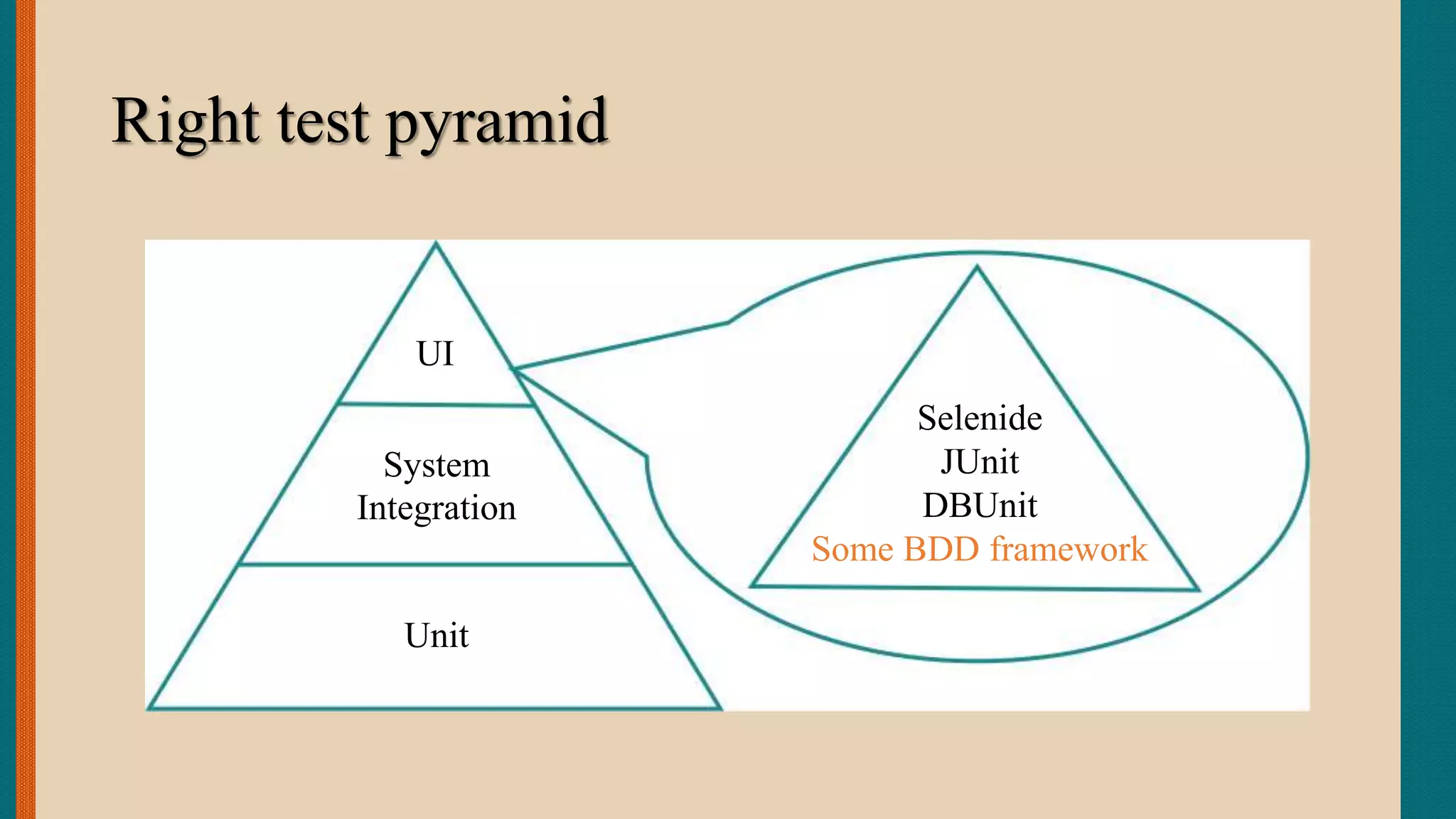
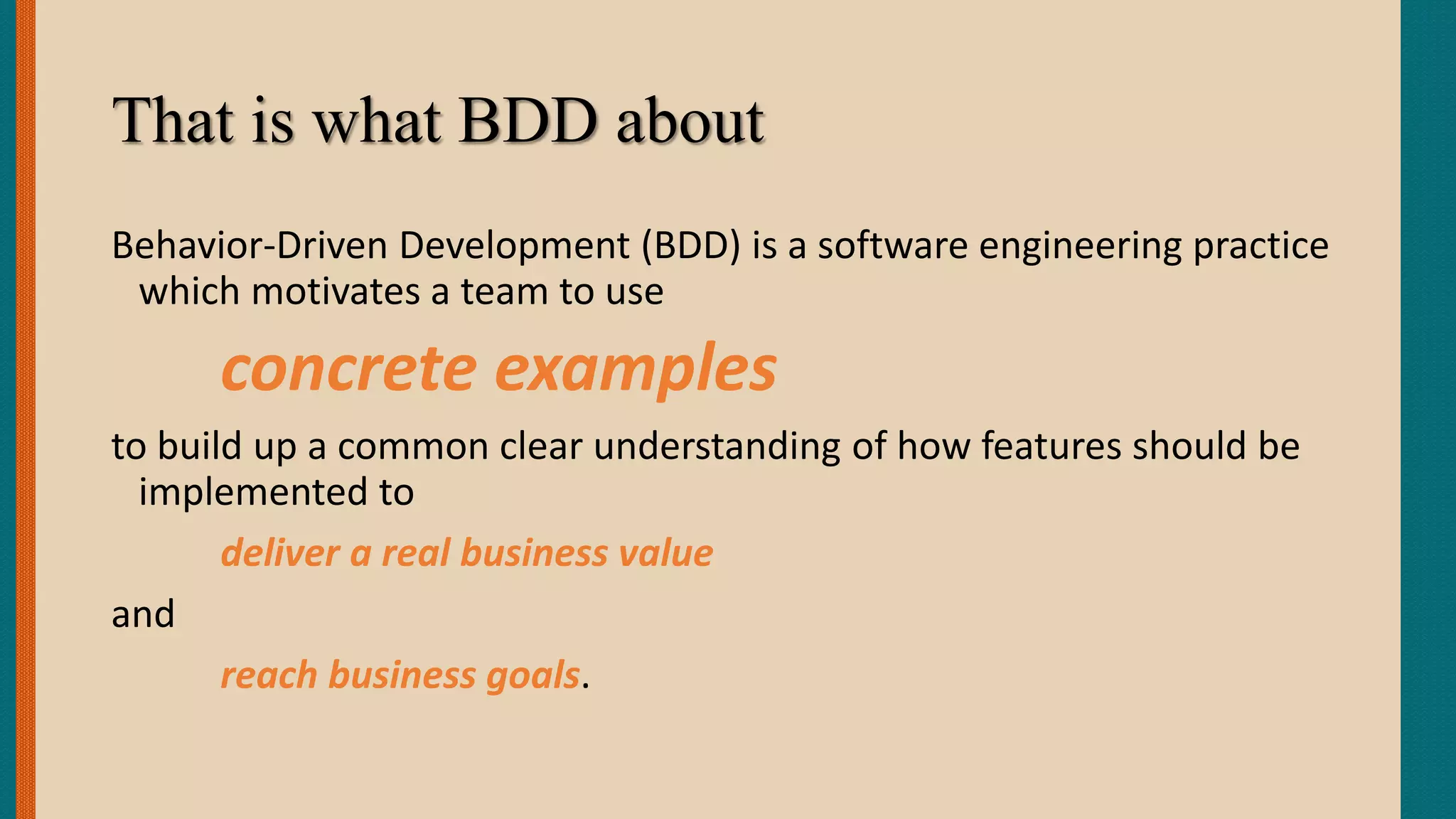
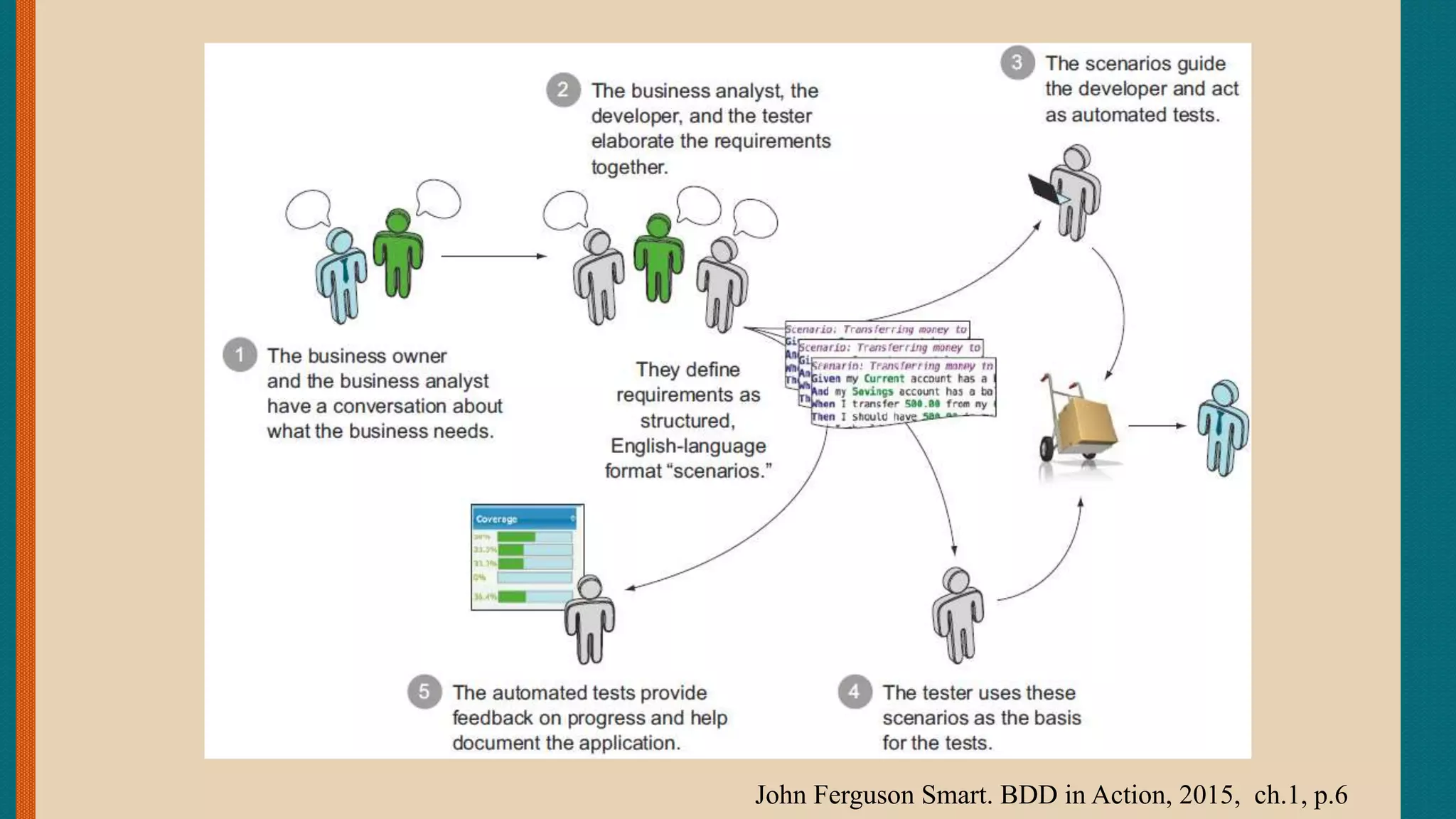
This document discusses Behavior-Driven Development (BDD), which is a software engineering practice that uses concrete examples to build a common understanding of how features should be implemented to deliver business value. BDD motivates teams to specify features by working with customers to develop executable documentation in the form of acceptance tests written in a natural language format. This approach facilitates communication between technical and non-technical stakeholders and helps ensure the delivered system meets the customer's needs. Tools like Cucumber automate the execution of acceptance tests written in a behavior-driven style to help validate features and provide living documentation.