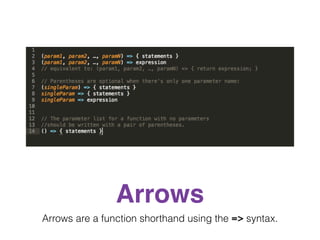
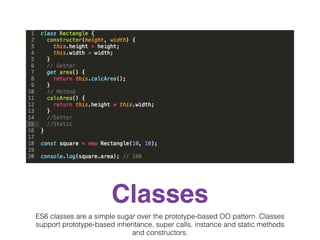
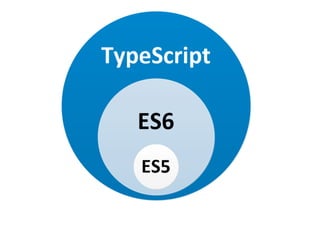
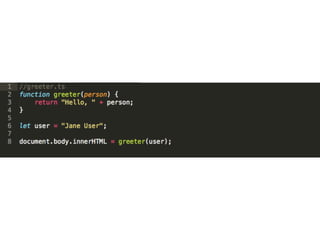
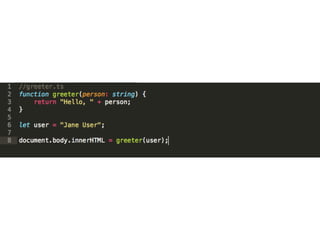
The document discusses Angular 2 and its integration with TypeScript, highlighting key features such as class-based object-oriented programming, static typing, and generics. It also outlines significant ECMAScript 6 enhancements that Angular supports, including improved dependency injection, template strings, and the spread operator. Additionally, it covers TypeScript's advantages over ES2015, including type annotations, interfaces, and future feature support, making it a powerful tool for JavaScript development.