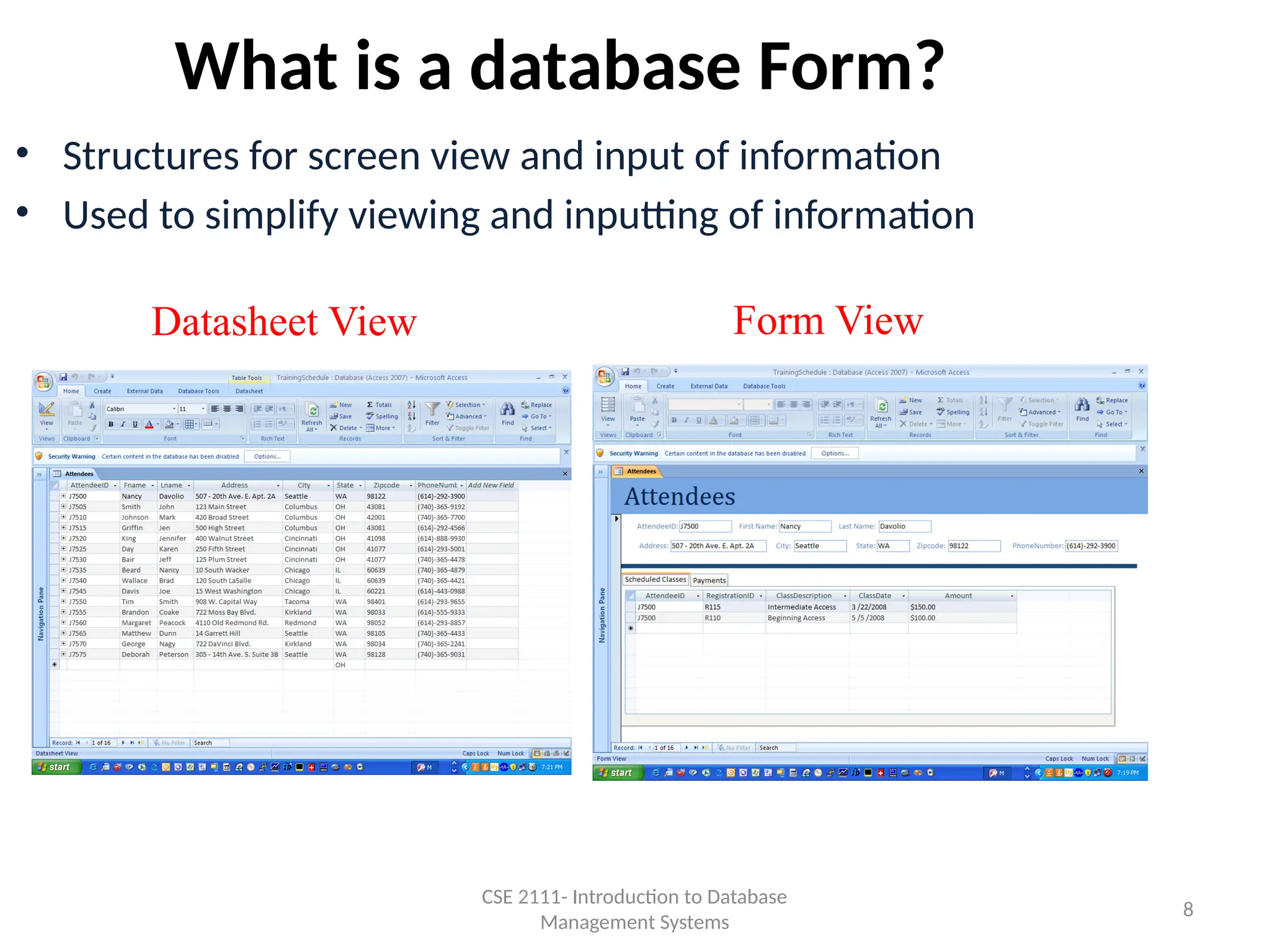
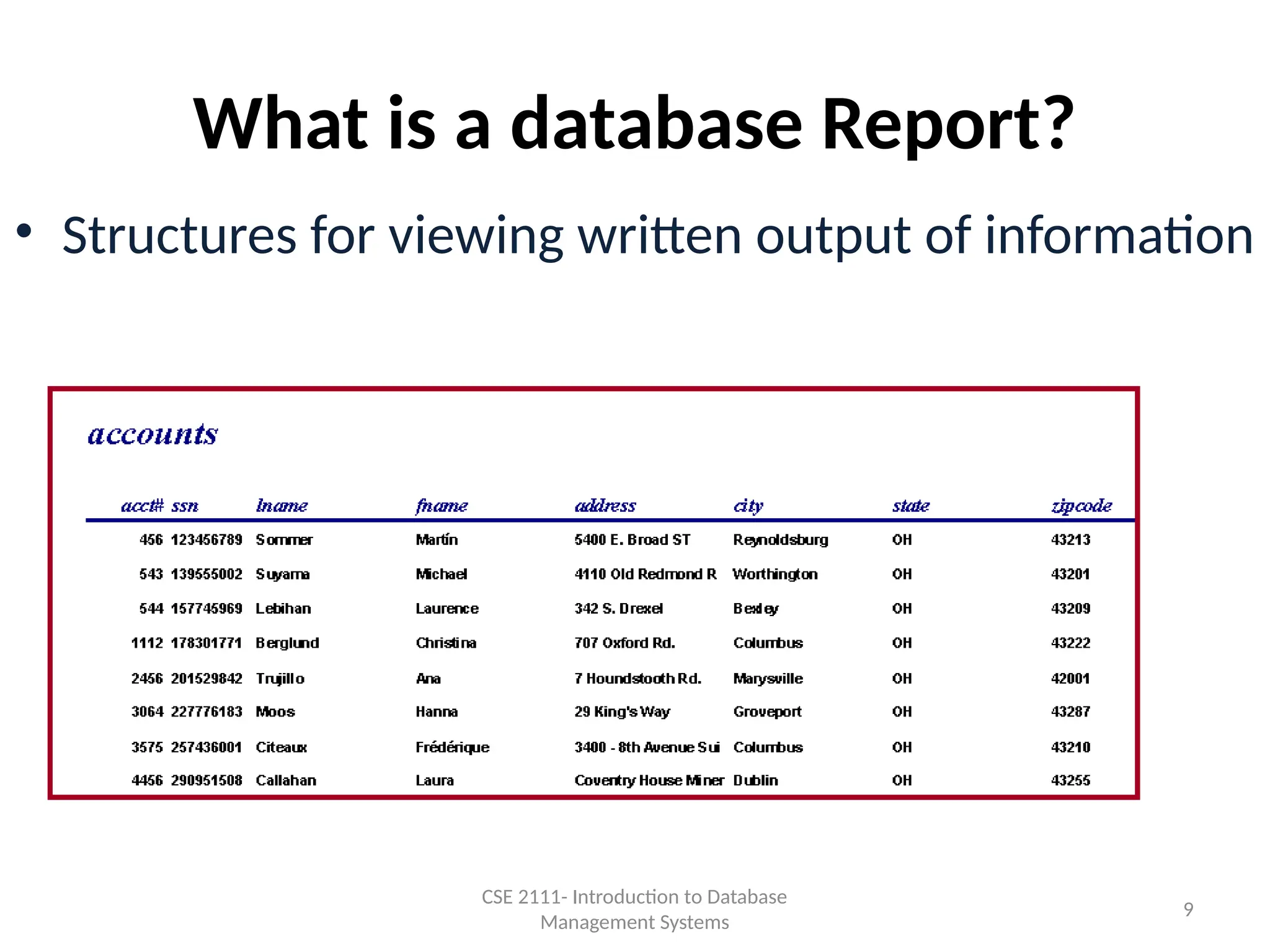
The document is an introduction to database systems, covering fundamental concepts like data, databases, tables, and queries. It discusses the process of creating a database, including designing tables, defining fields, and establishing relationships between them. Various database management systems, such as MS Access, and their functions for managing information are also mentioned.