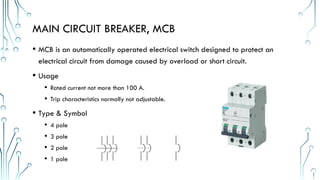
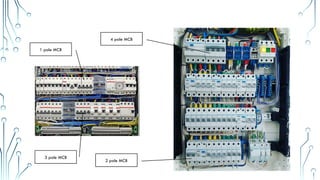
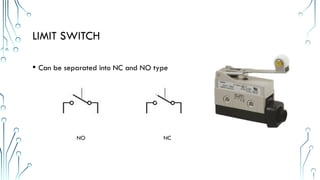
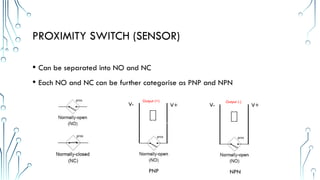
The document provides an overview of essential electrical components, including various circuit breakers (MCCB, MCB, RCCB, ELCB) used for protection against overloads and short circuits, as well as fuses and transformers for power conversion. It also discusses different types of relays, including magnetic contactors and thermal overload relays, emphasizing their roles in controlling electrical circuits. Additionally, the document highlights switches and sensors like limit switches, push buttons, and proximity switches, outlining their functions and classifications.