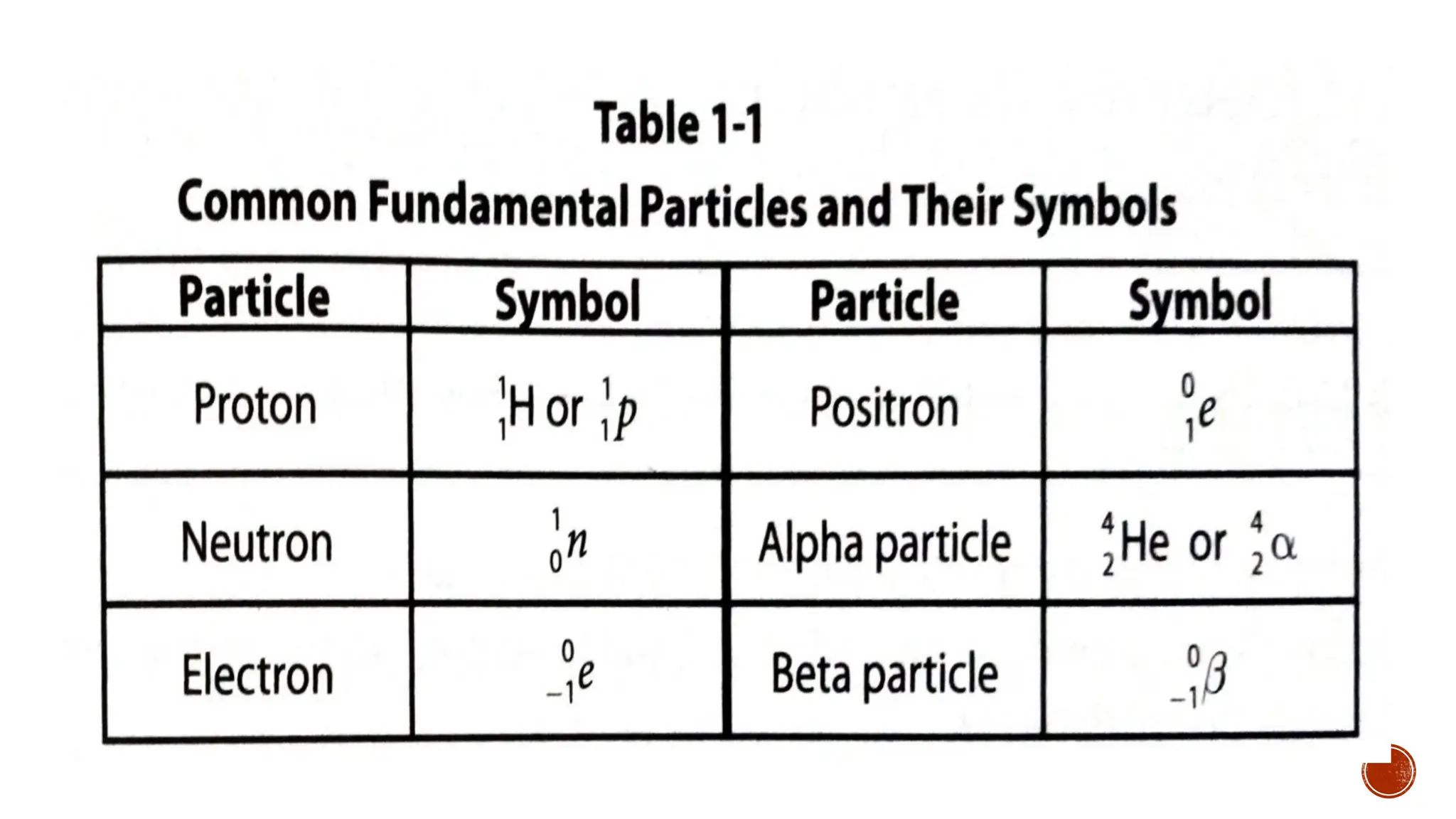
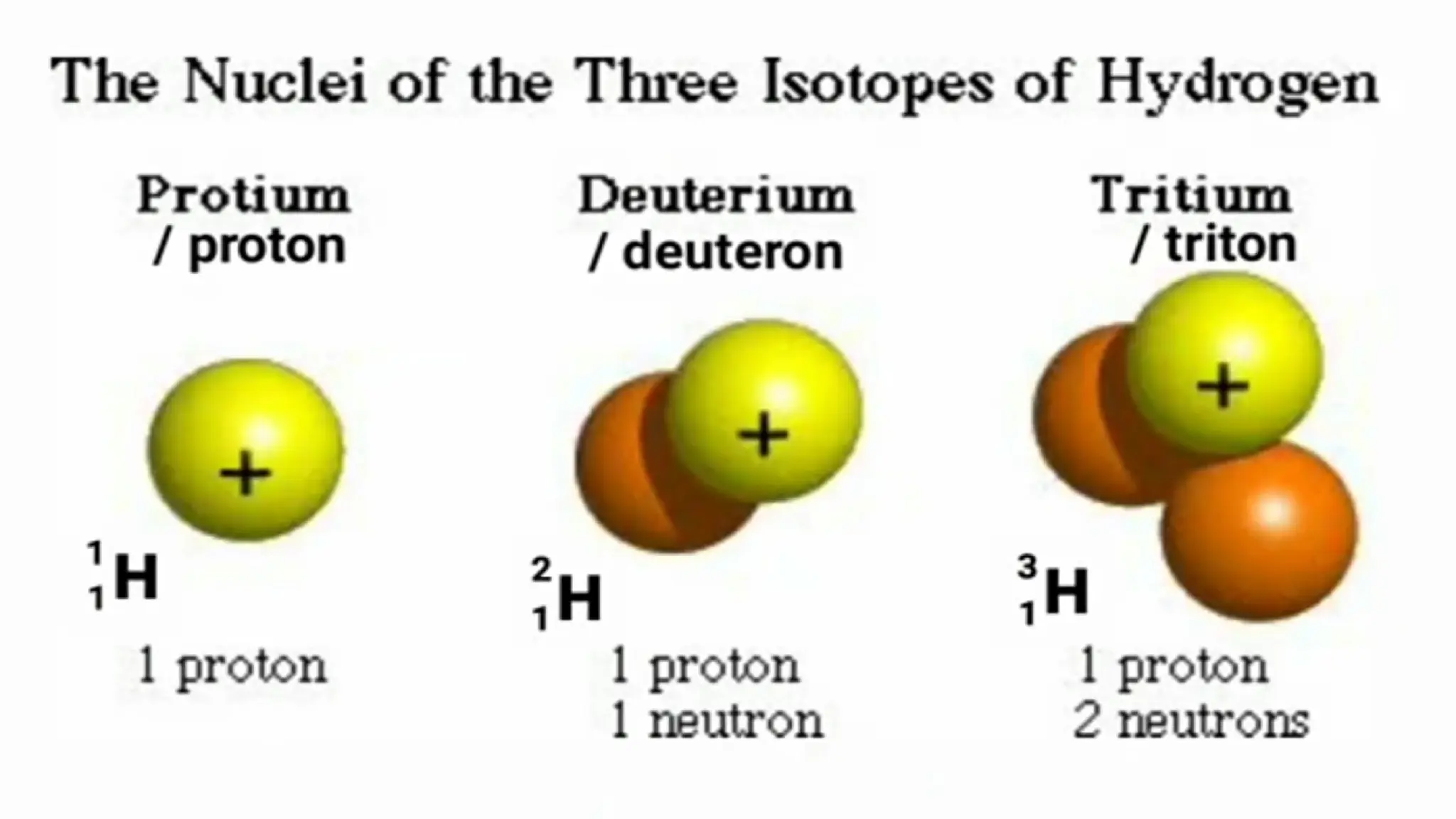
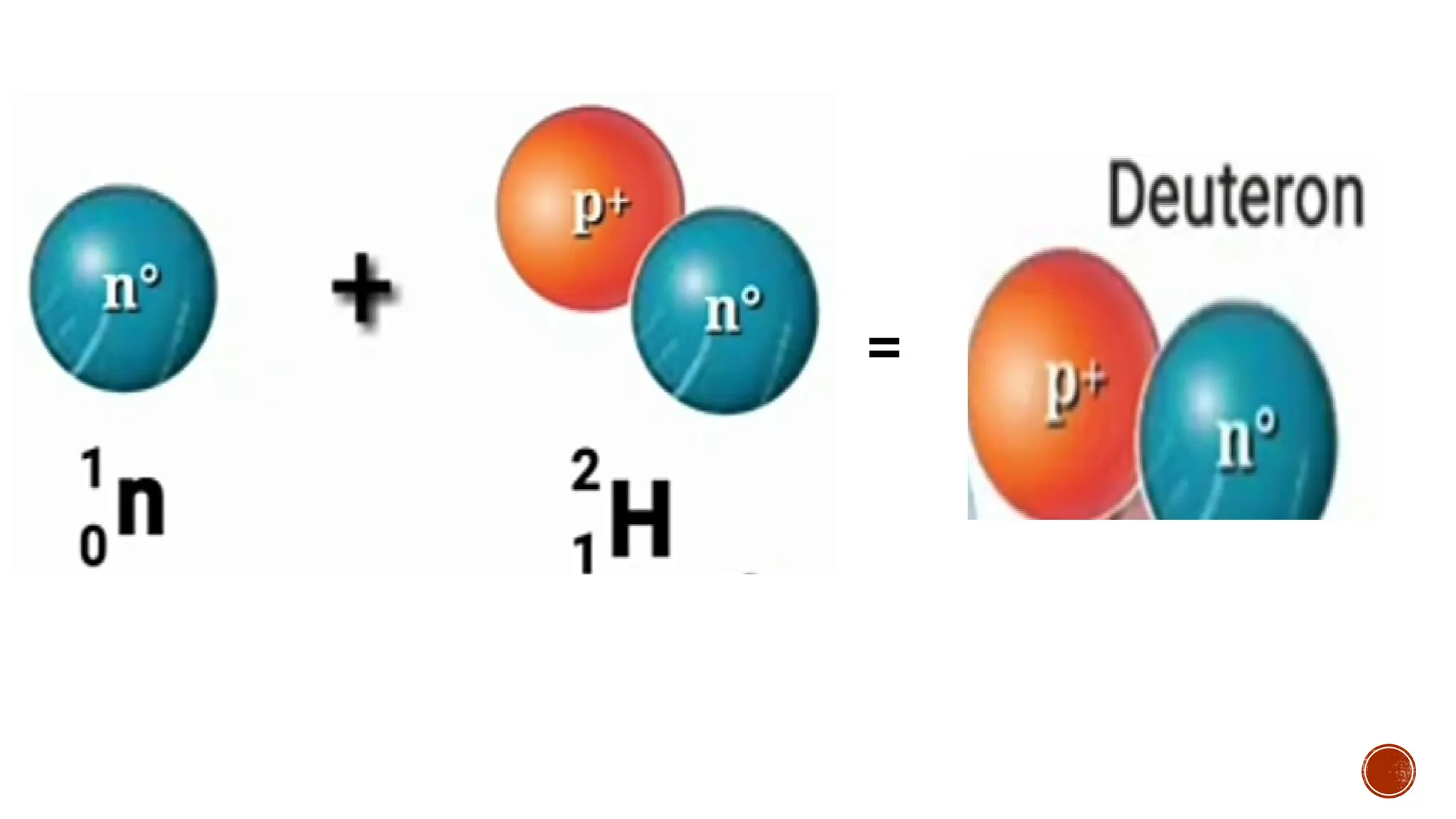
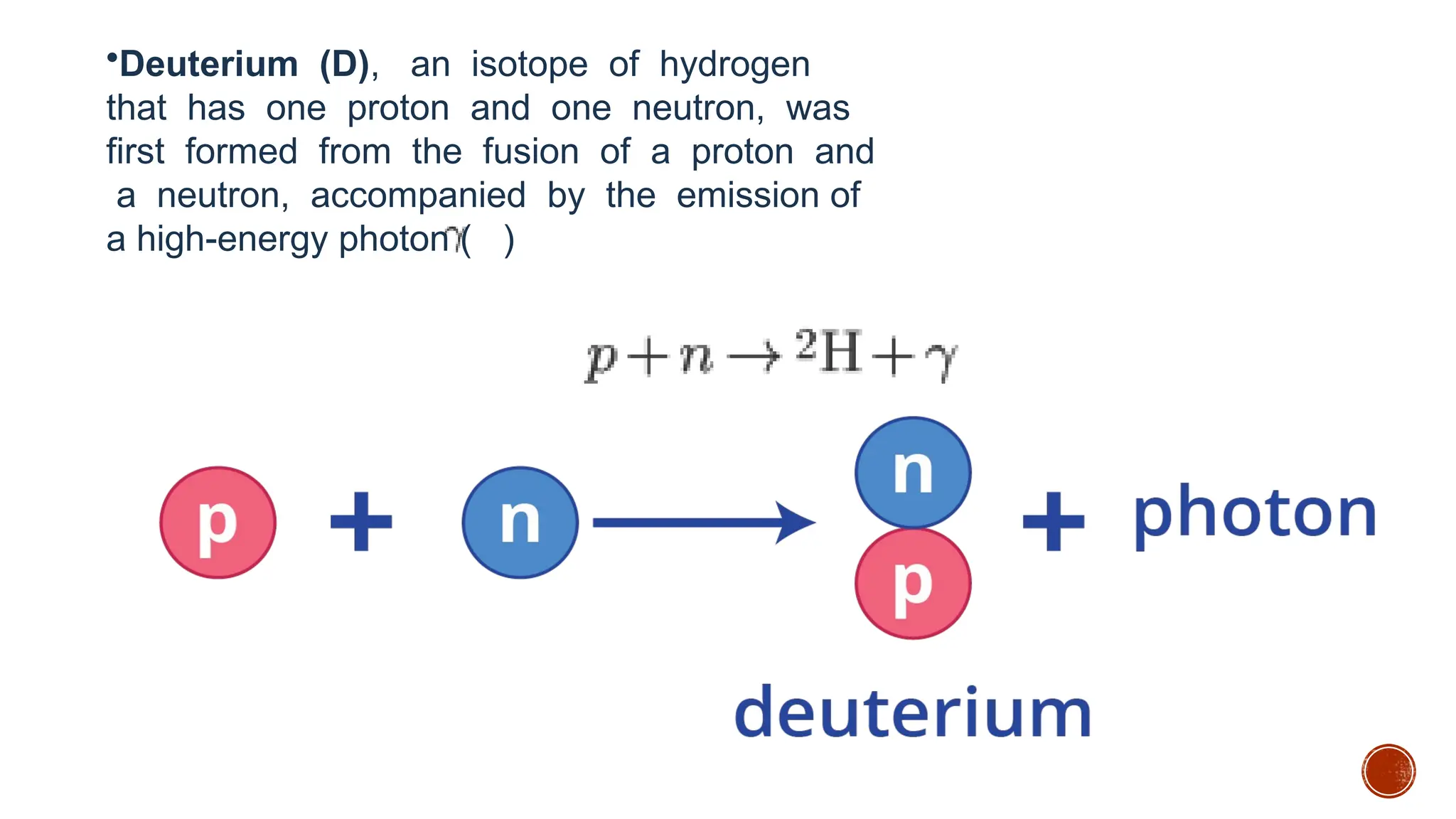
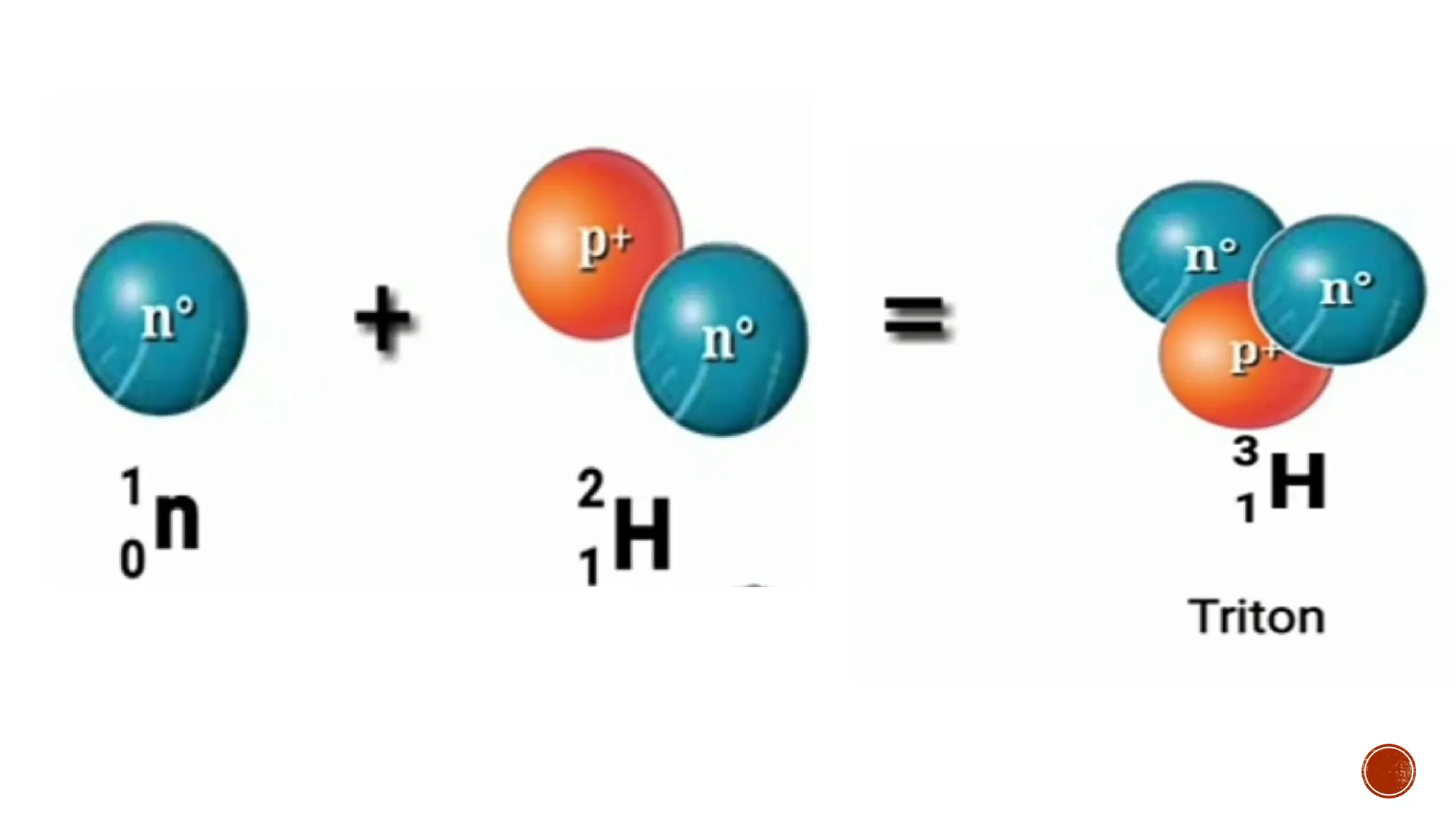
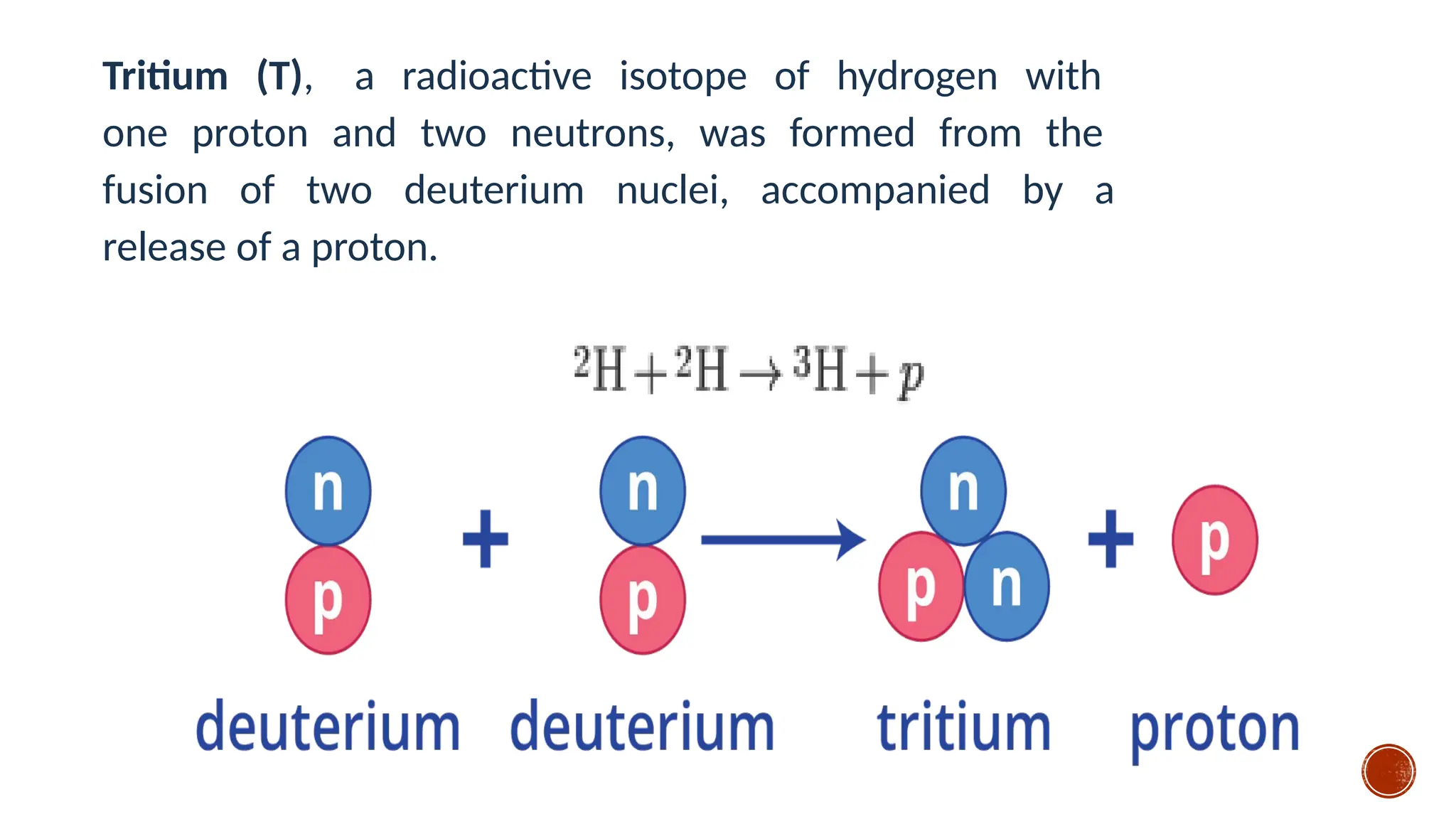
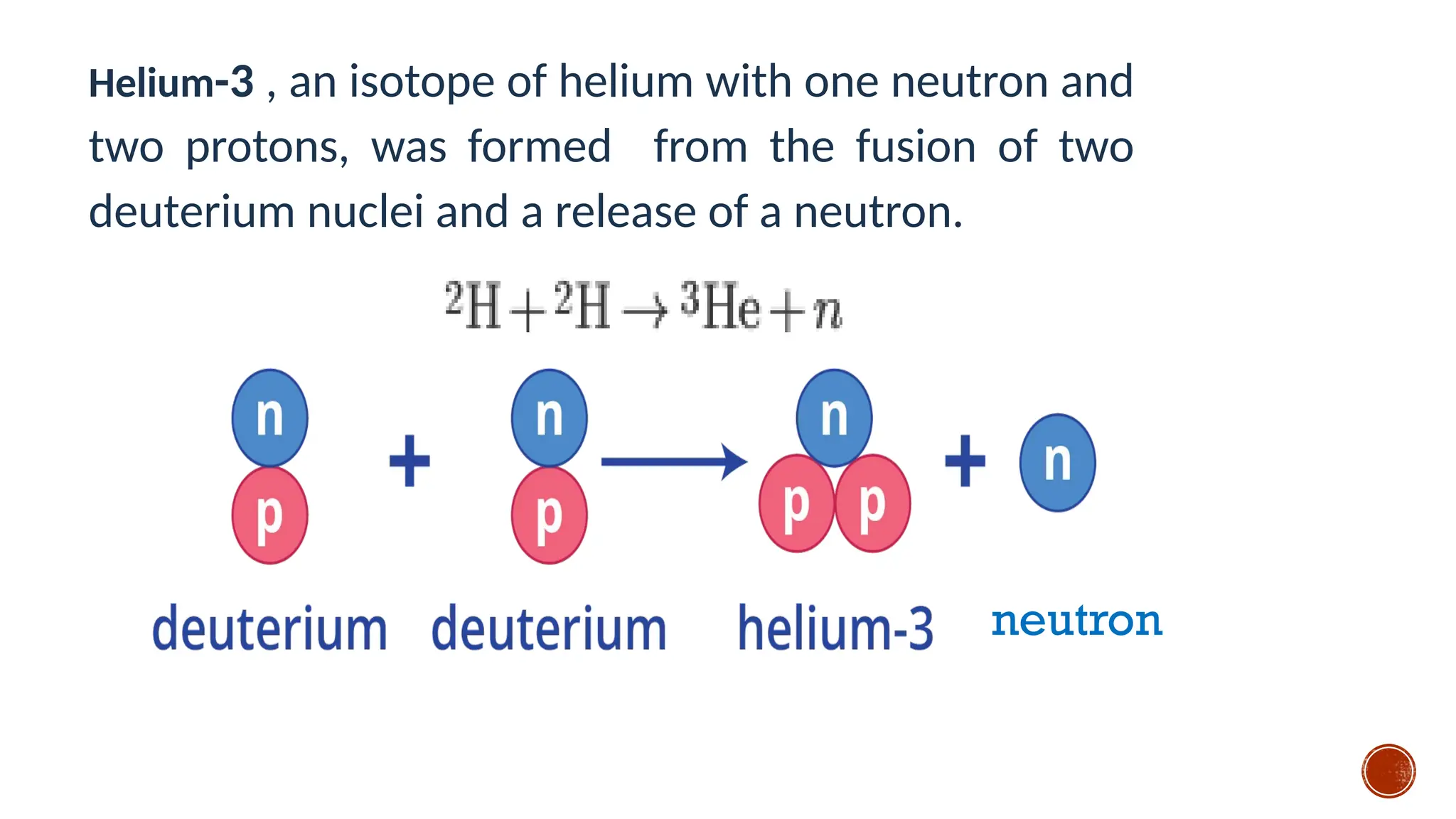
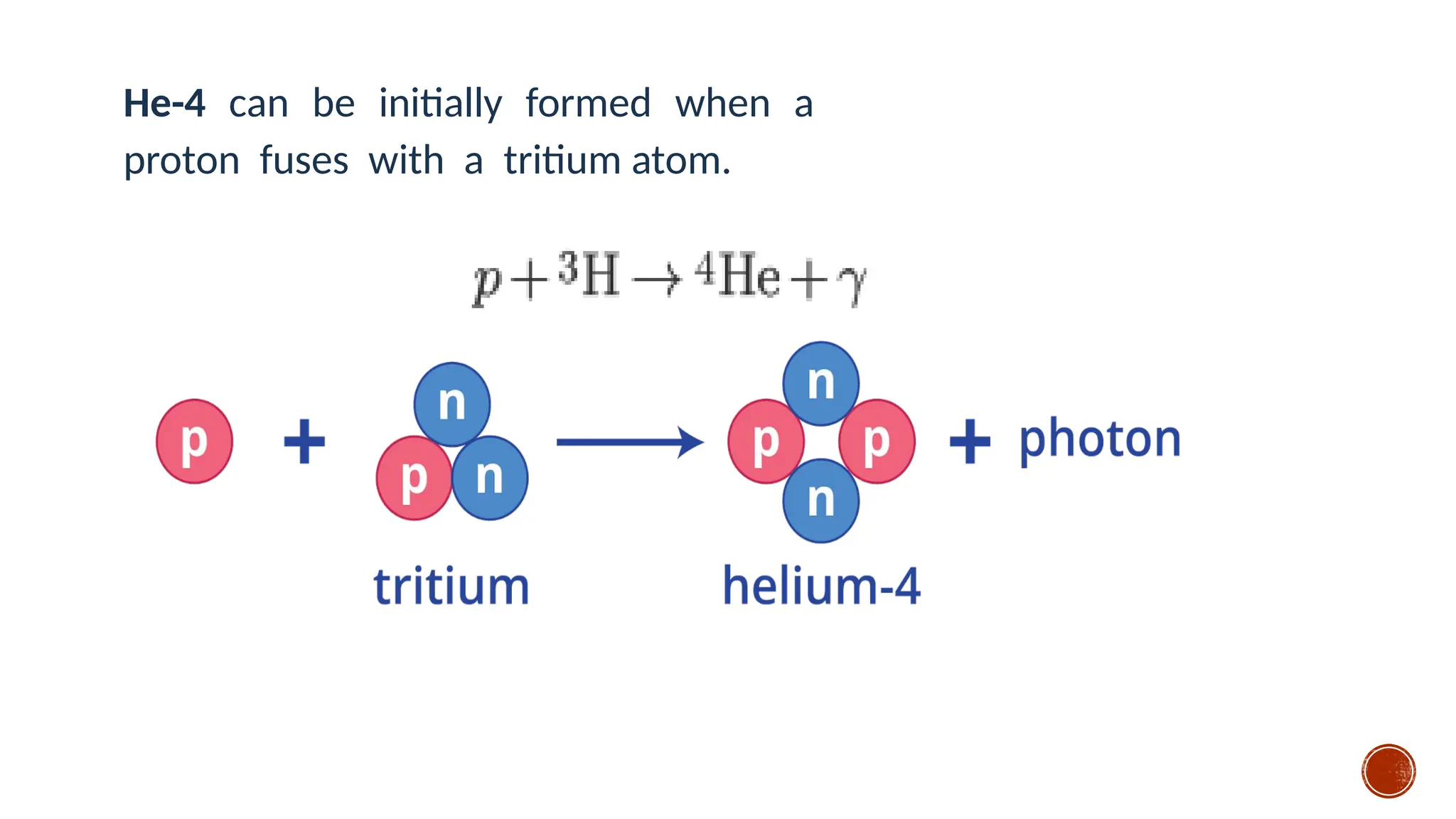
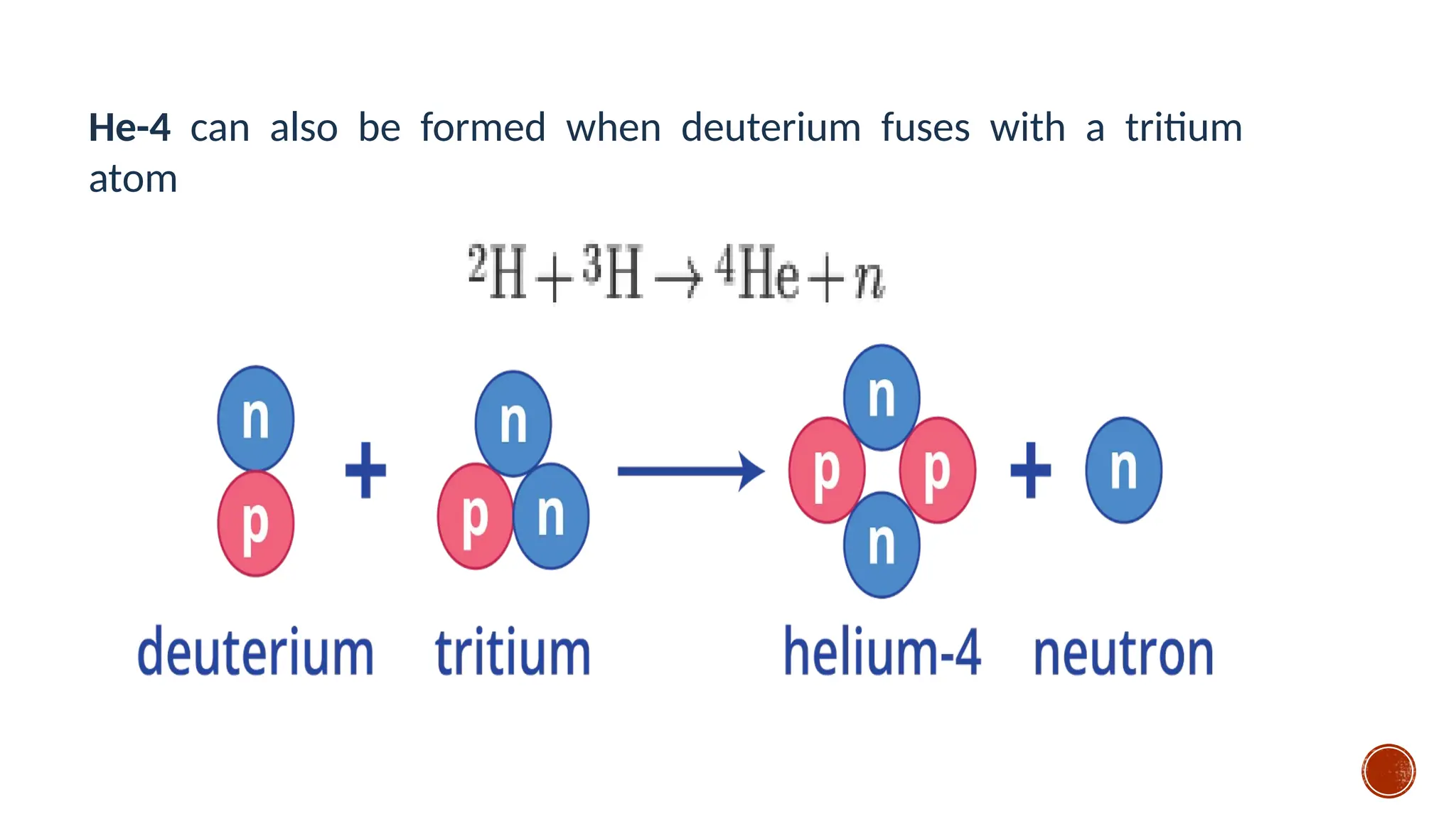
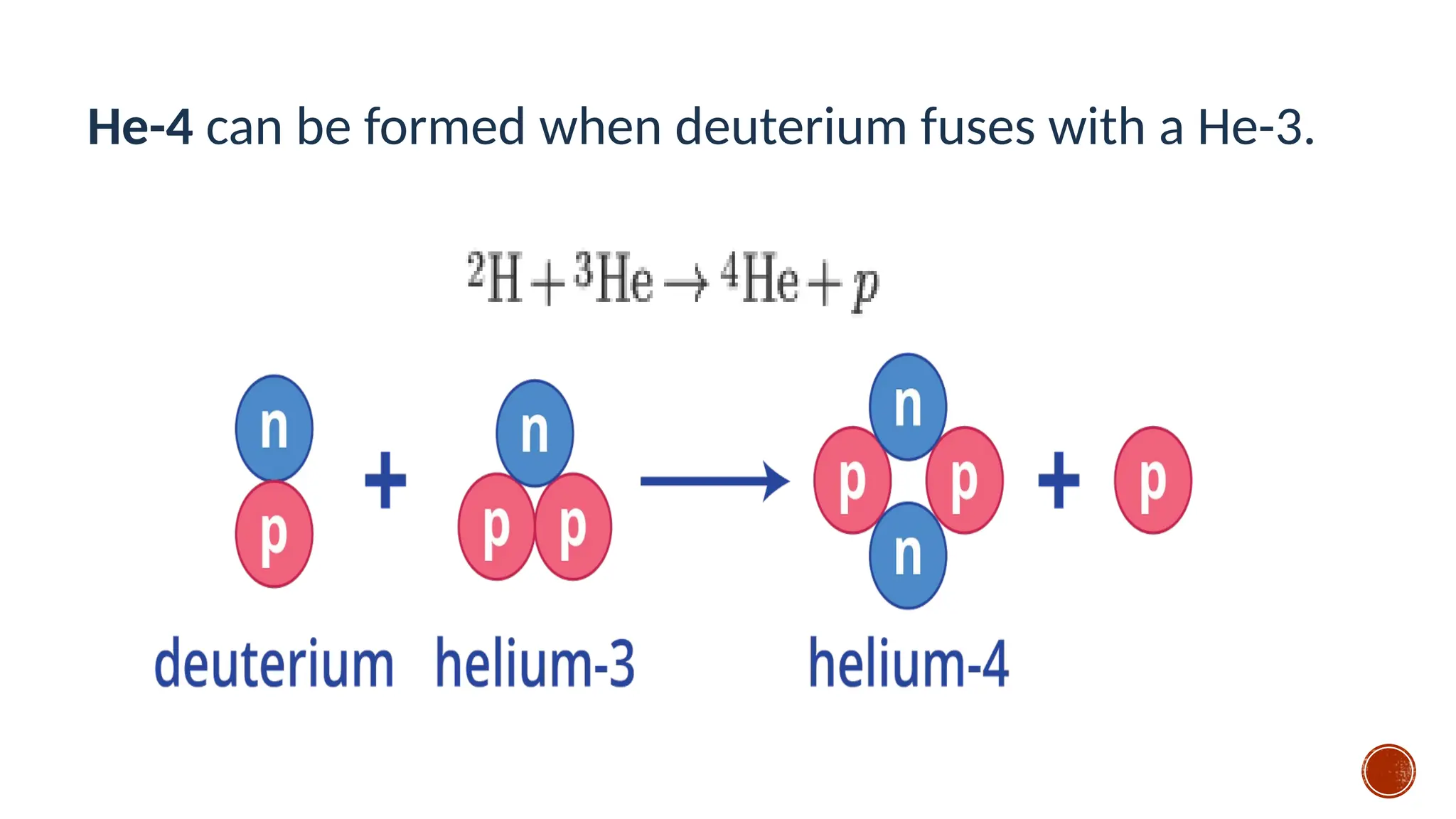
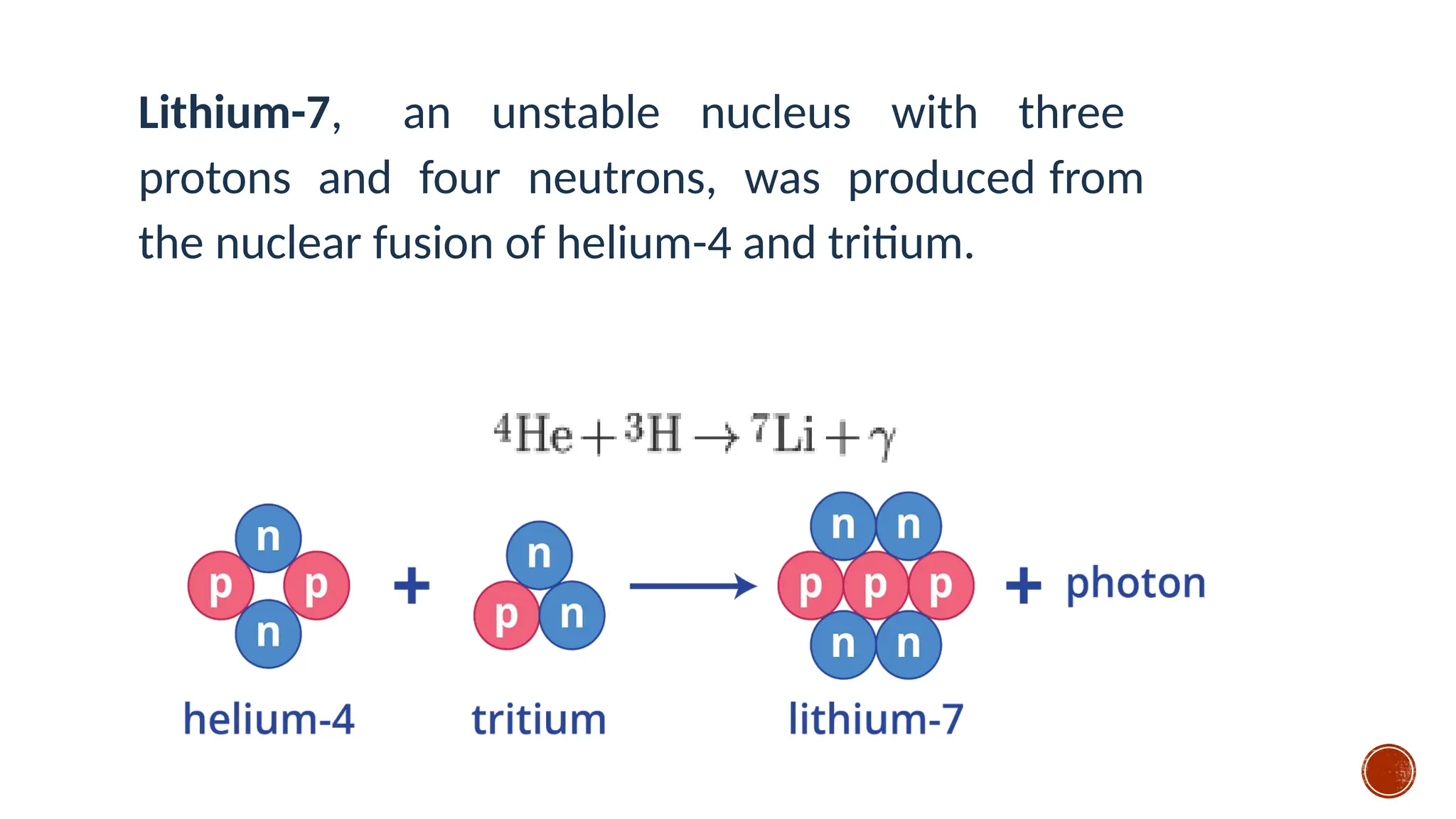
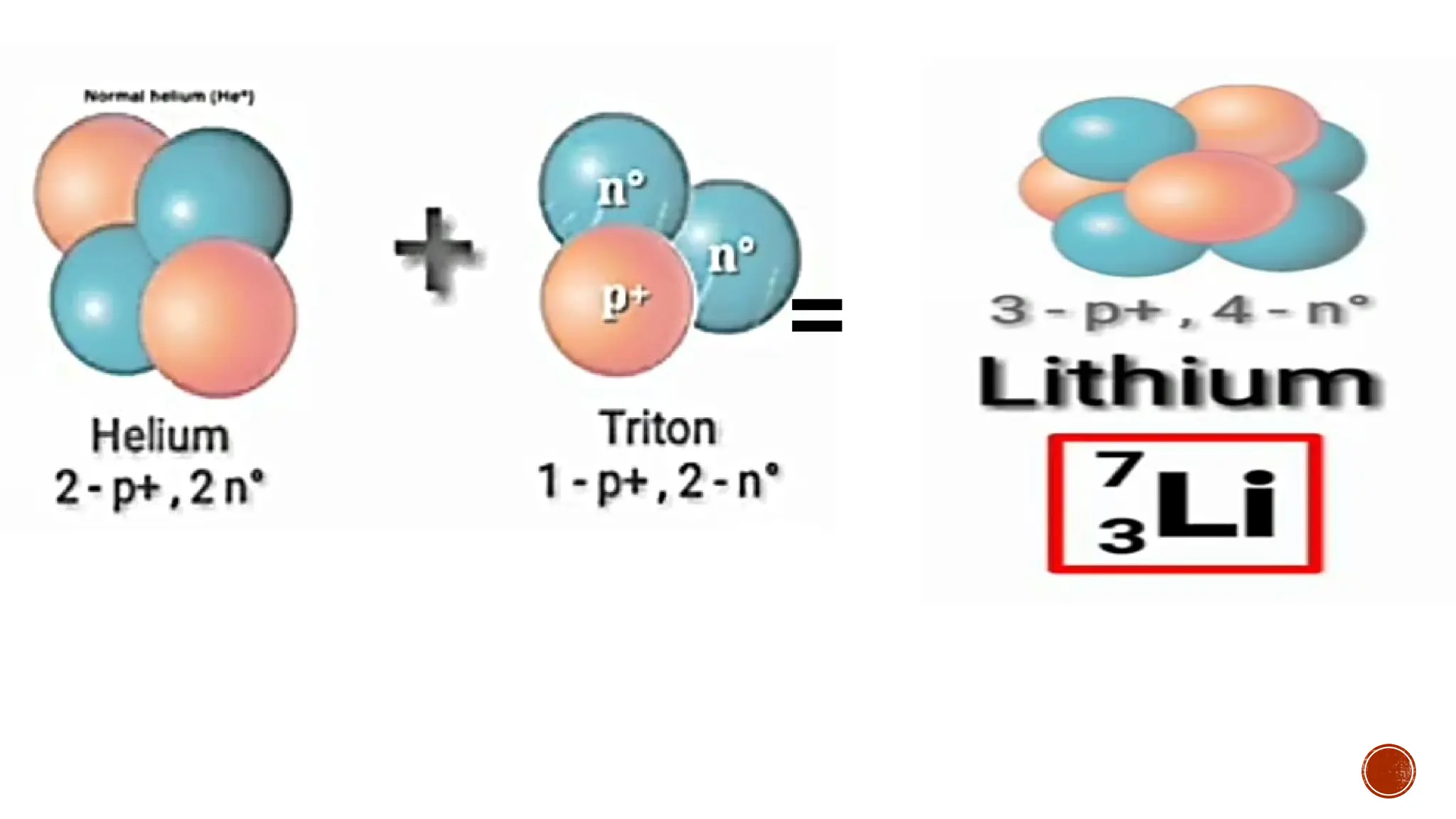
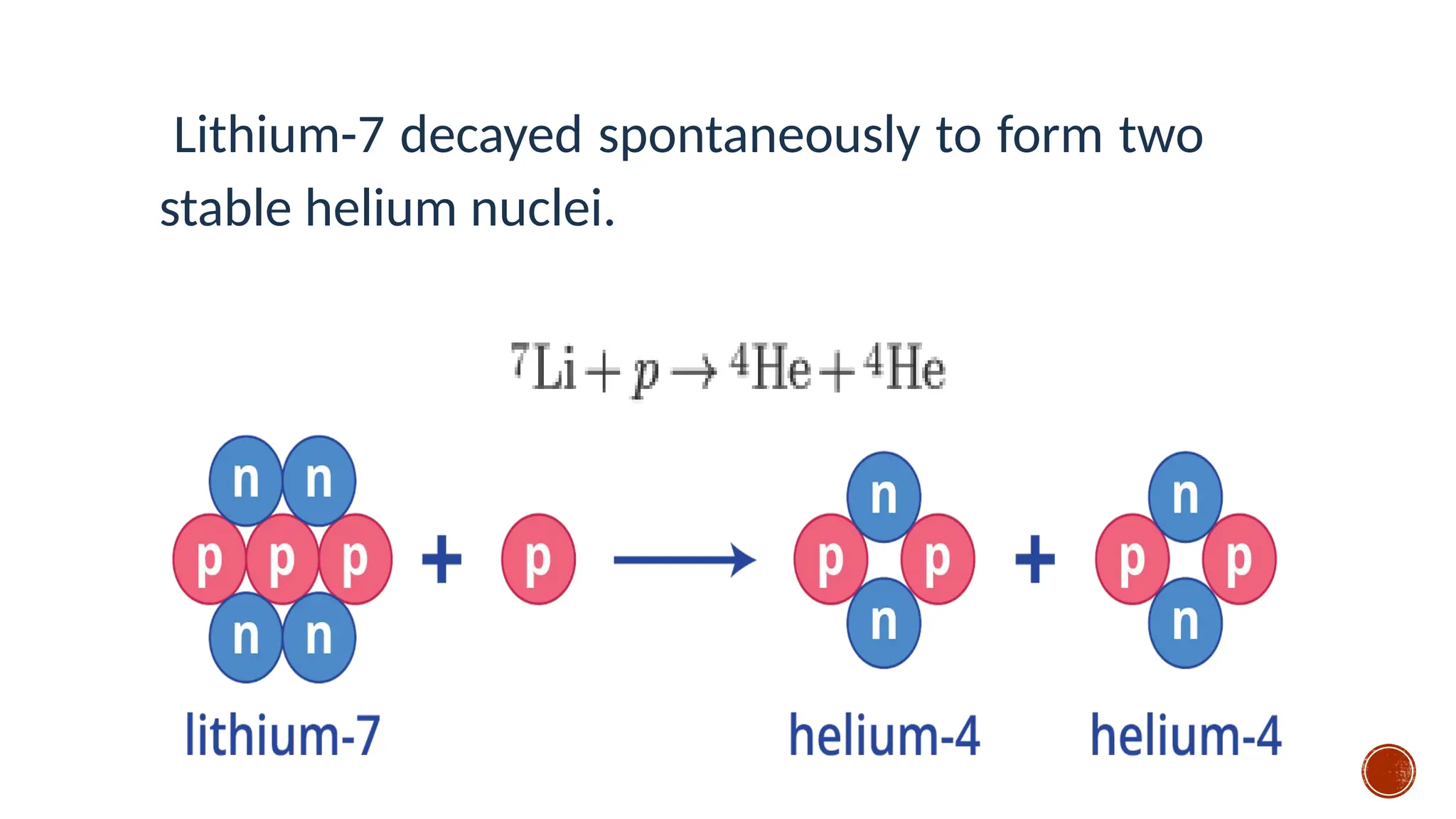
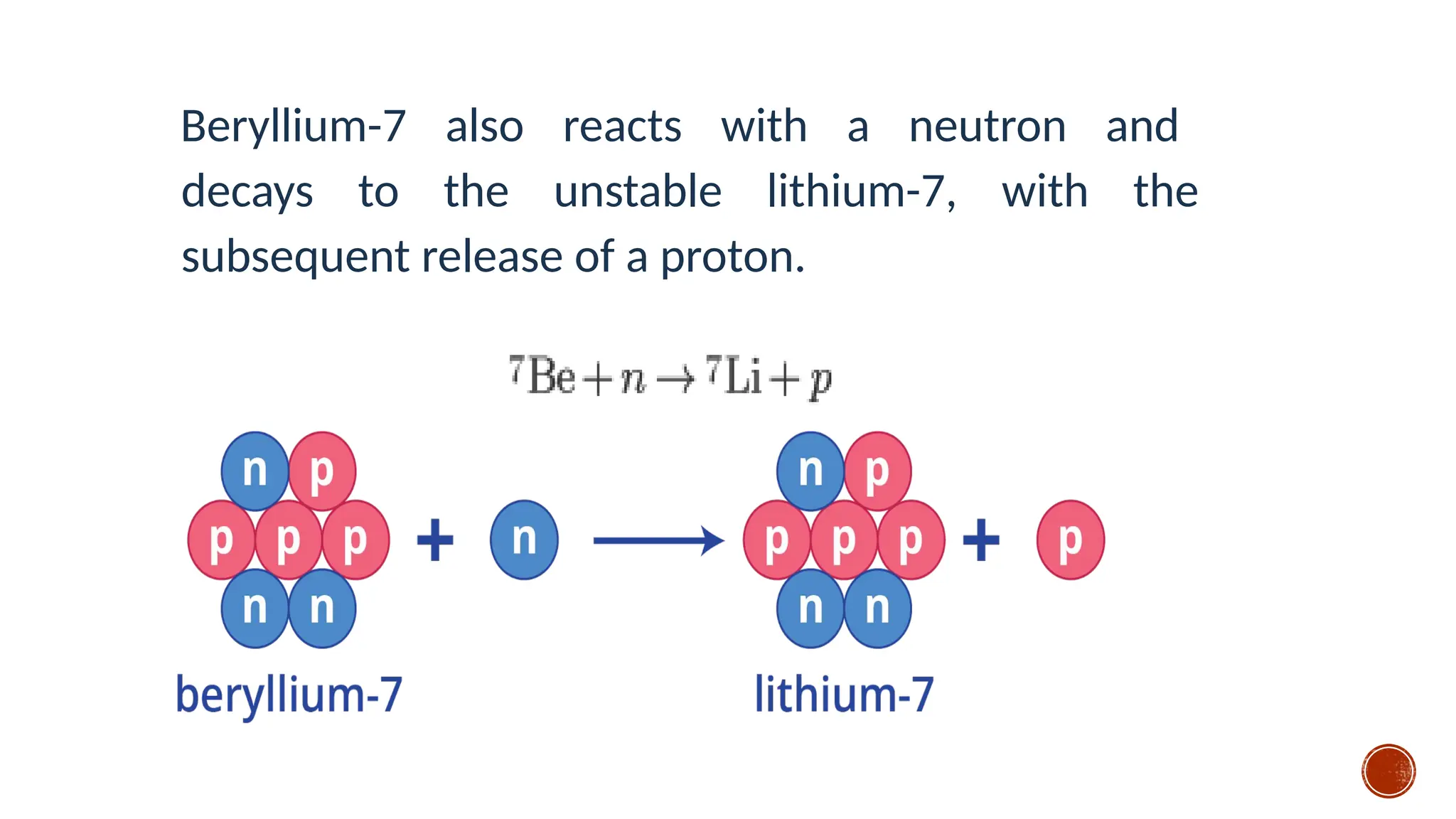
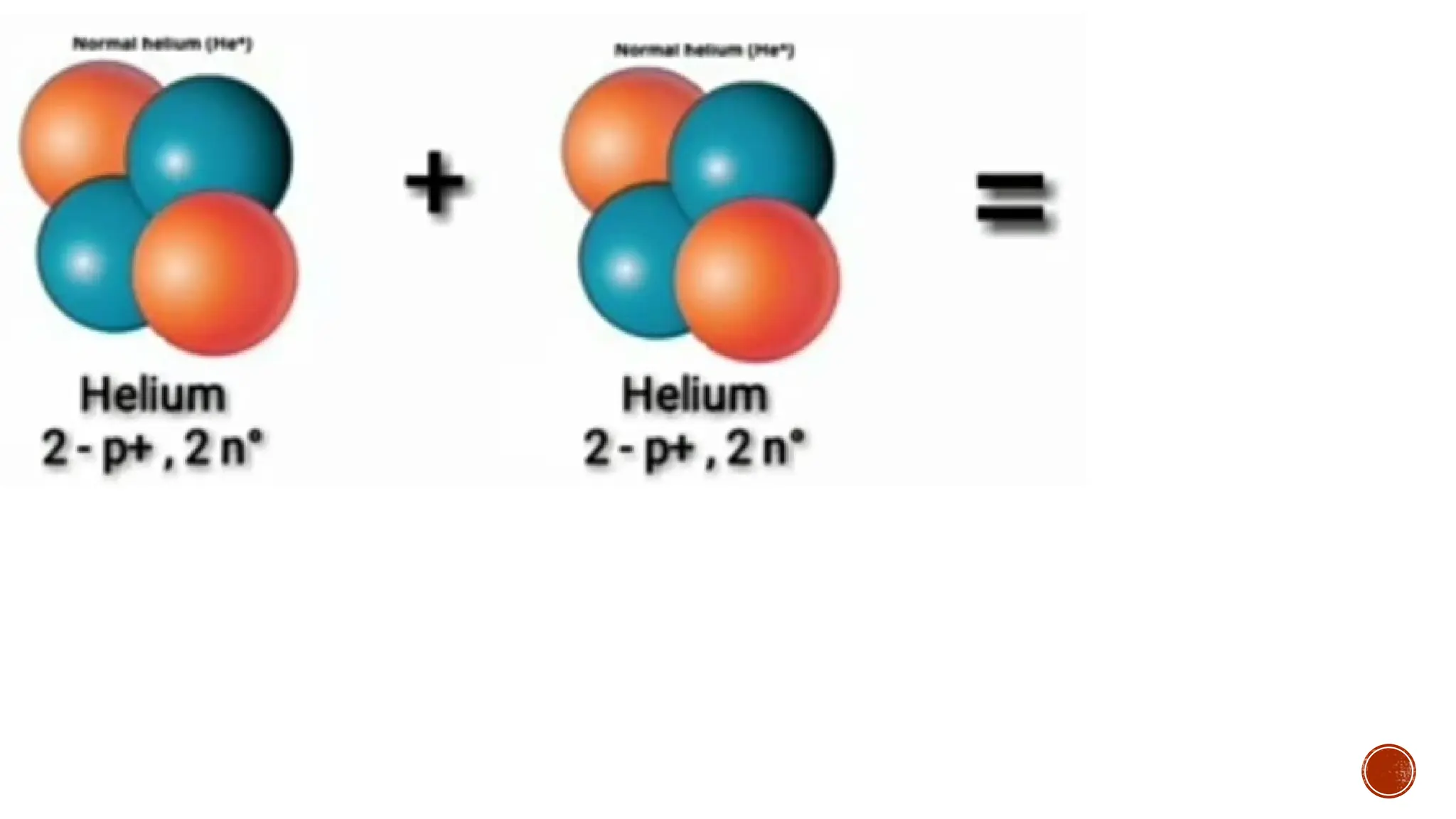
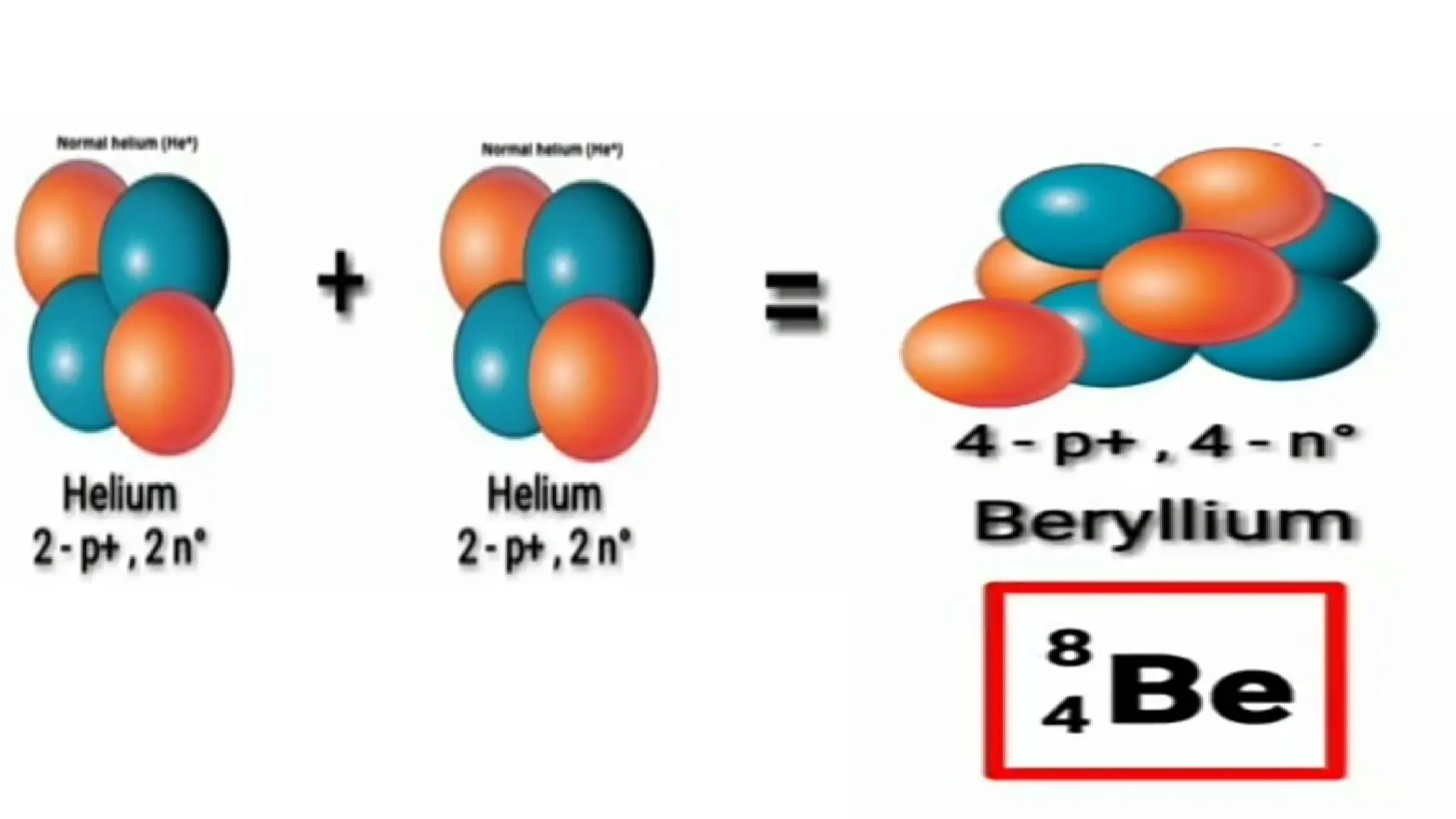
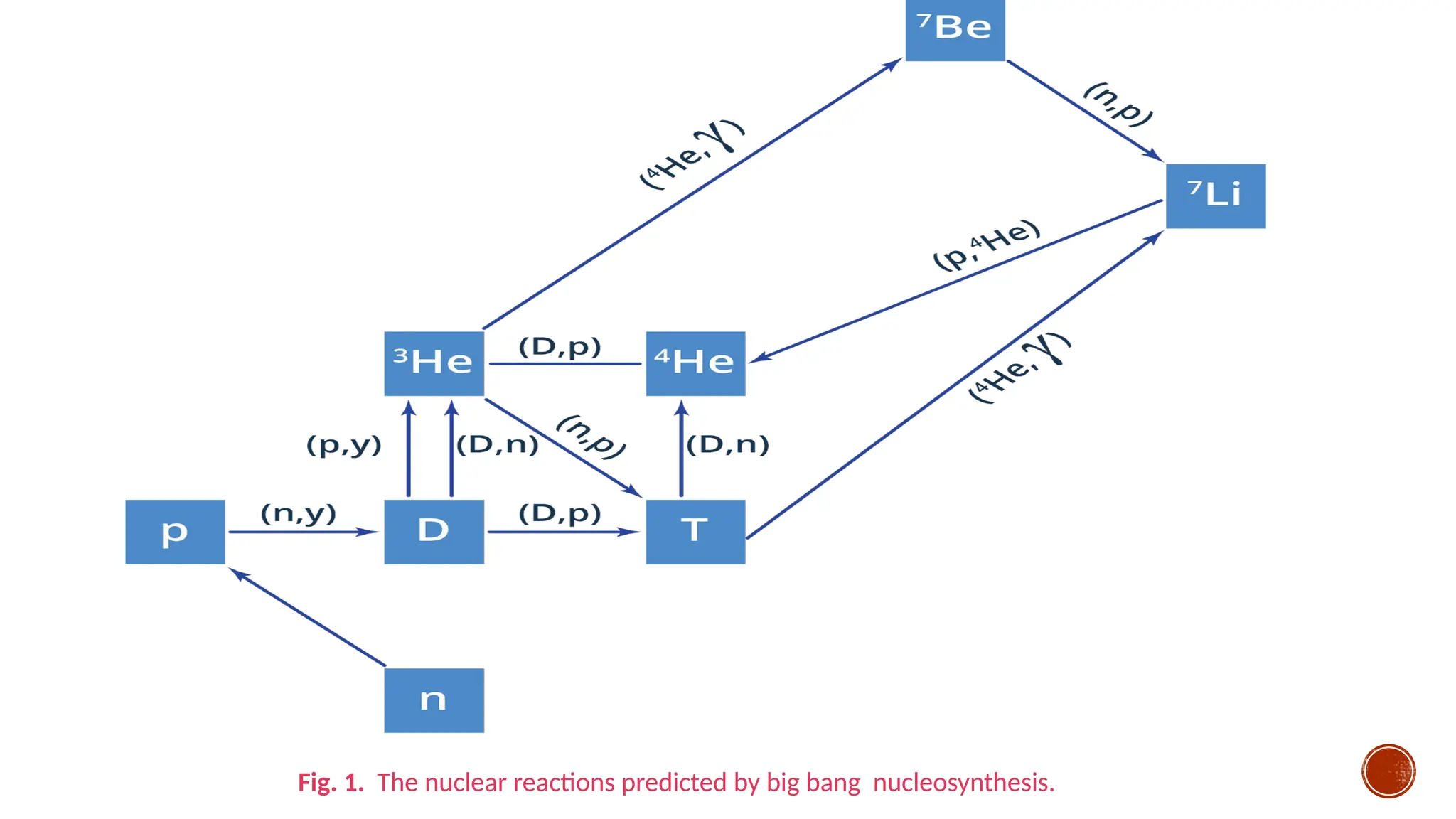
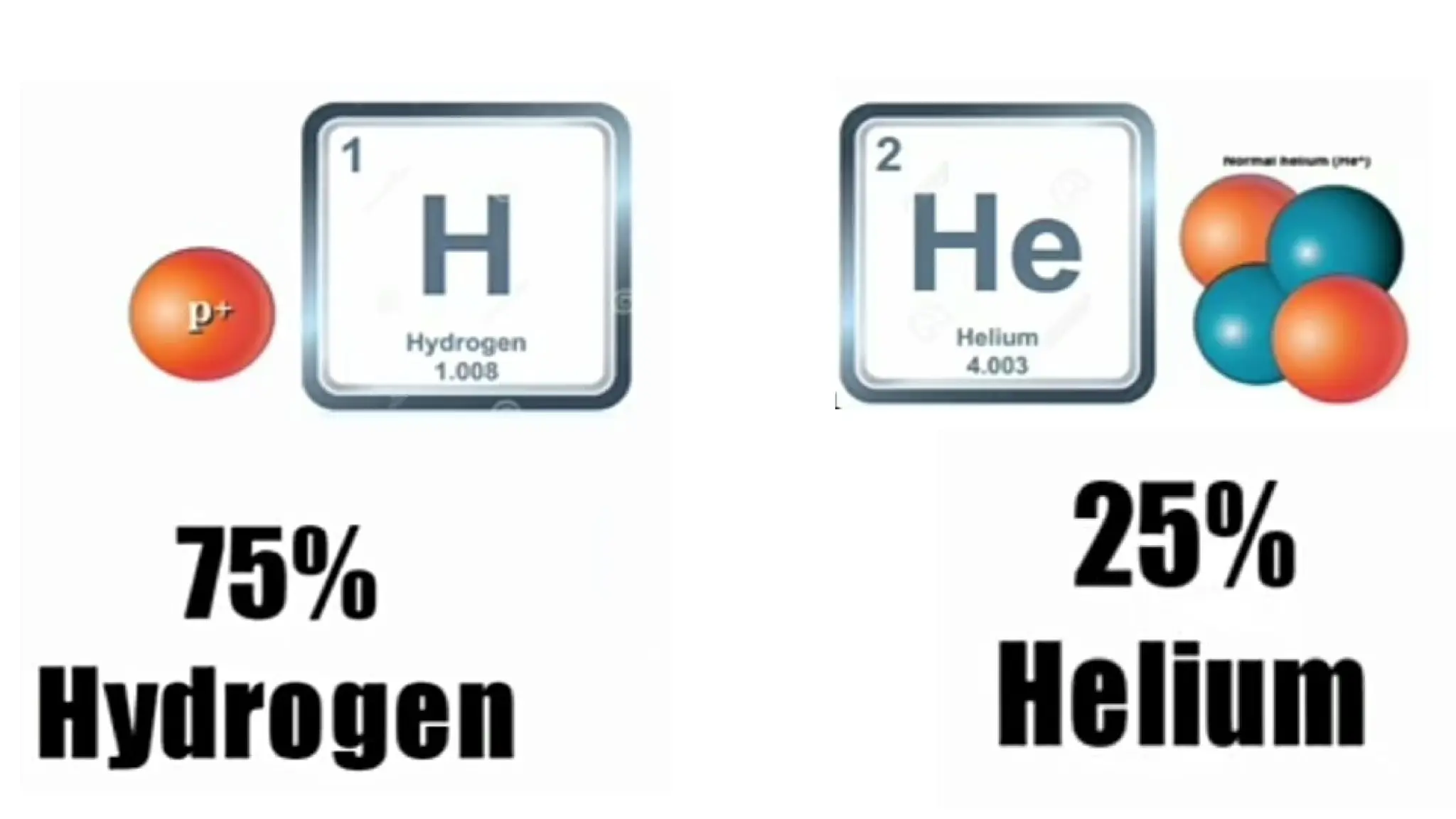
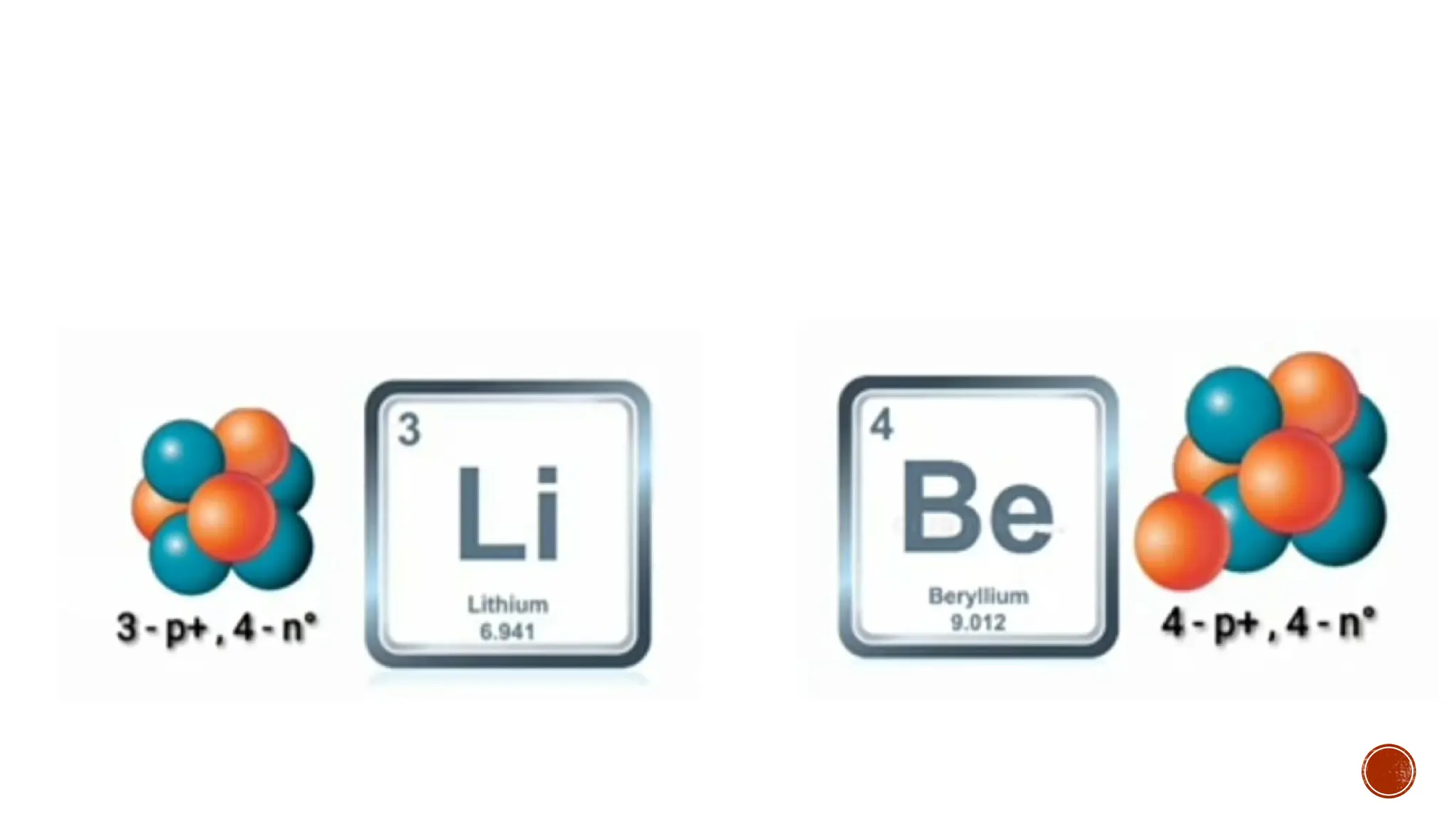
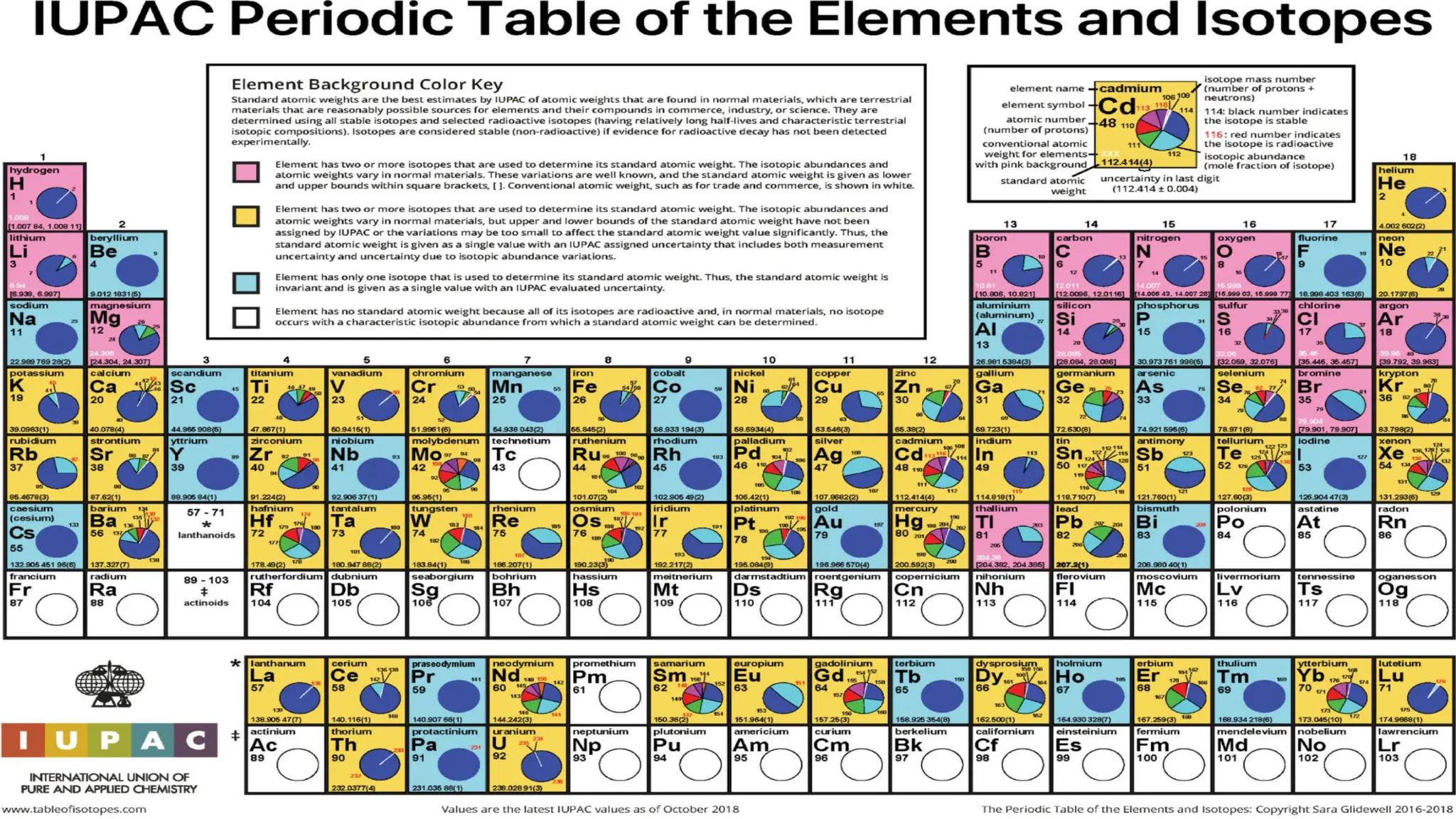
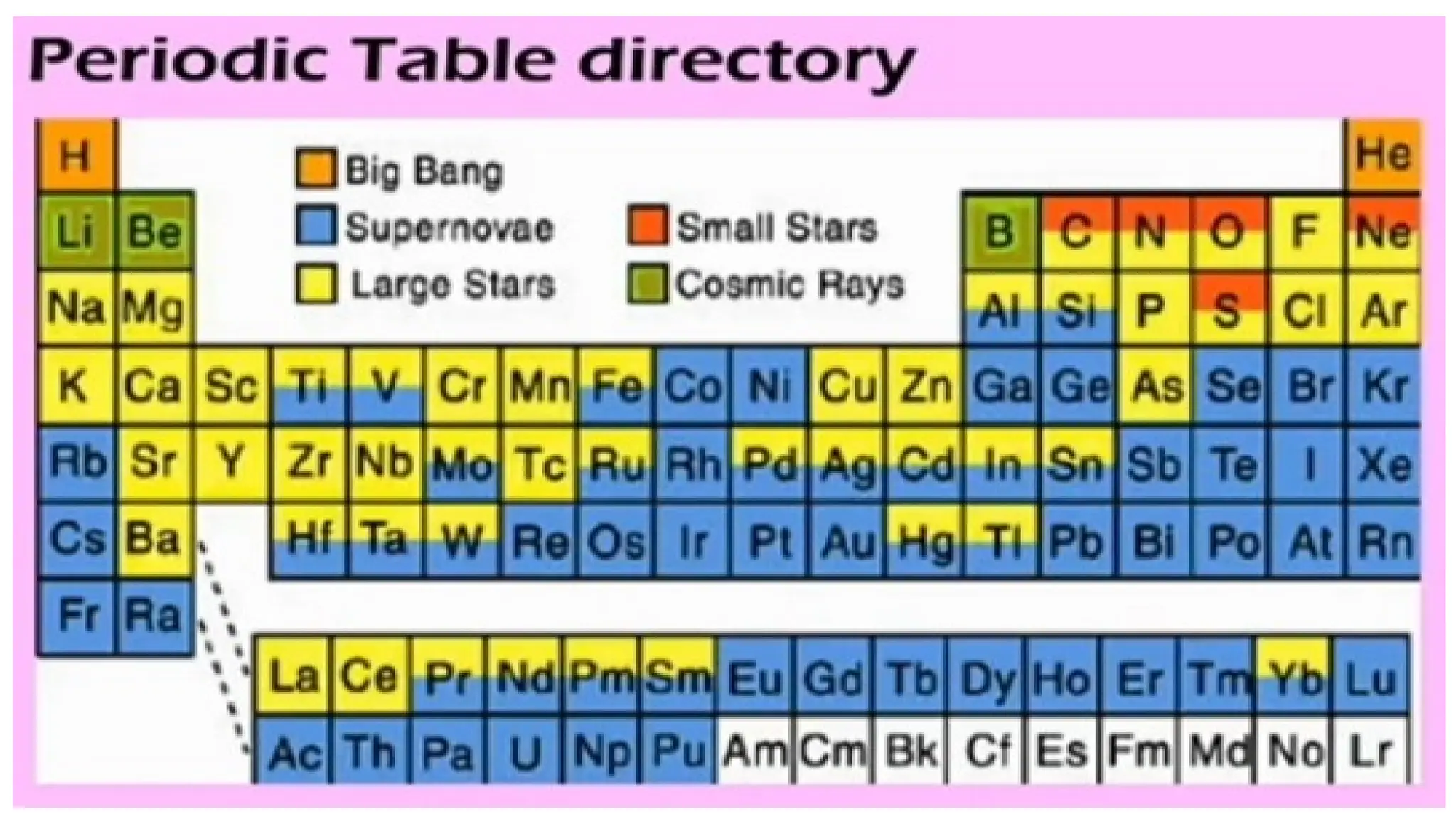
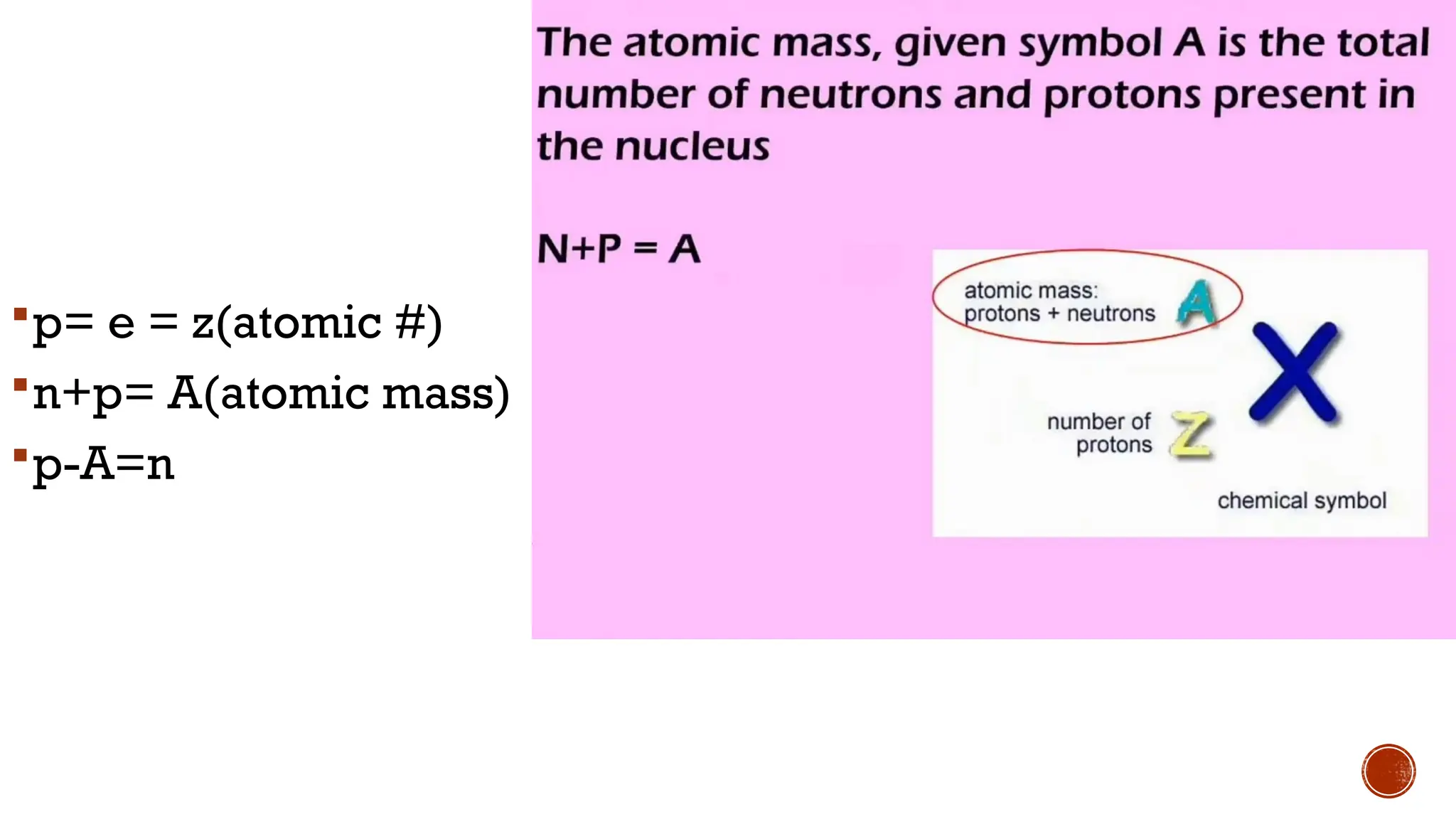
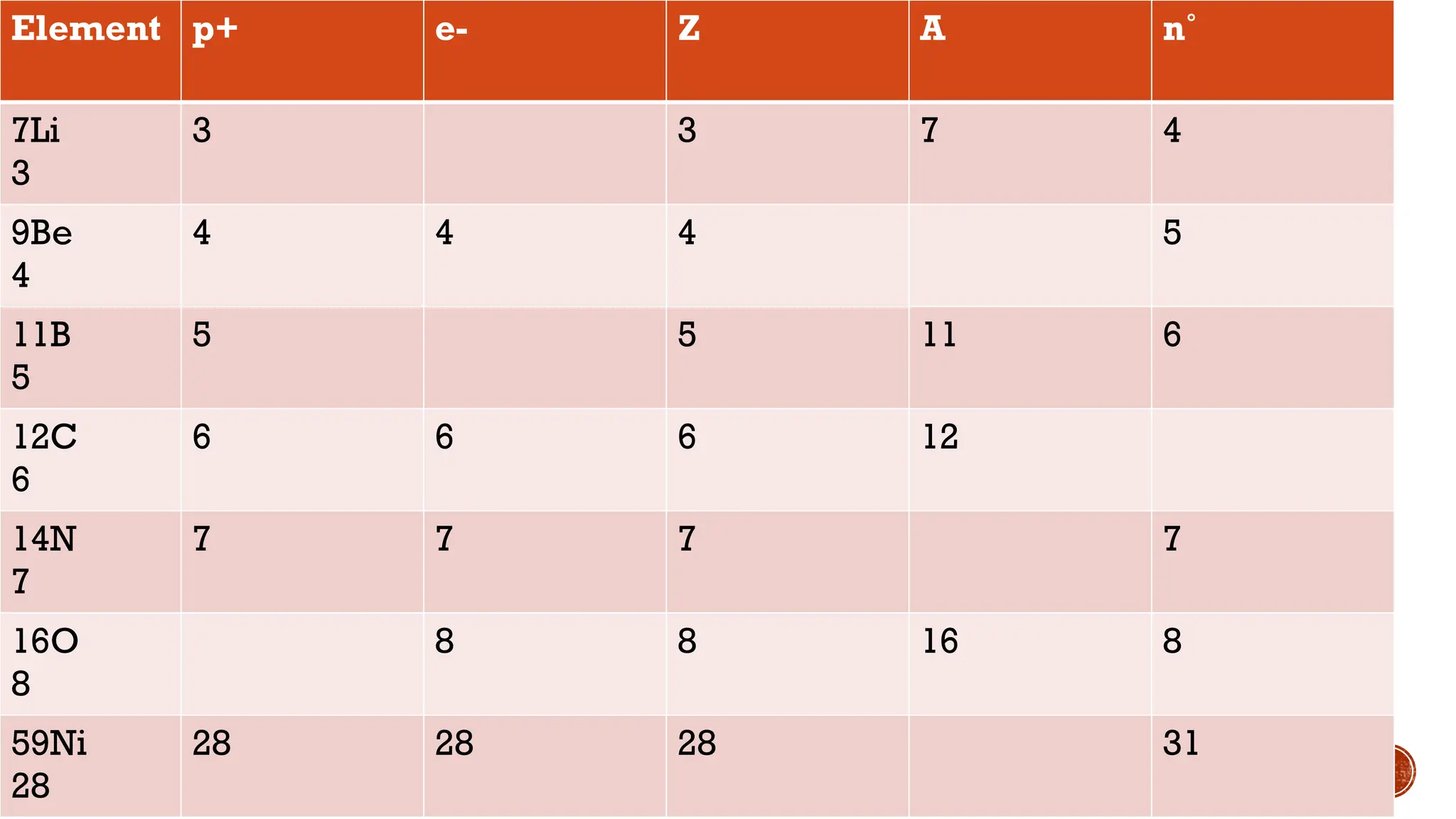
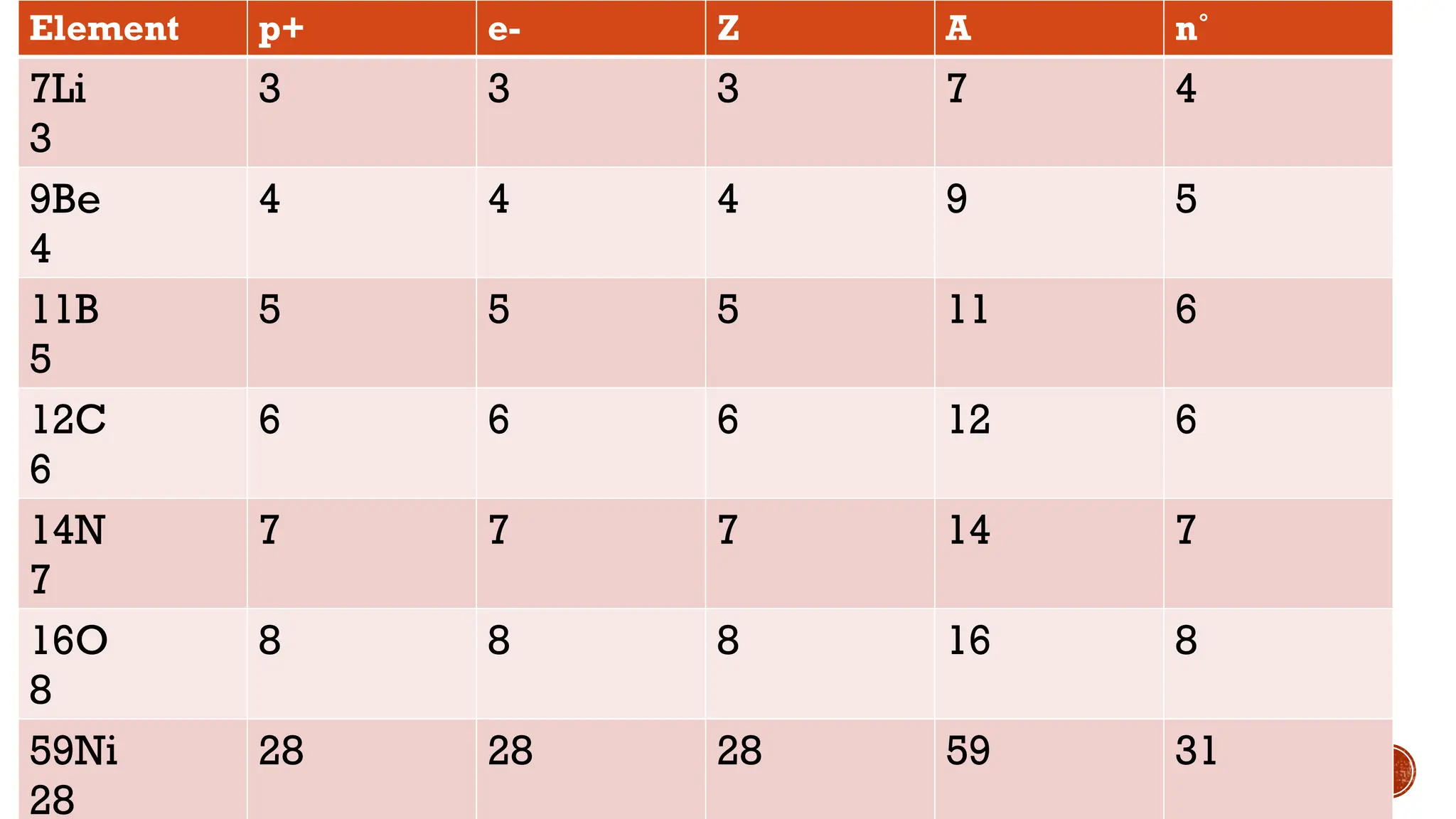
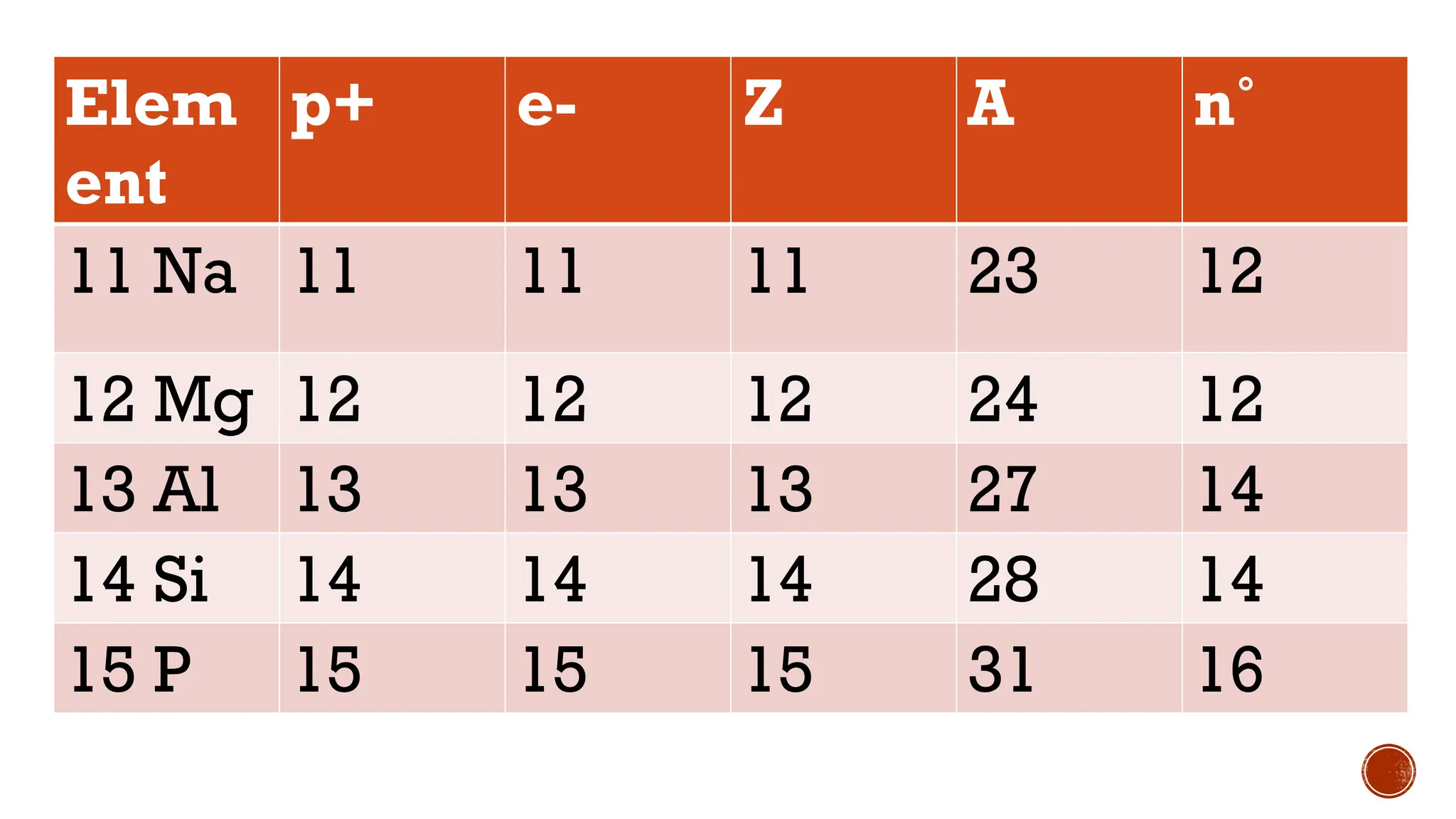
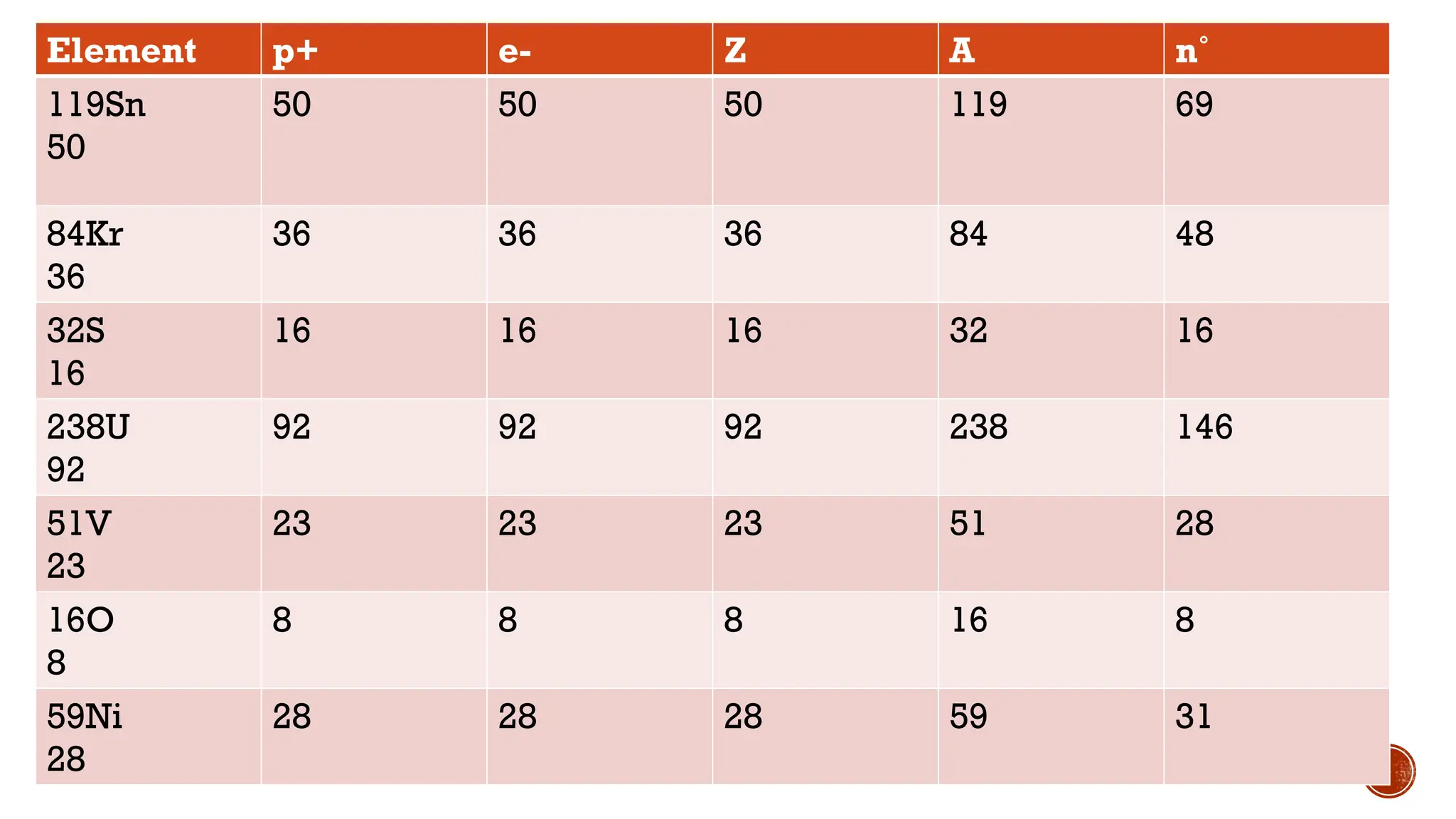
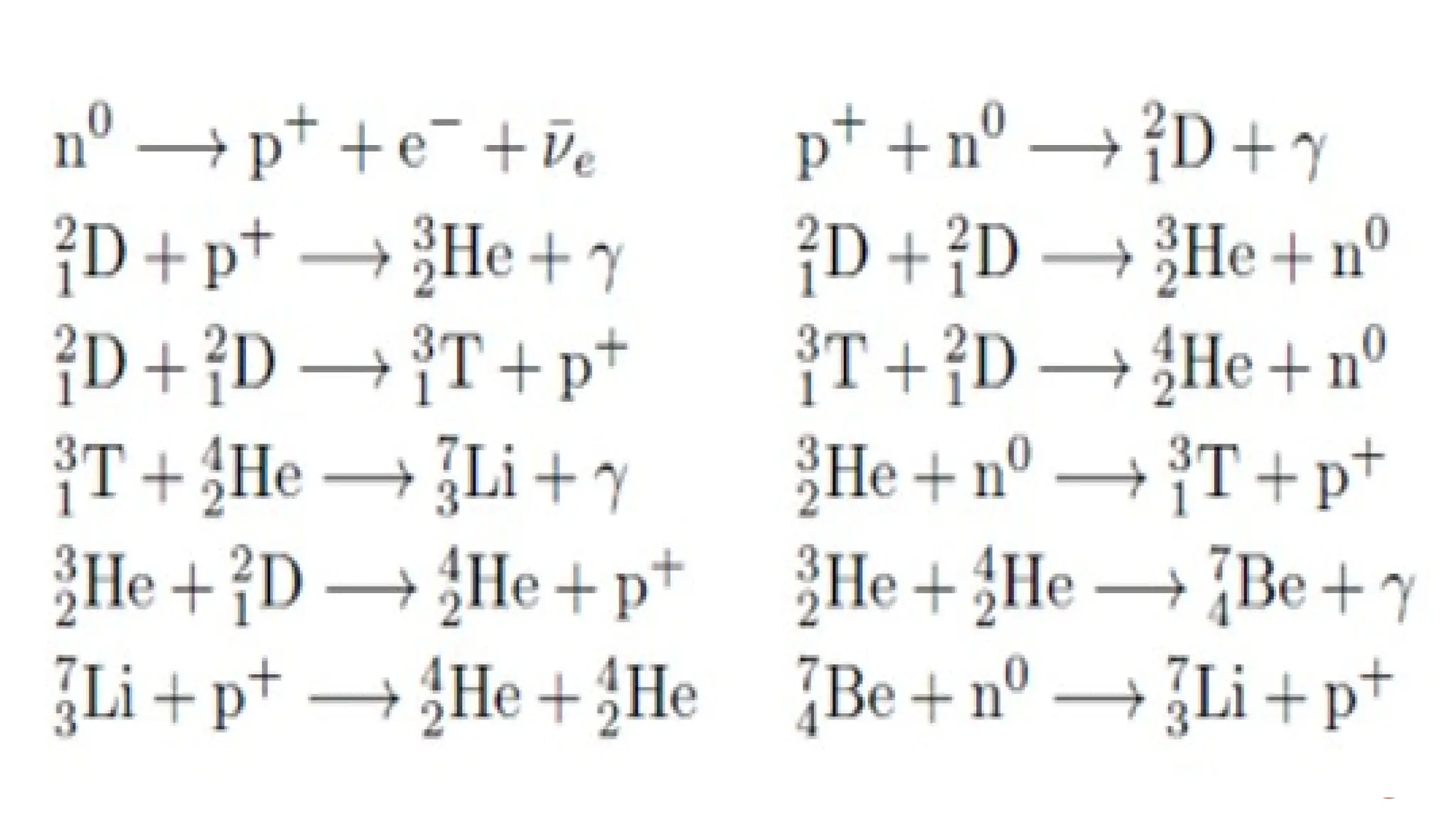The document discusses the Big Bang theory, which posits that the universe began as a singular point approximately 13.8 billion years ago and underwent rapid expansion and cooling, leading to the formation of light elements through nucleosynthesis. Key events include the creation of hydrogen and helium isotopes, the formation of atomic nuclei, and the eventual emergence of galaxies and planets, including Earth. Supporting evidence for the theory includes observations of cosmic redshift and the cosmic microwave background radiation.