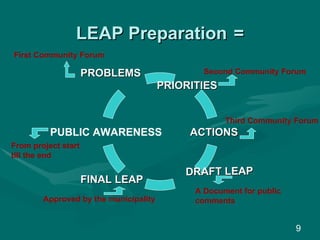
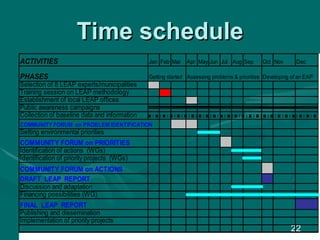
The document provides an overview of the Local Environmental Action Programme (LEAP) process. LEAP is a participatory process that leads to concrete environmental investments within a local community. It focuses on short-term priorities and action plans that can be implemented with available local or national resources. Key steps in the LEAP process include identifying environmental problems, setting priorities, developing actions, and involvement of various stakeholders from the community, local authorities, industries and NGOs. The document outlines the roles and resources provided by the LEAP facilitators, project support, and local municipalities to guide the LEAP planning and implementation process.