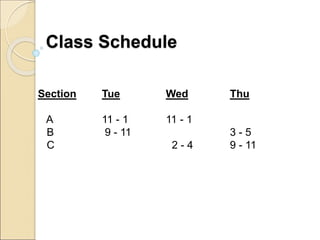
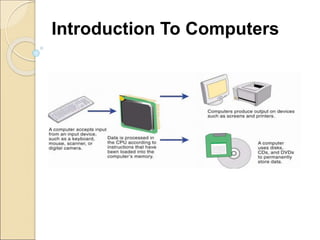
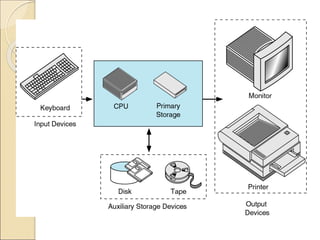
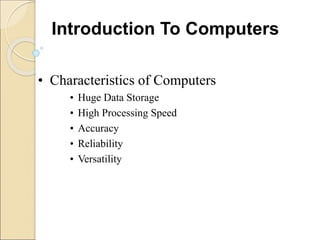
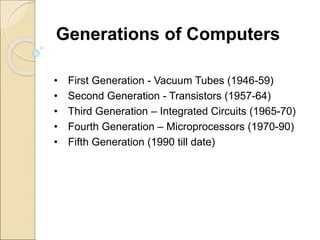
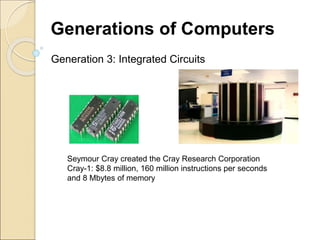
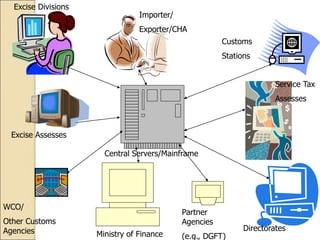
This document provides an introduction to business intelligence and computer applications in management. It begins with defining what a business is - an organization involved in manufacturing, trade, or services. It then discusses different forms of business like sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, cooperatives, franchises, and direct selling. Next, it explains how businesses are run by maximizing profits through increasing sales and decreasing costs. Business intelligence is then introduced as using data and analytics to improve business decision making. The relevance of computer applications is that they allow businesses to gather and analyze large amounts of data. The document continues by covering topics like the history of computers, uses of computers in different industries and organizations, challenges of information systems, and the concept of a