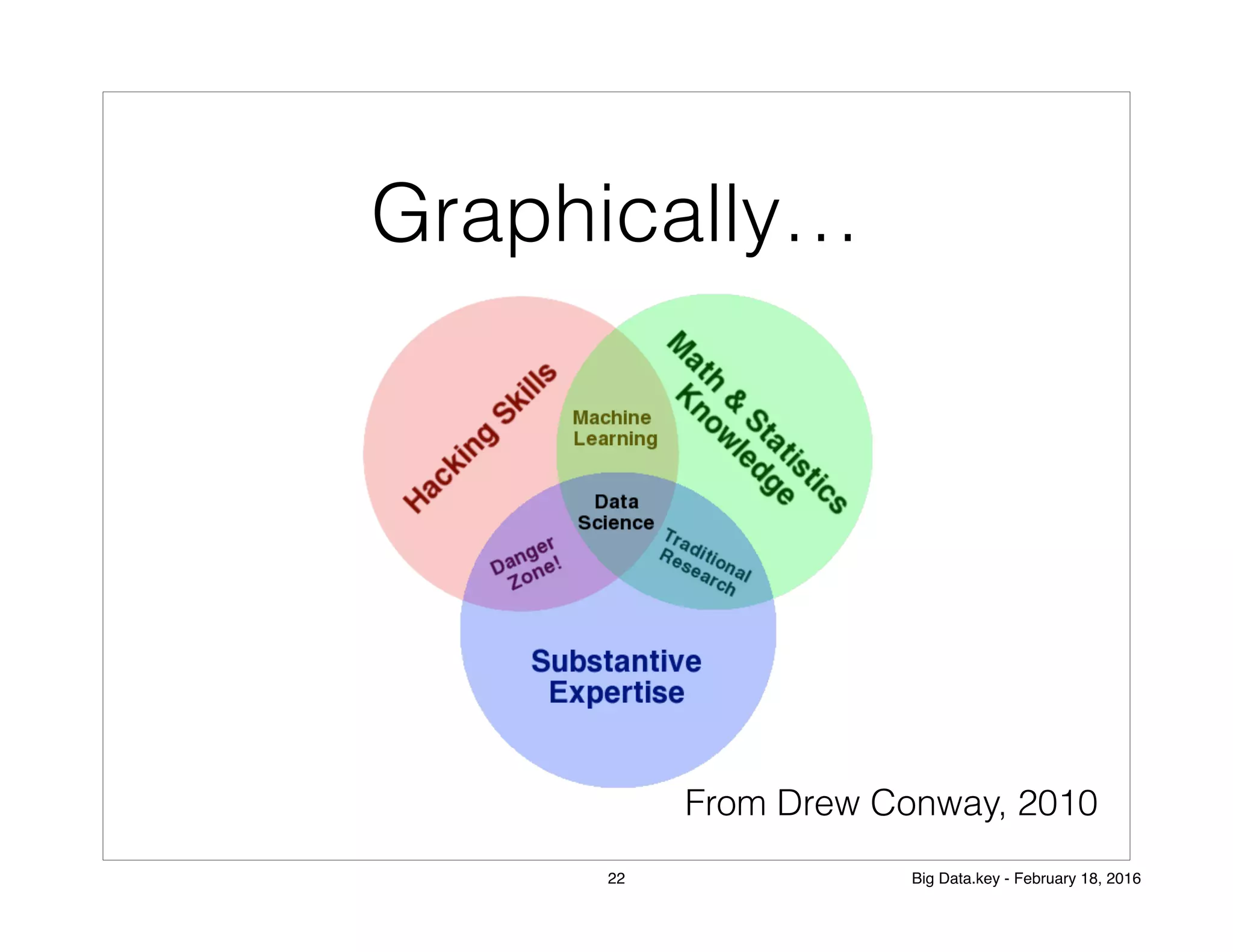
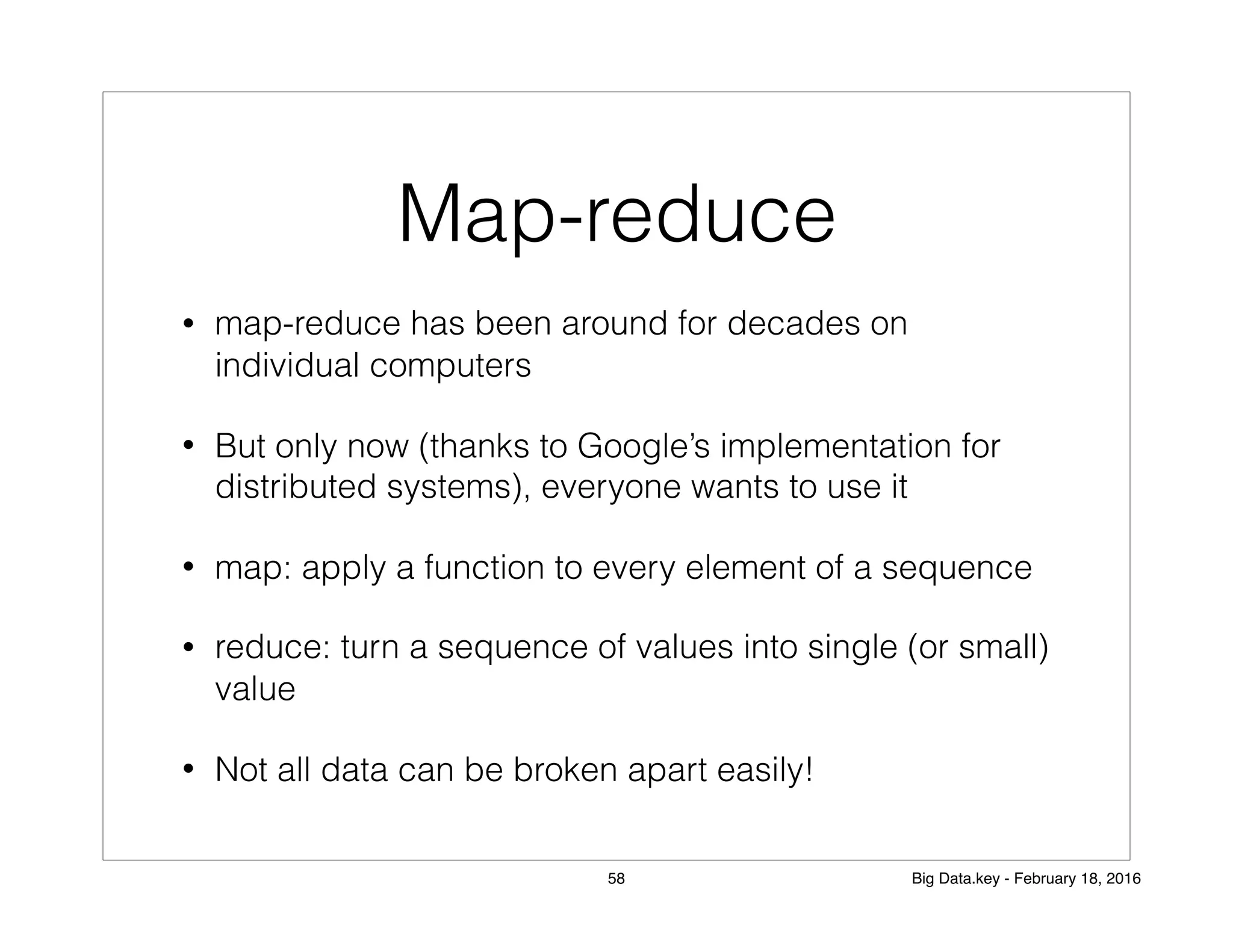
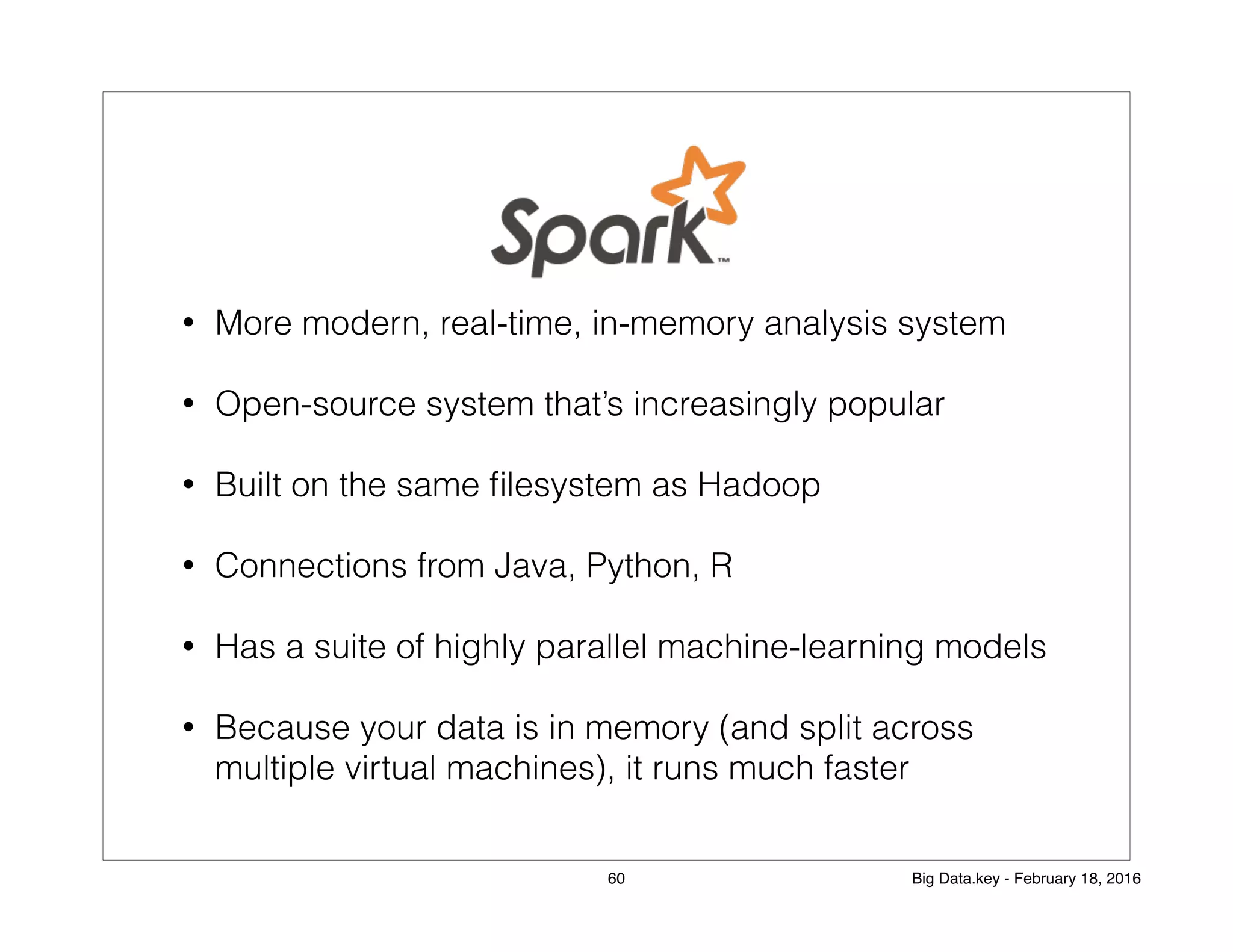
The document discusses the concept of big data and its applications, particularly in elections and business decision-making. It explains the role of data scientists in processing and analyzing data to uncover correlations that inform strategies, such as marketing and fraud detection. Additionally, it touches on machine learning and distributed processing systems that handle large data sets effectively.