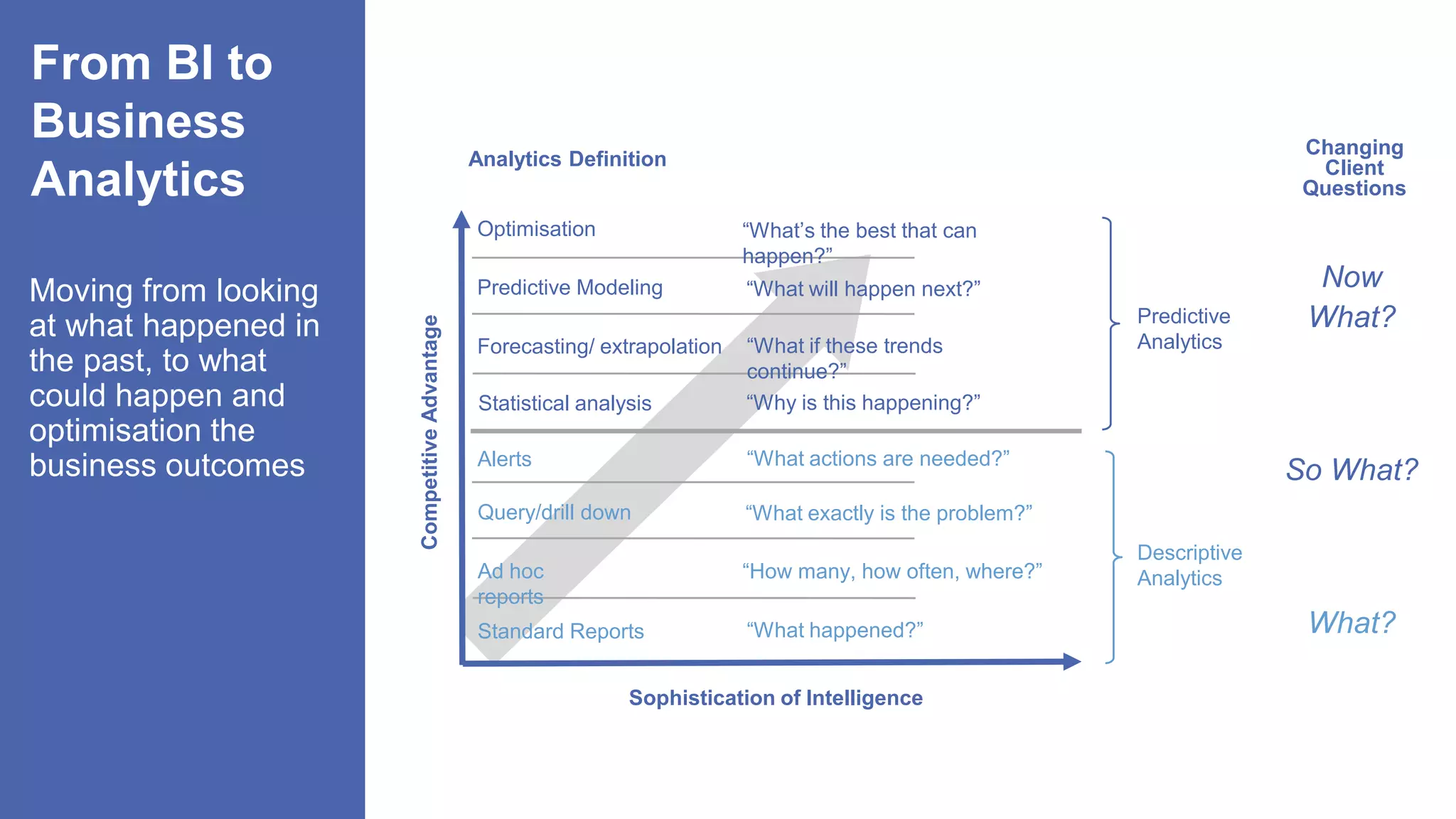
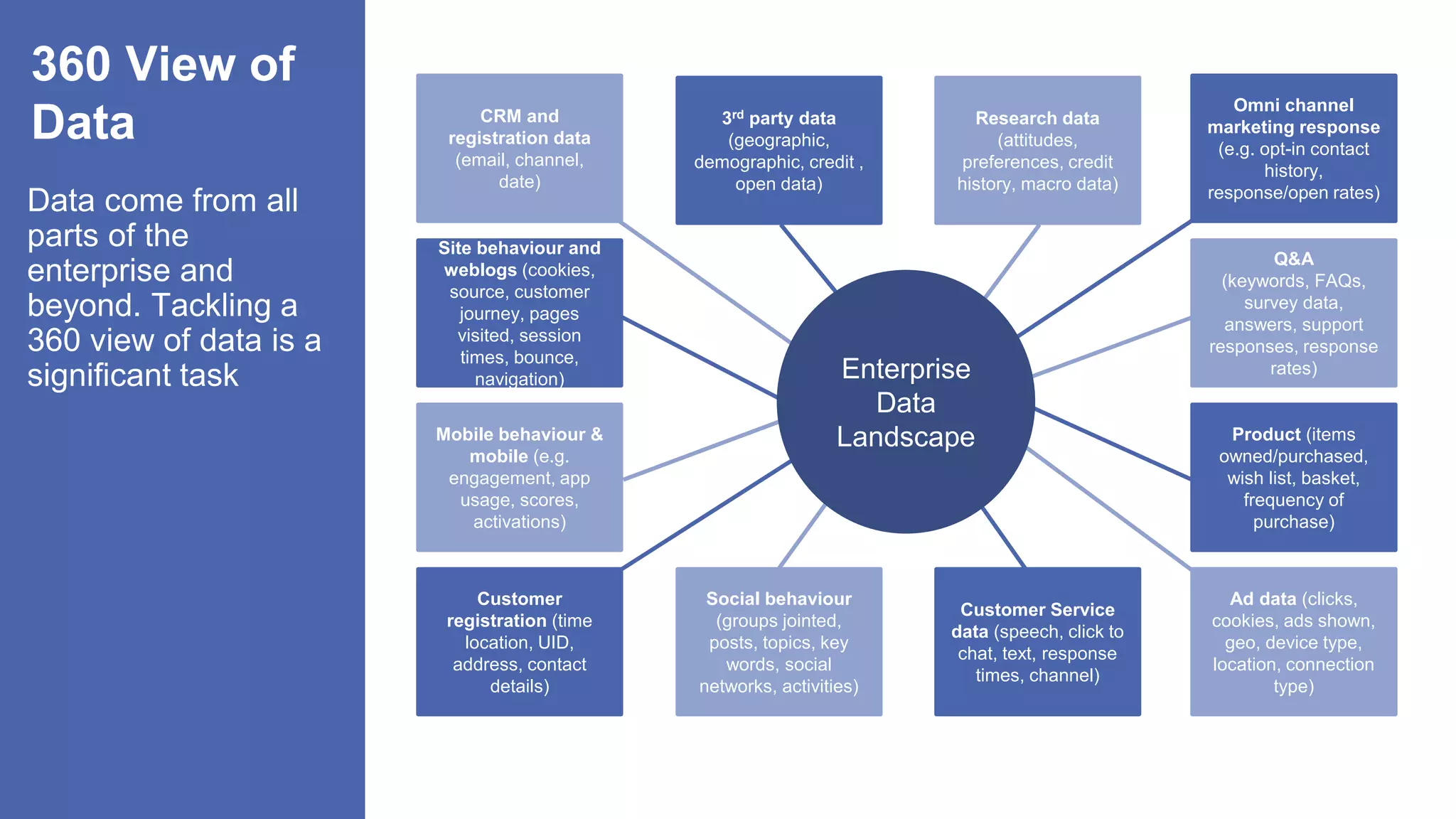
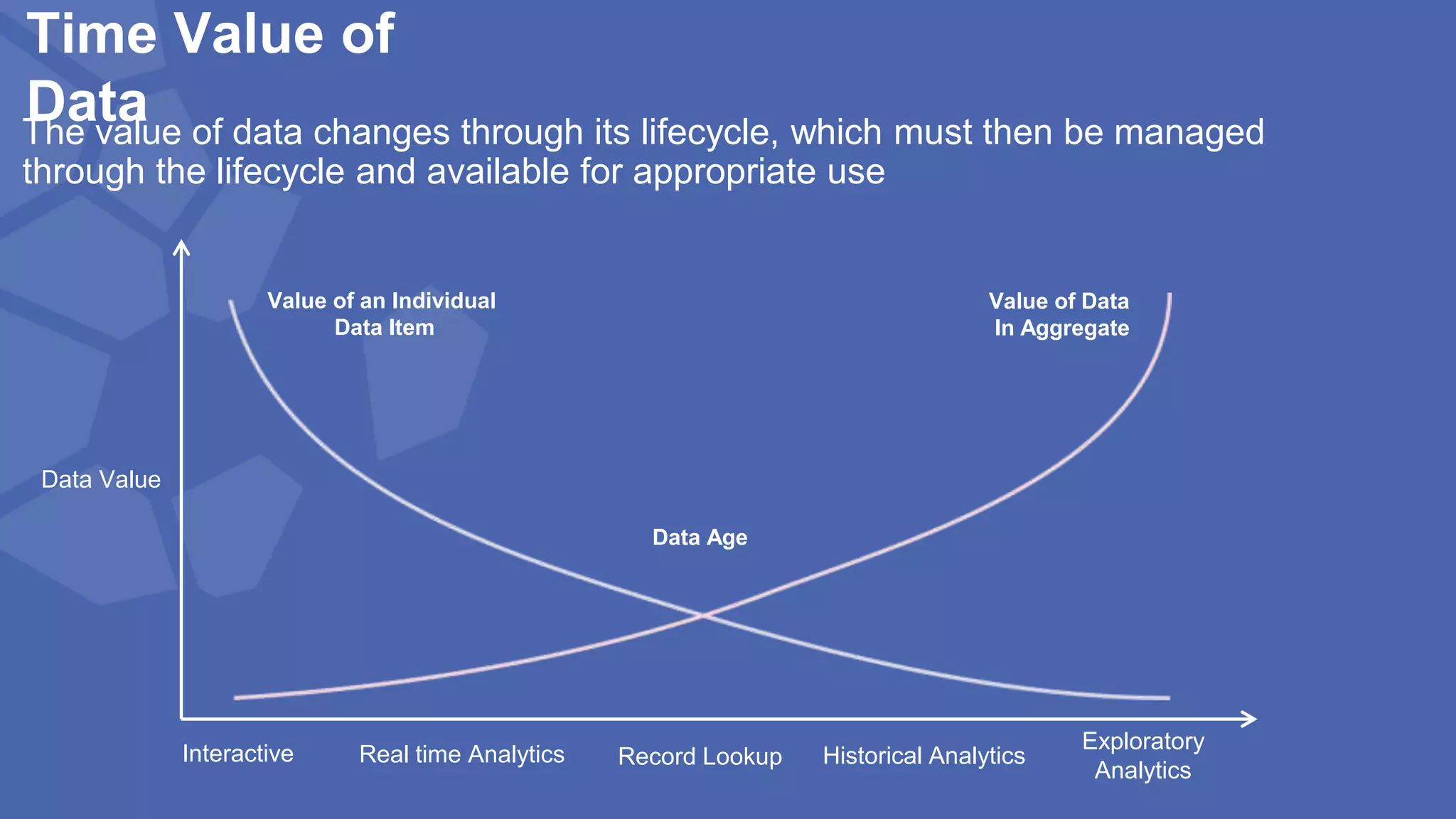
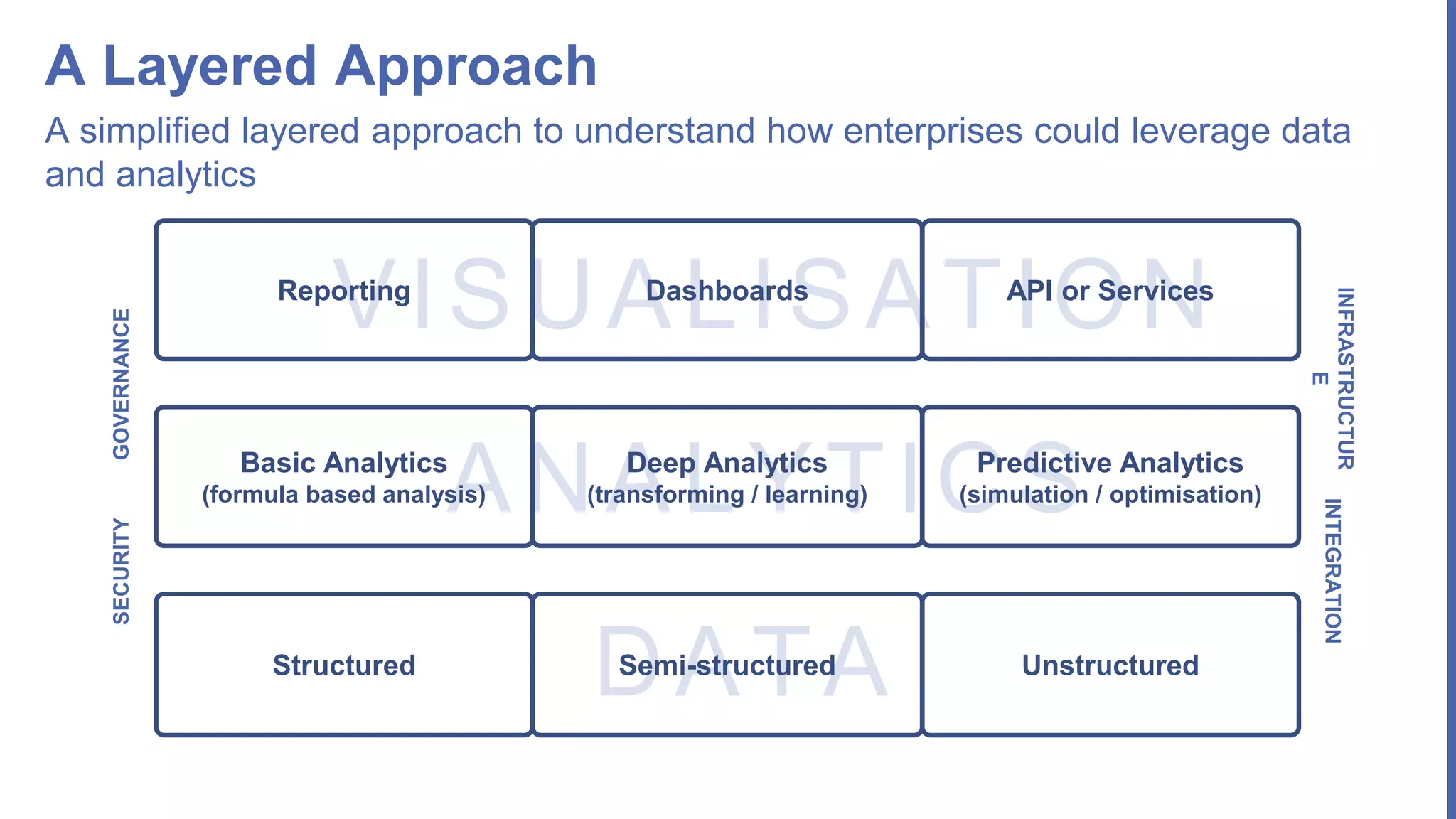
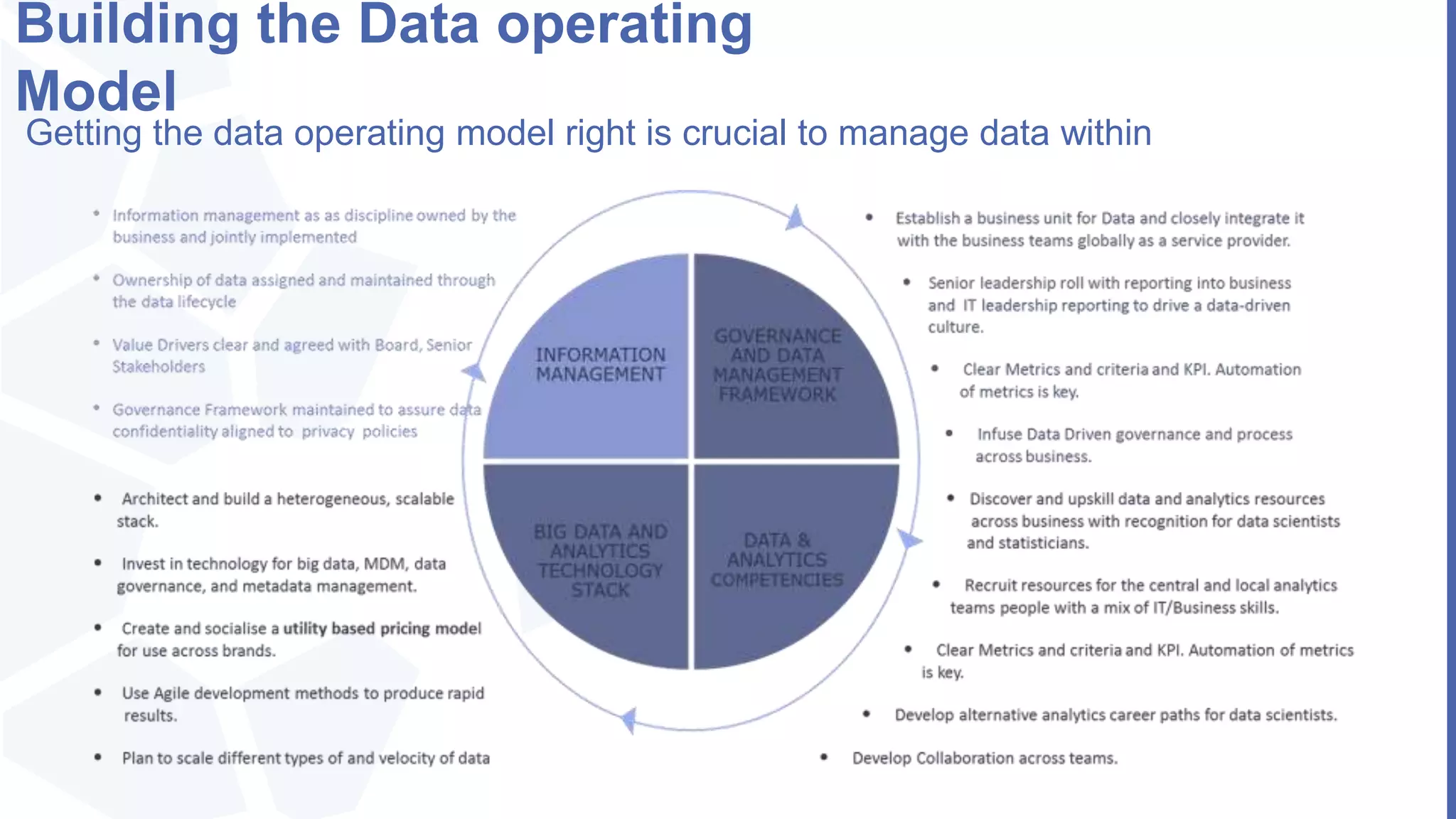
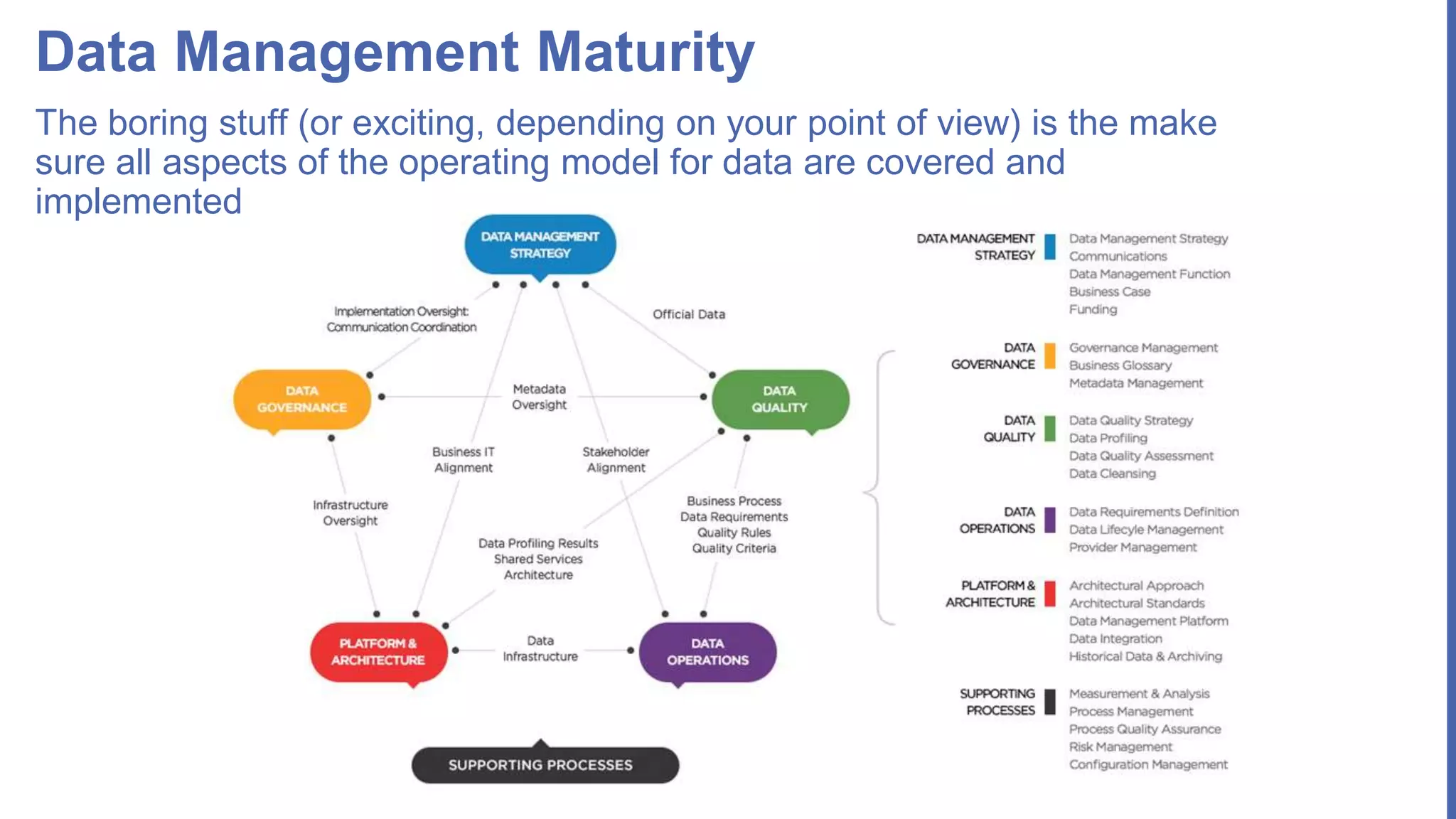
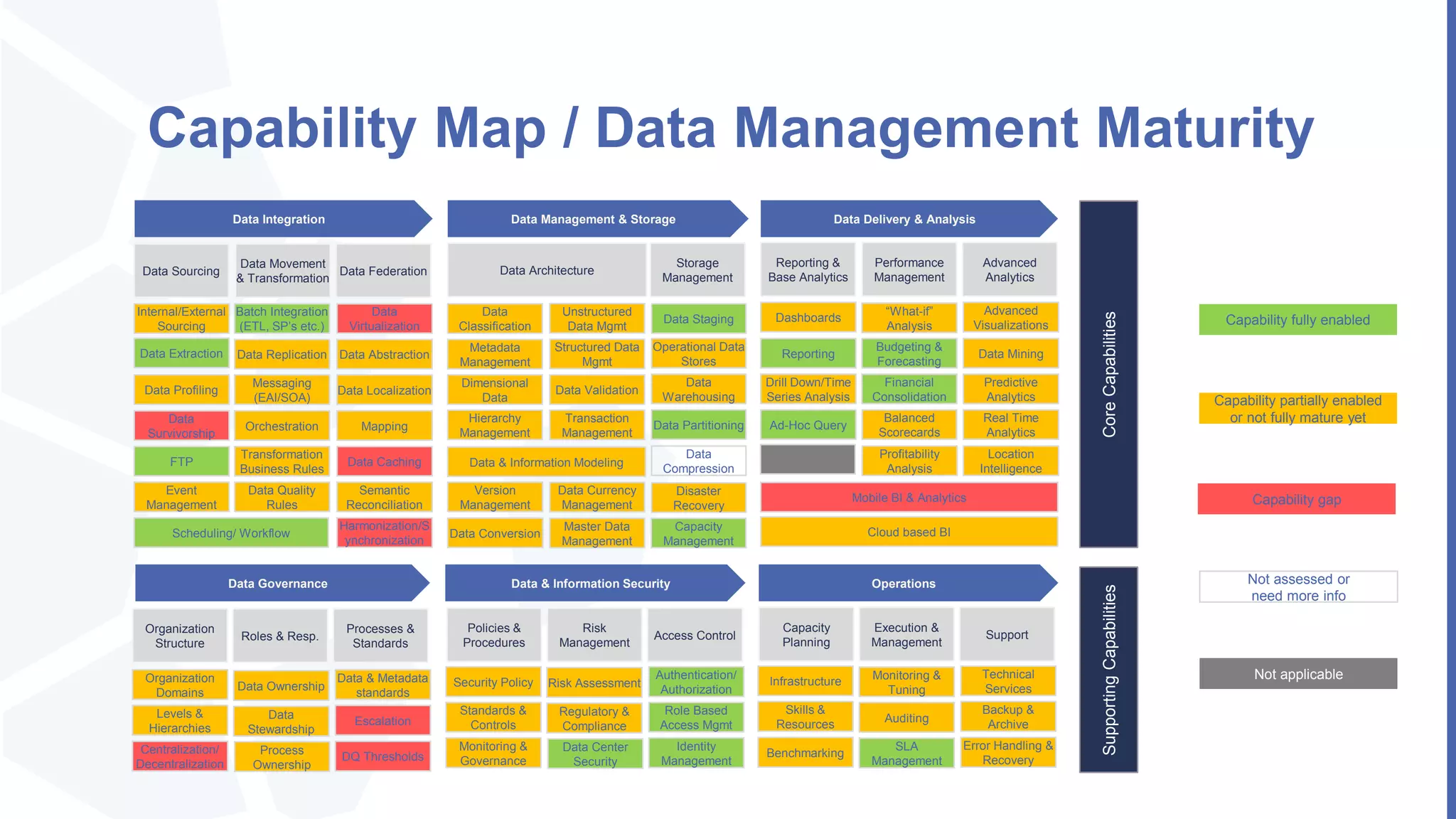
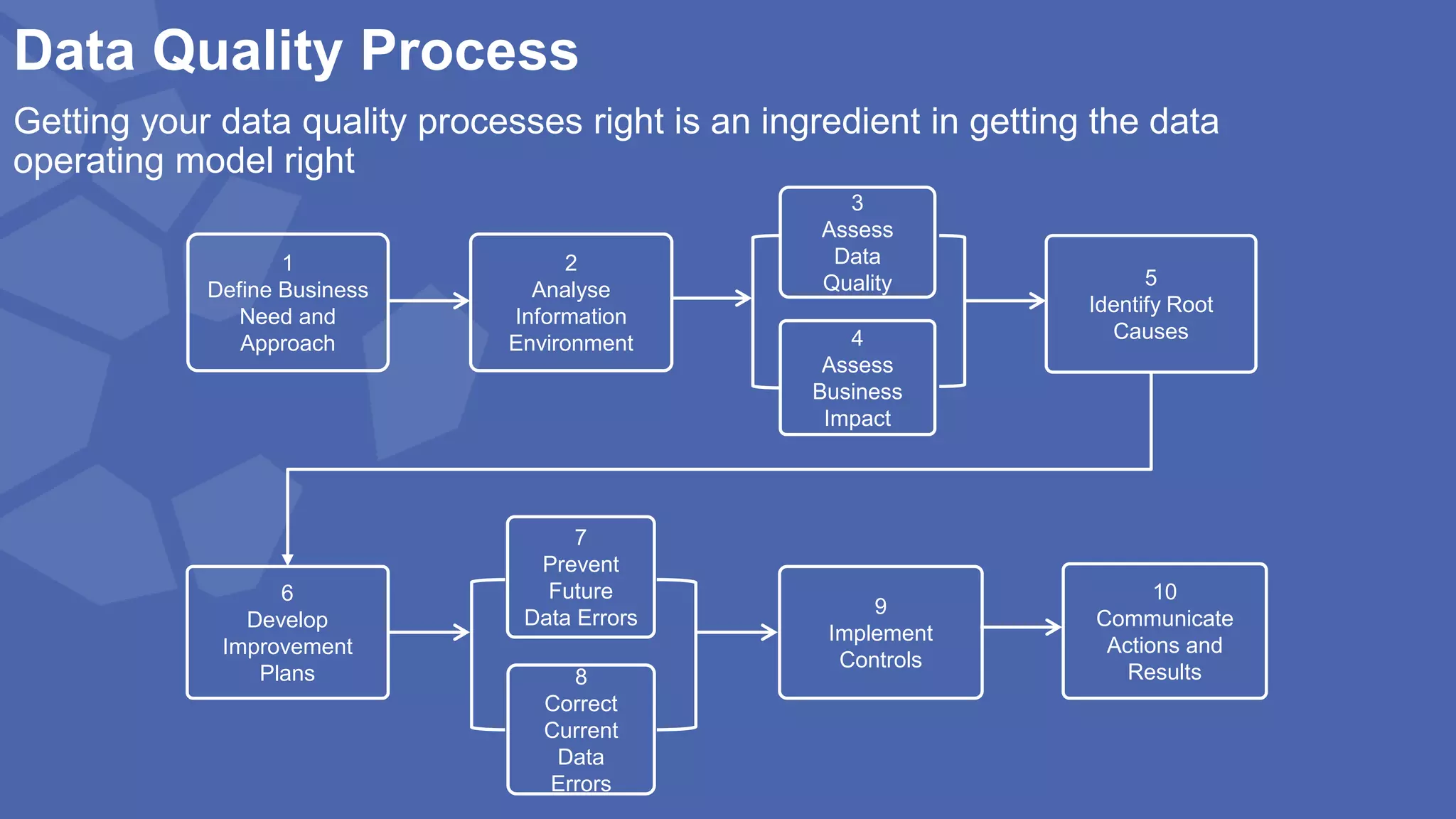
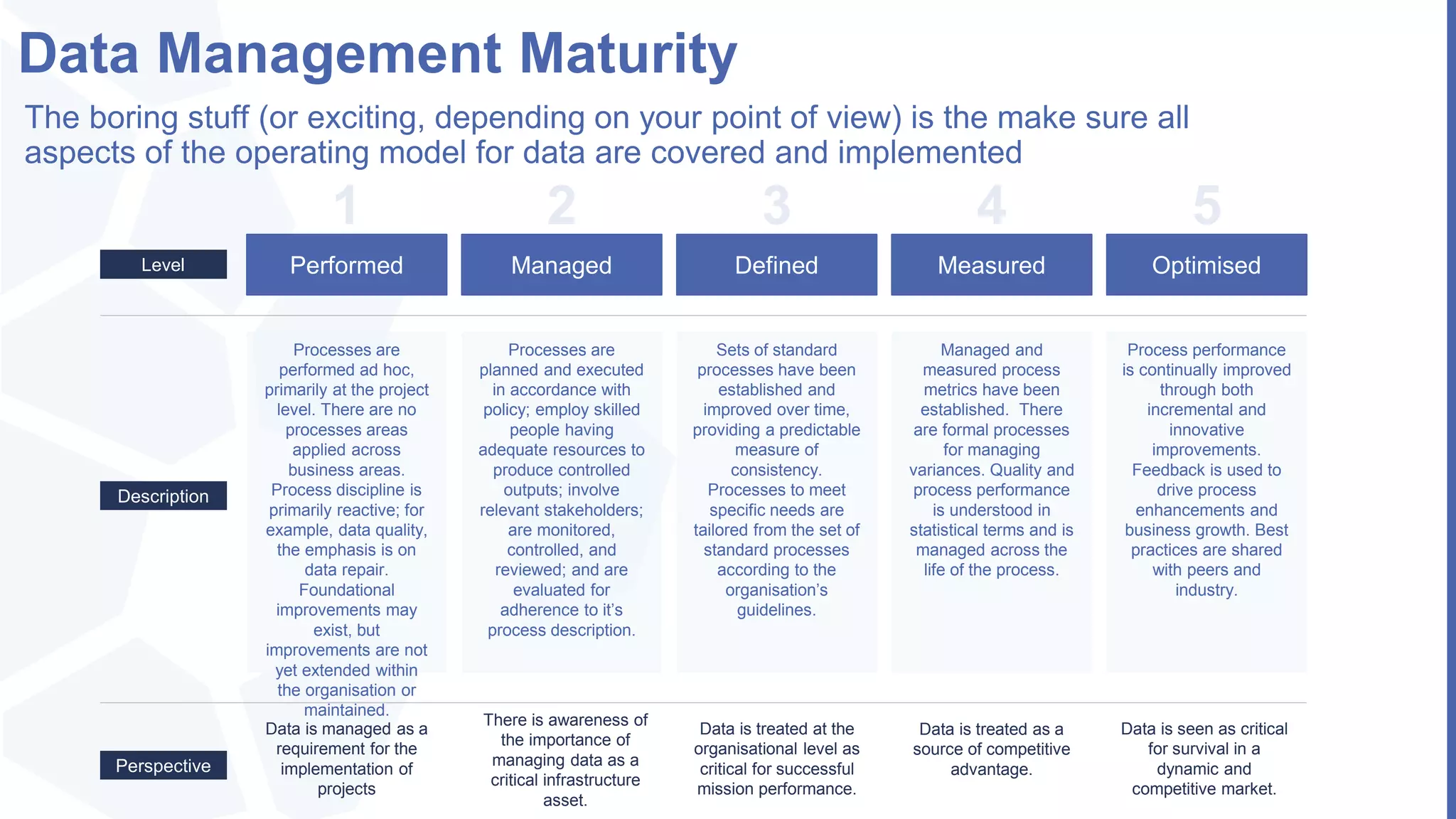
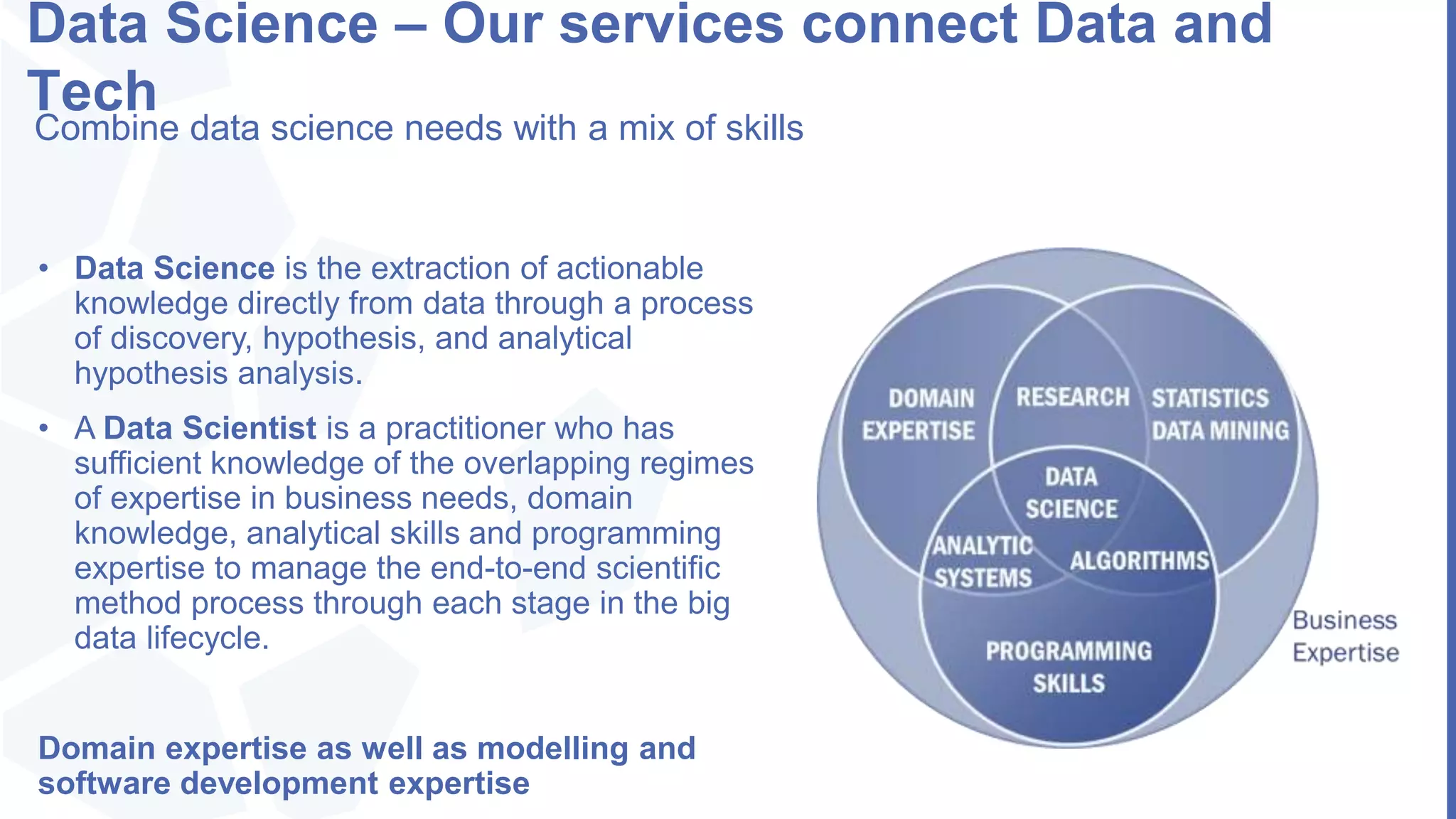
The document, presented by Alpesh Doshi at the Predictive Analytics & Innovation Summit, explores digital transformation through big data and predictive analytics. It emphasizes the importance of adopting disruptive technologies and creating a comprehensive data operating model, highlighting the significance of data in achieving competitive advantage and innovation. Key components include the value and management of data throughout its lifecycle, the establishment of data quality processes, and the role of data science in deriving actionable insights.