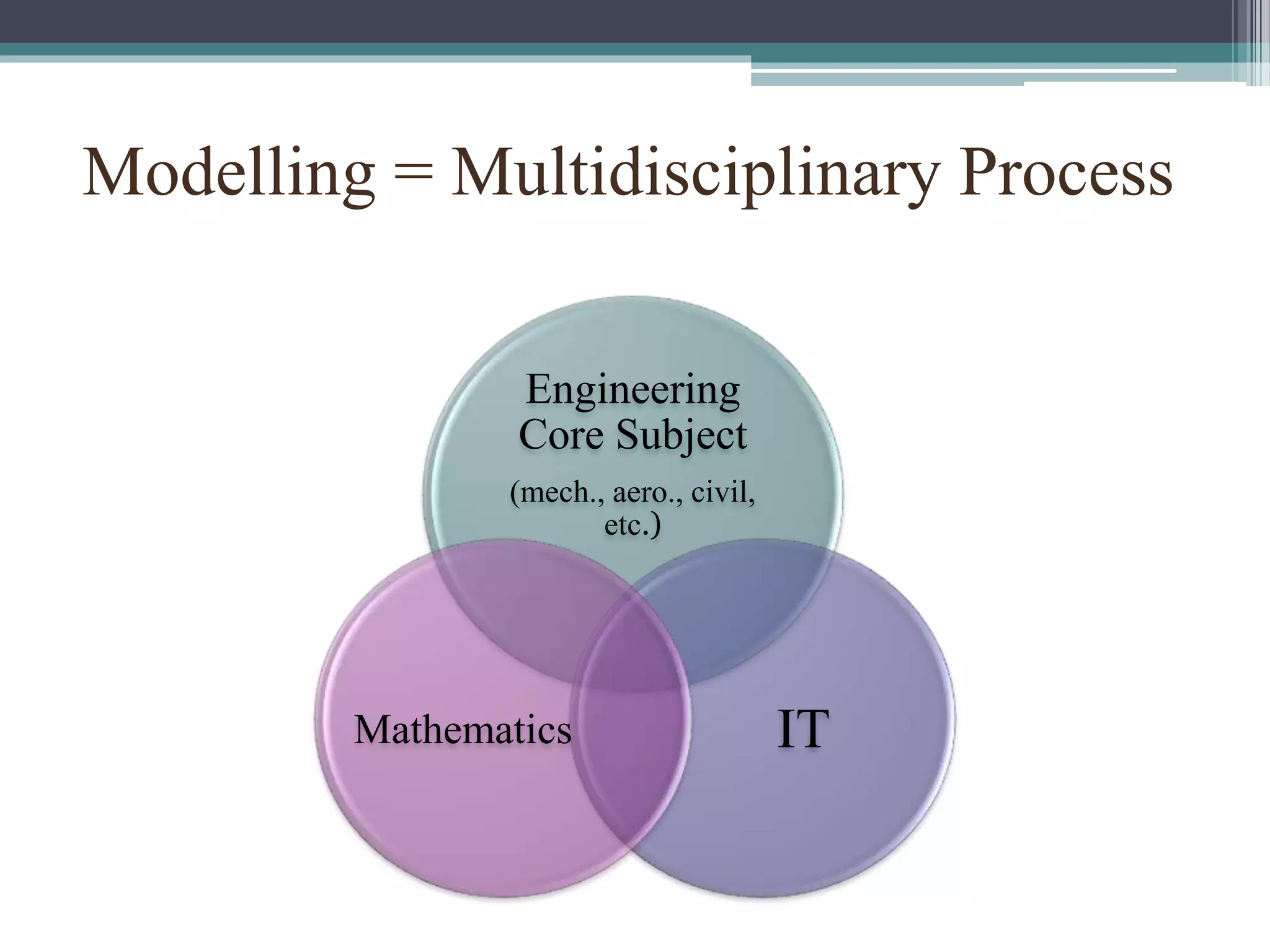
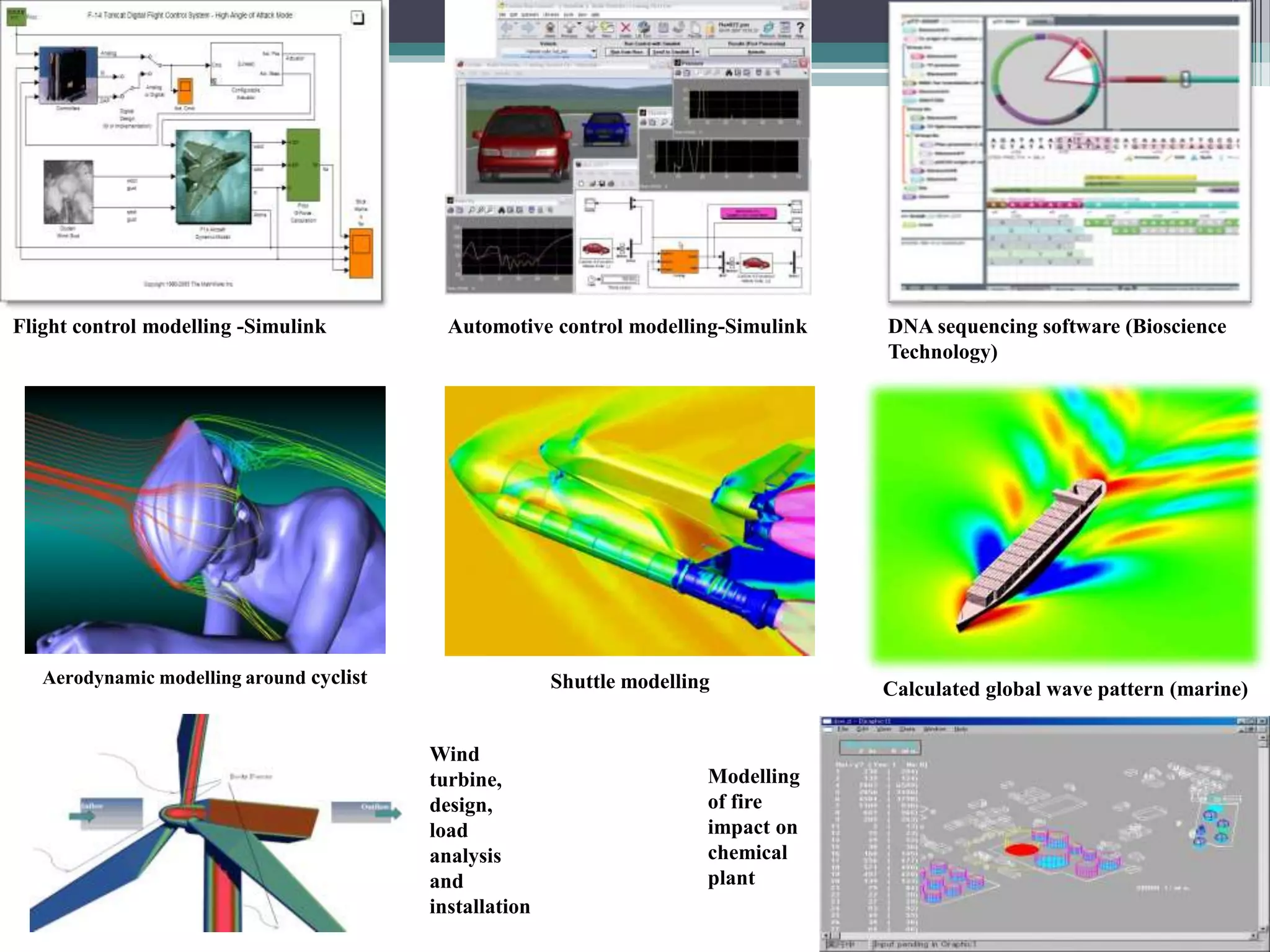
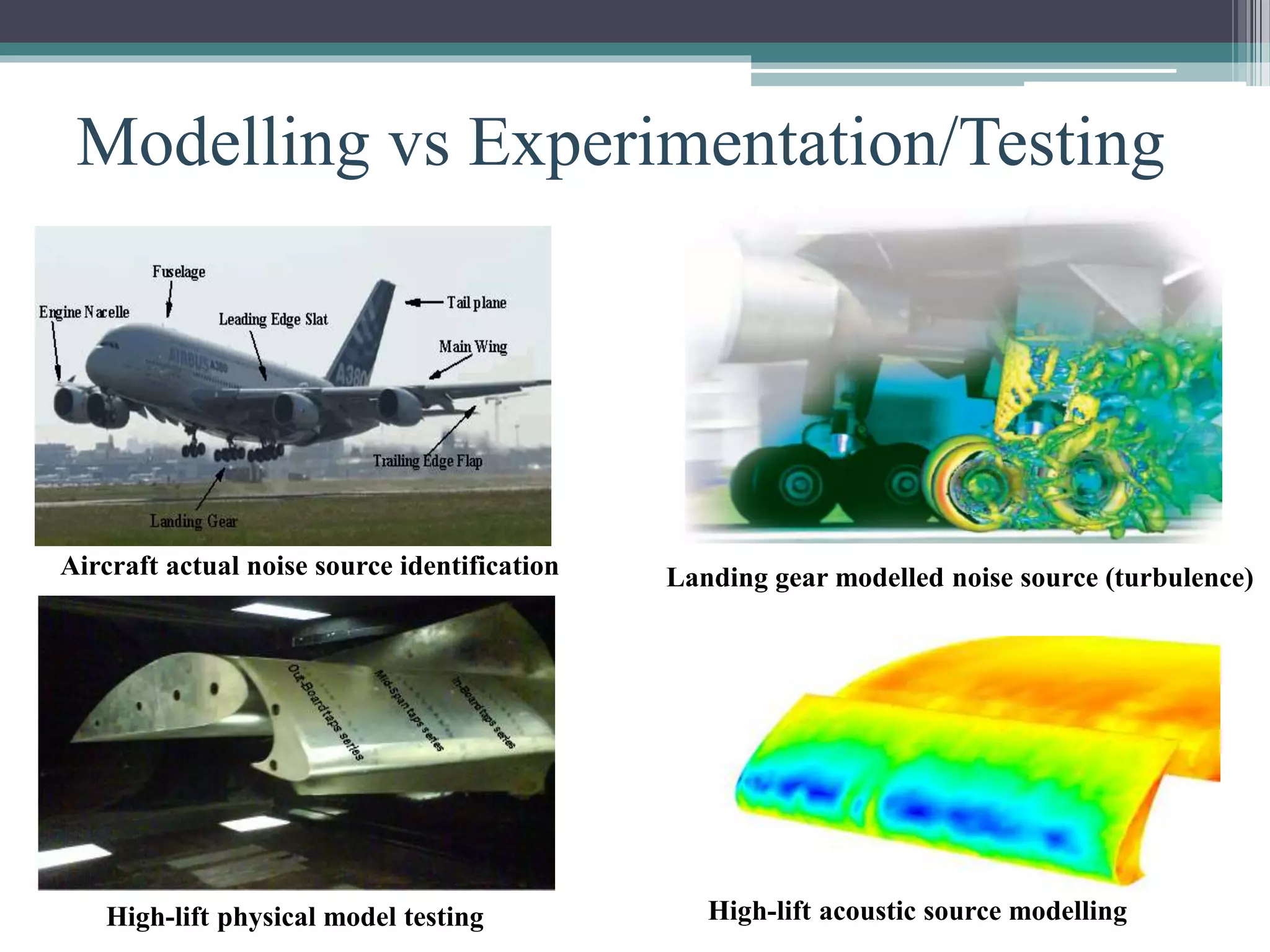
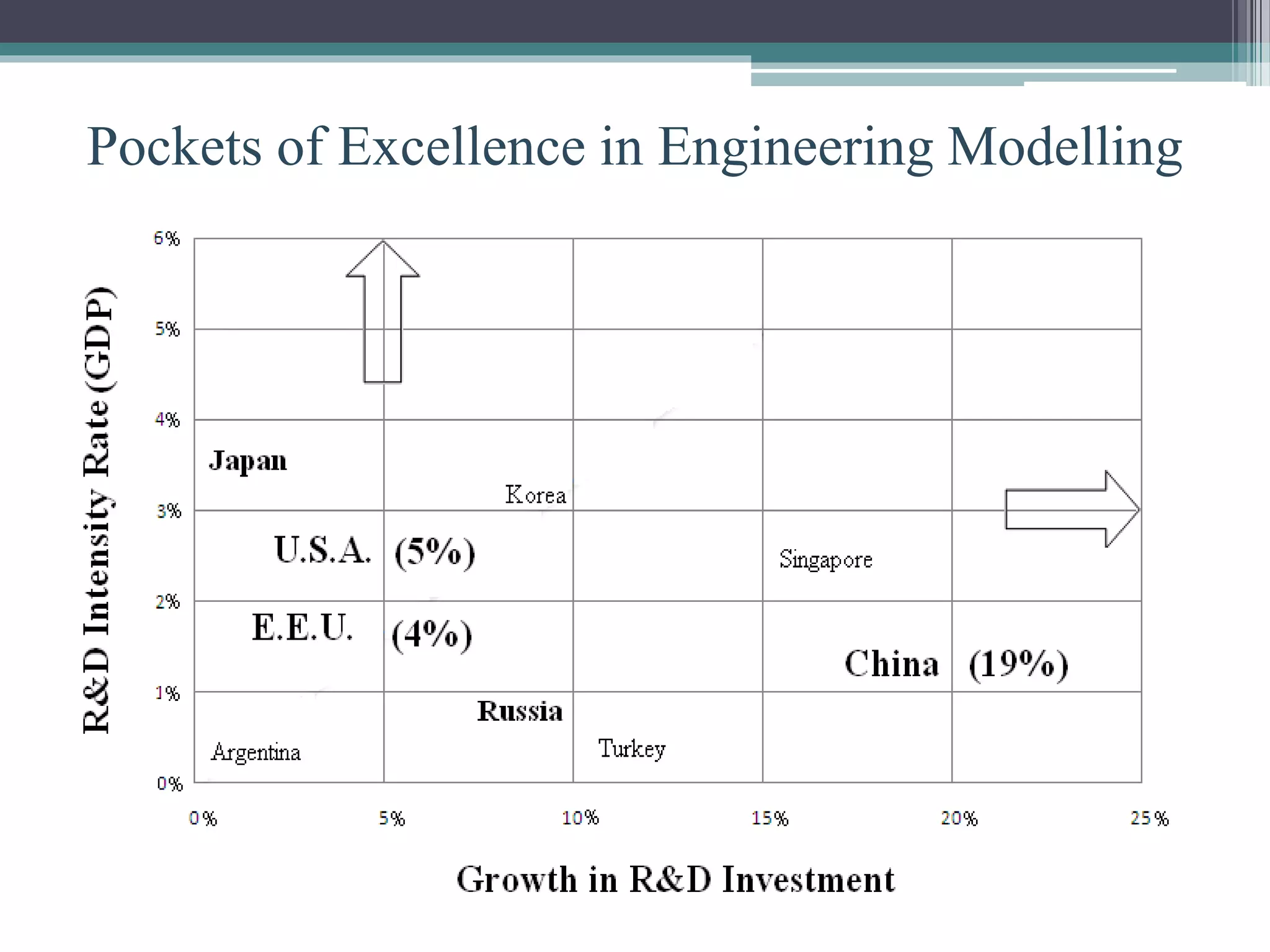
This document discusses engineering modelling and numerical simulation. It outlines the objectives of discussing breakthroughs in engineering research using simulation, key industries that utilize simulation, and examples of simulation applications. Engineering modelling is a multidisciplinary process that uses computer programs to model physical phenomena and predict system performance, complementing physical testing. Modelling is now widely used across various engineering fields and is attracting more university and industry interest due to its capabilities.




![Simulation-Modelling In Science & Engineering [Bassam Rakhshani]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bassamrakhshani-simulation-modellinginscienceengineering-101117084343-phpapp02/75/Simulation-Modelling-In-Science-Engineering-Bassam-Rakhshani-13-2048.jpg)