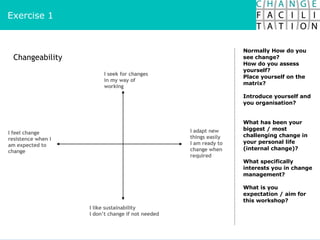
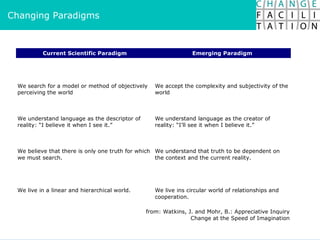
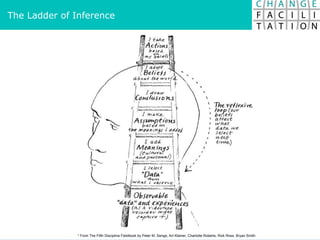
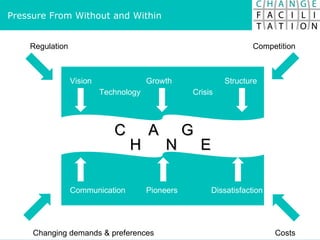
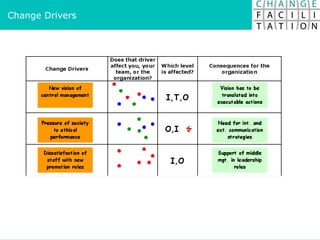
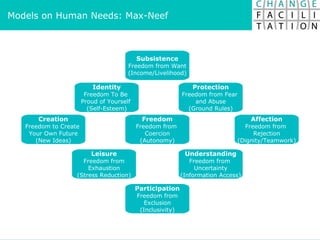
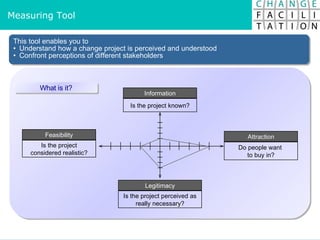
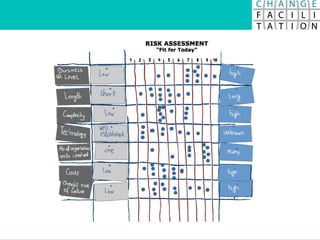
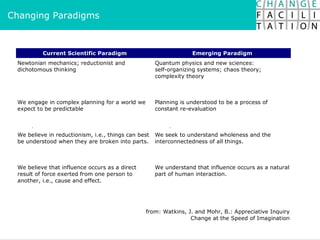
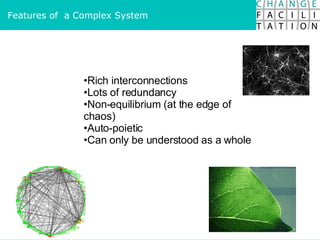
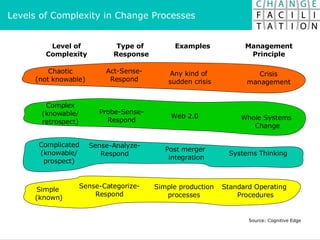
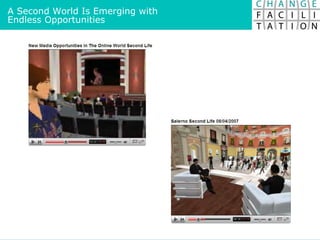
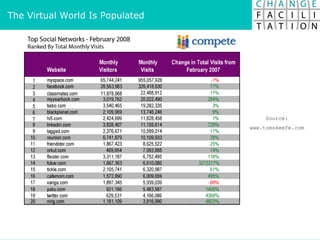
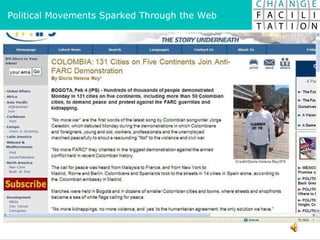
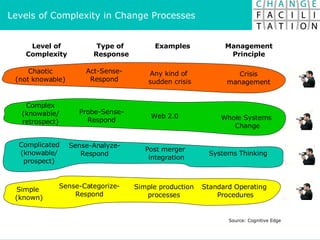
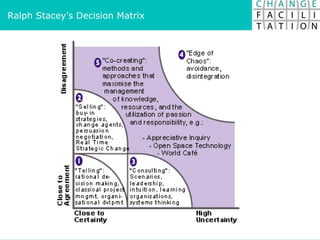
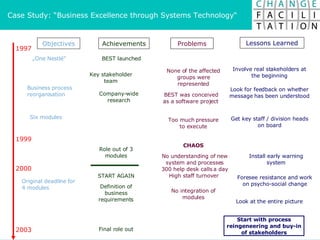
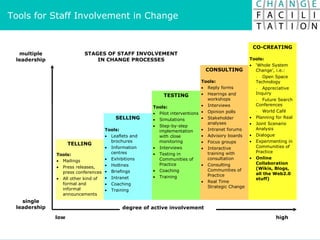
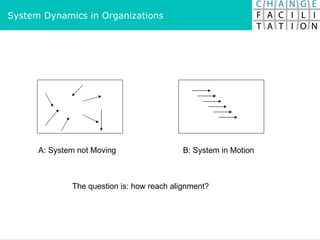
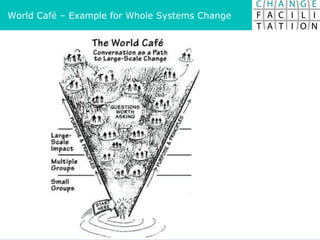
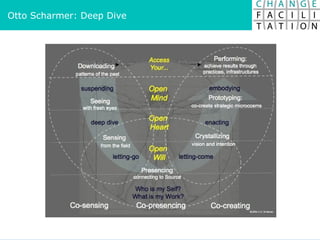
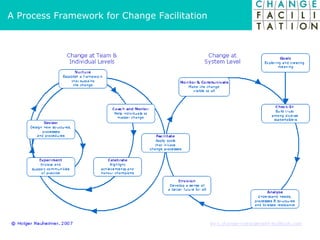
The document discusses change management and facilitating change. It introduces various tools and techniques for understanding change processes at different levels of complexity. It also discusses the importance of involving stakeholders and using whole systems approaches, such as appreciative inquiry, to create engagement and alignment around change initiatives.