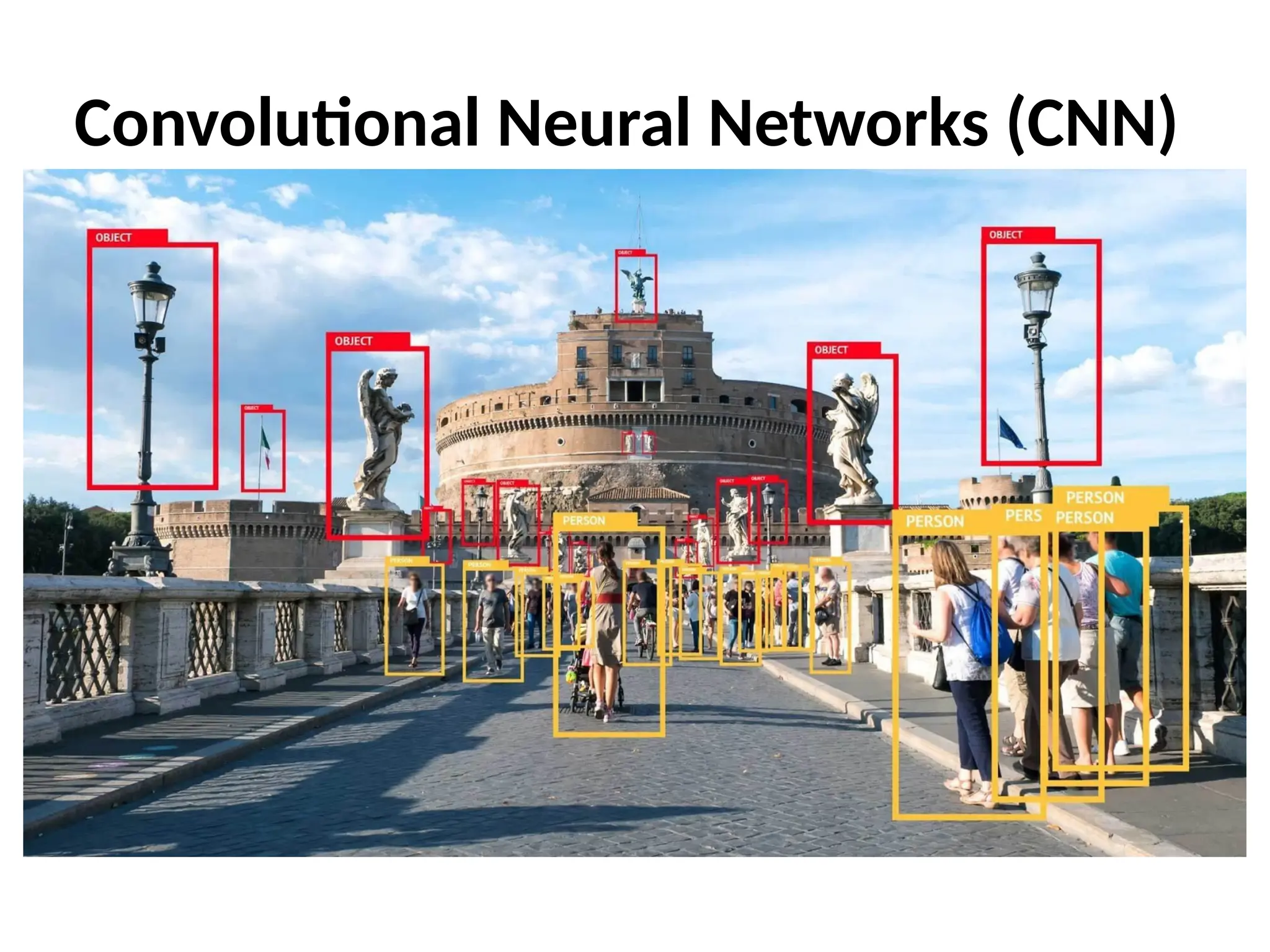
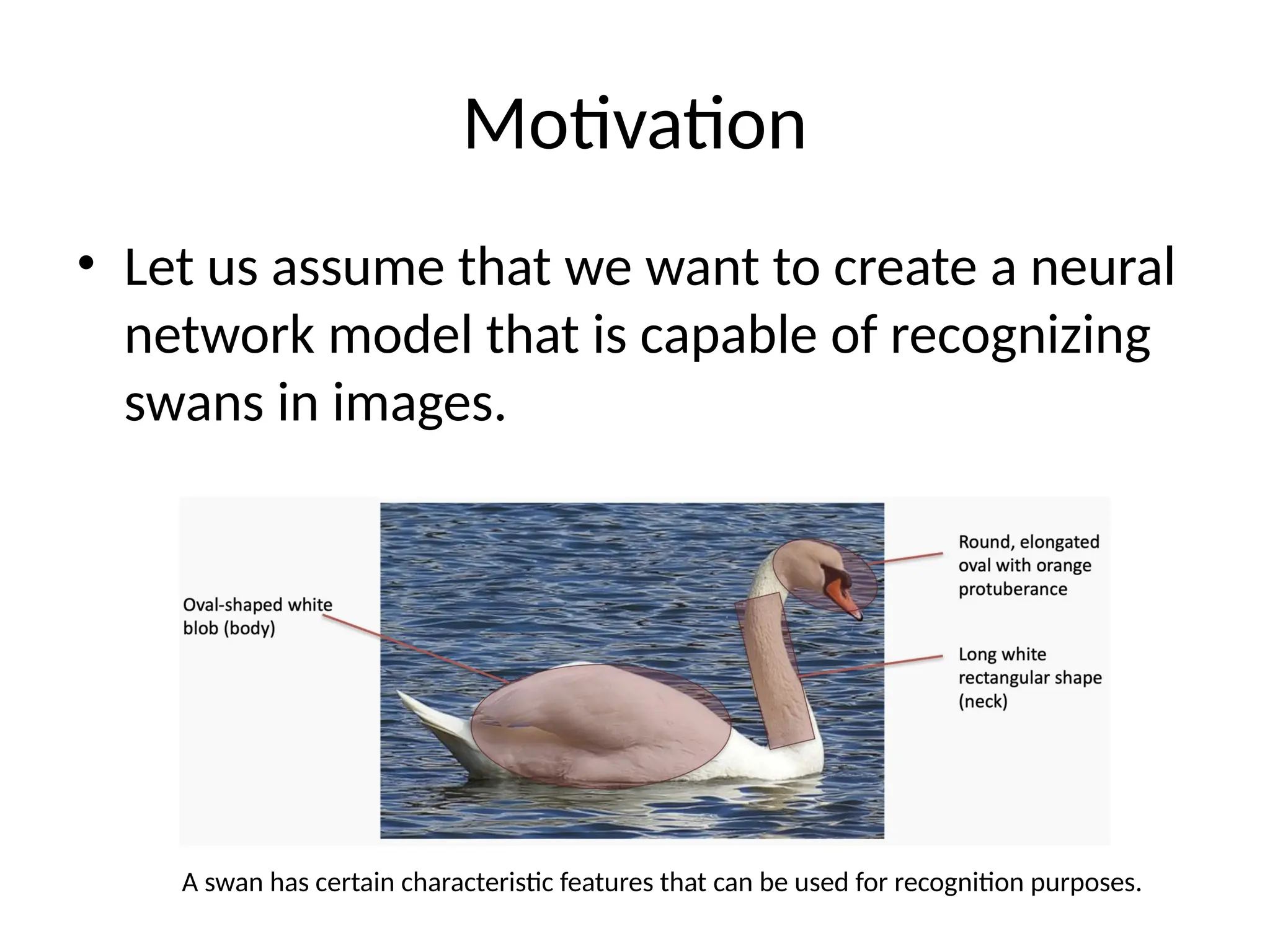
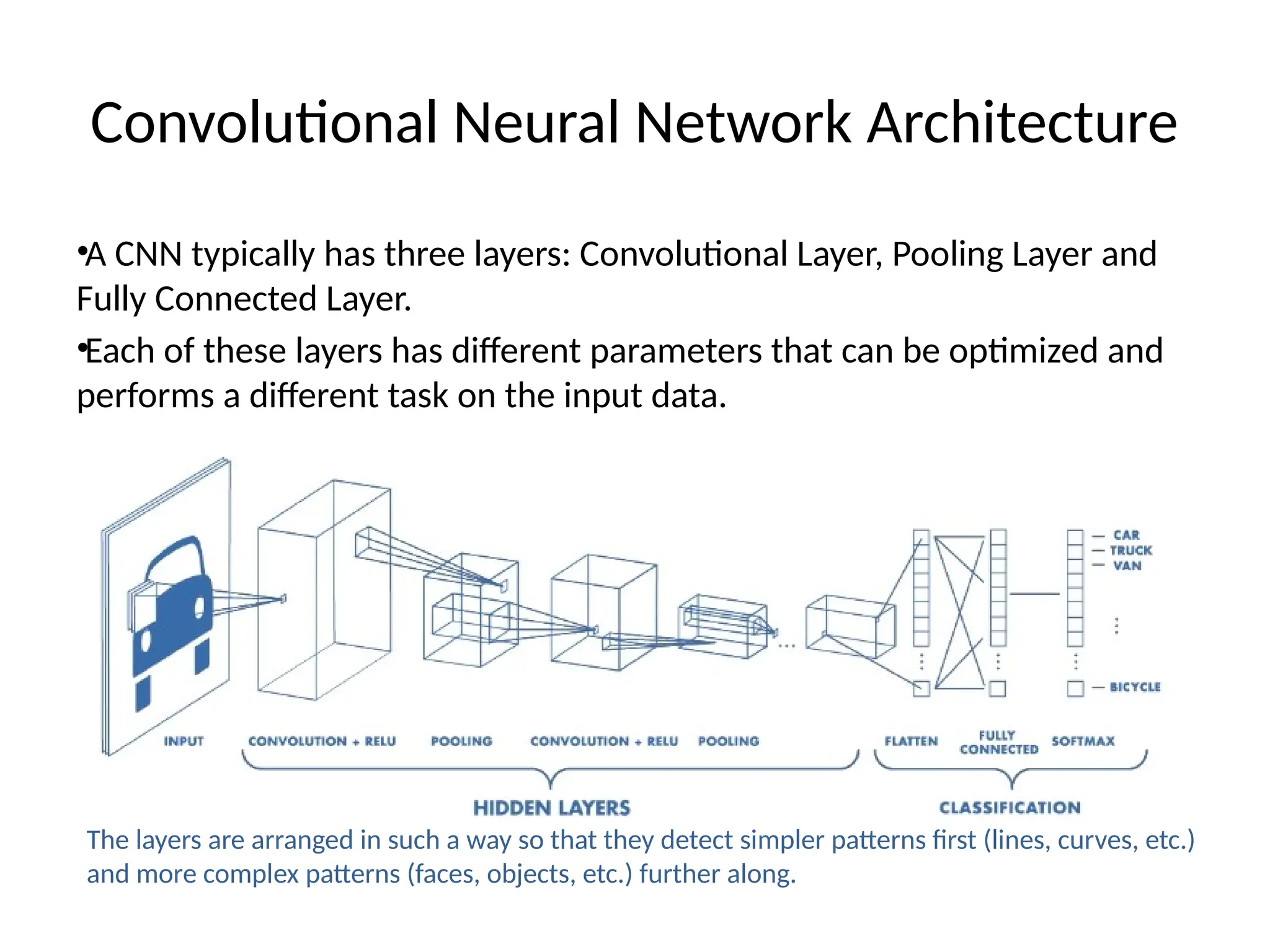
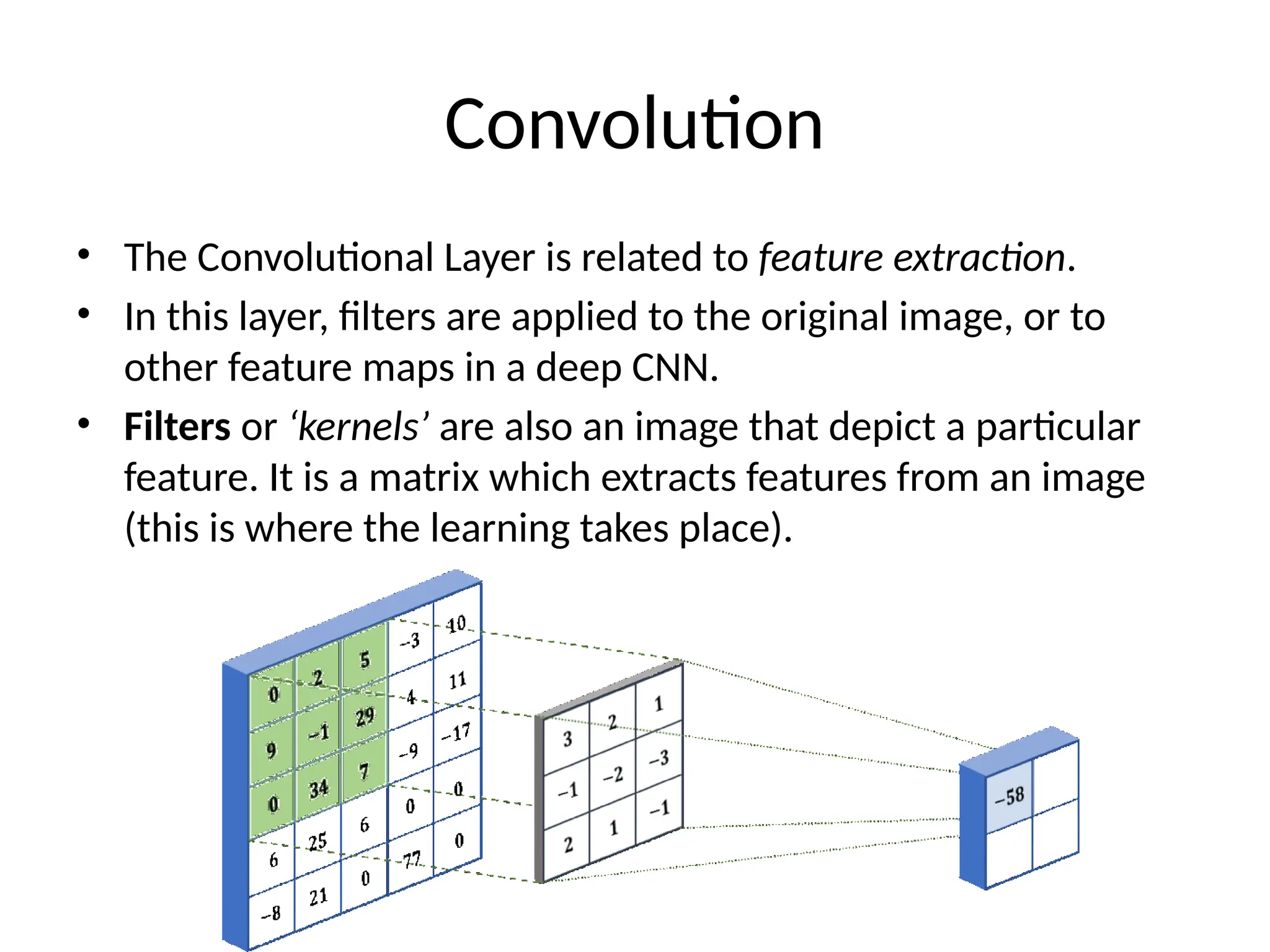
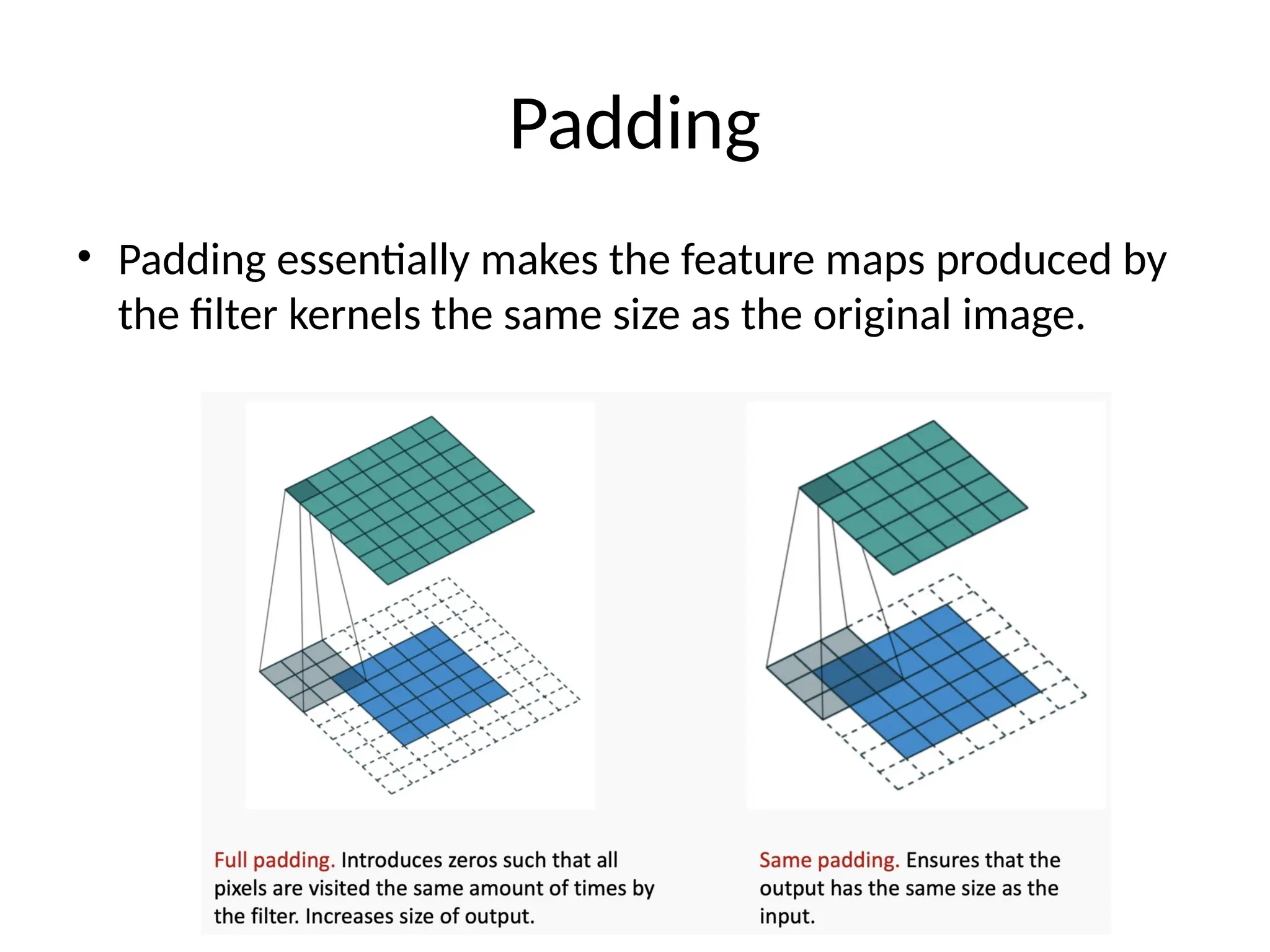
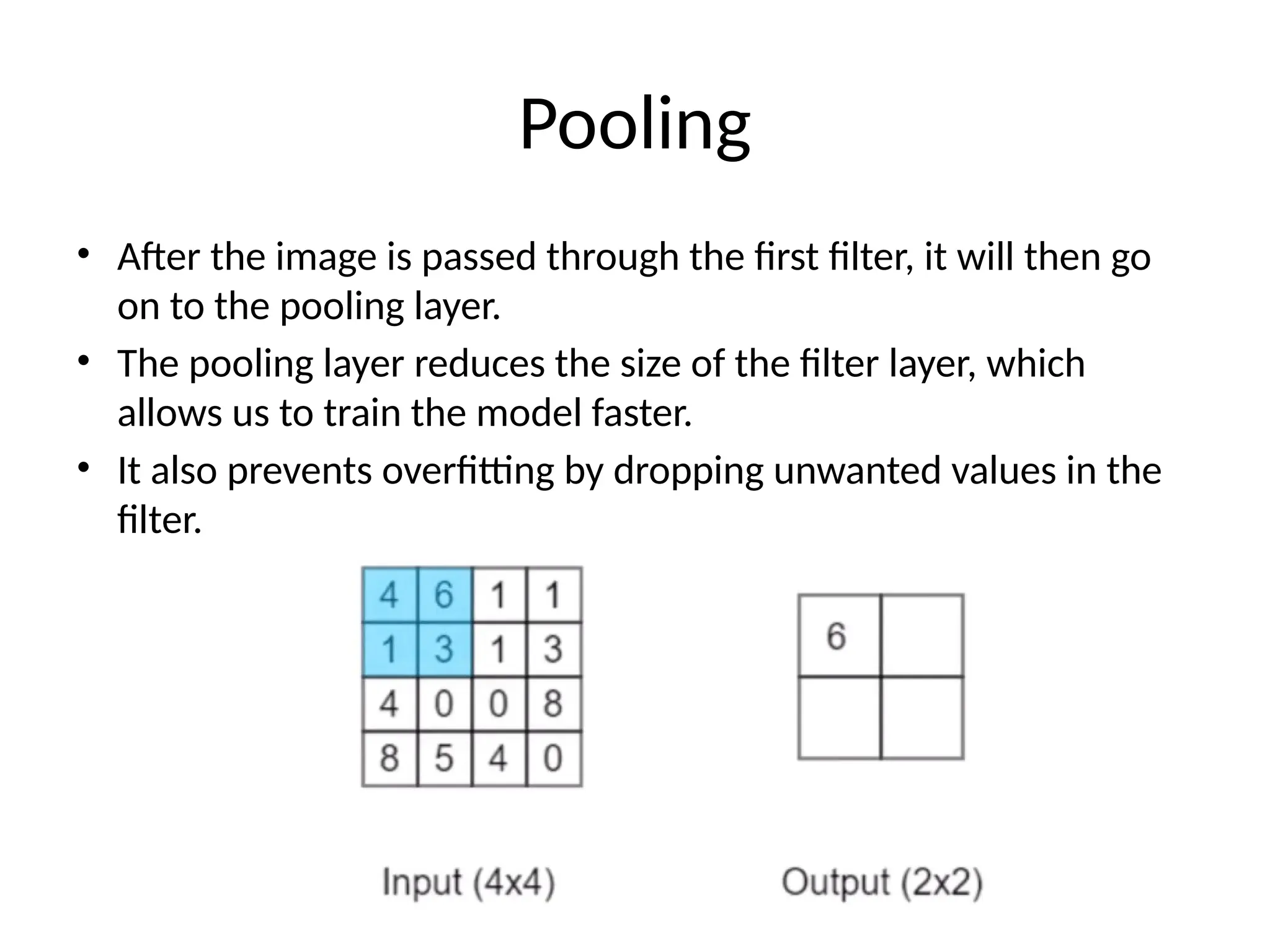
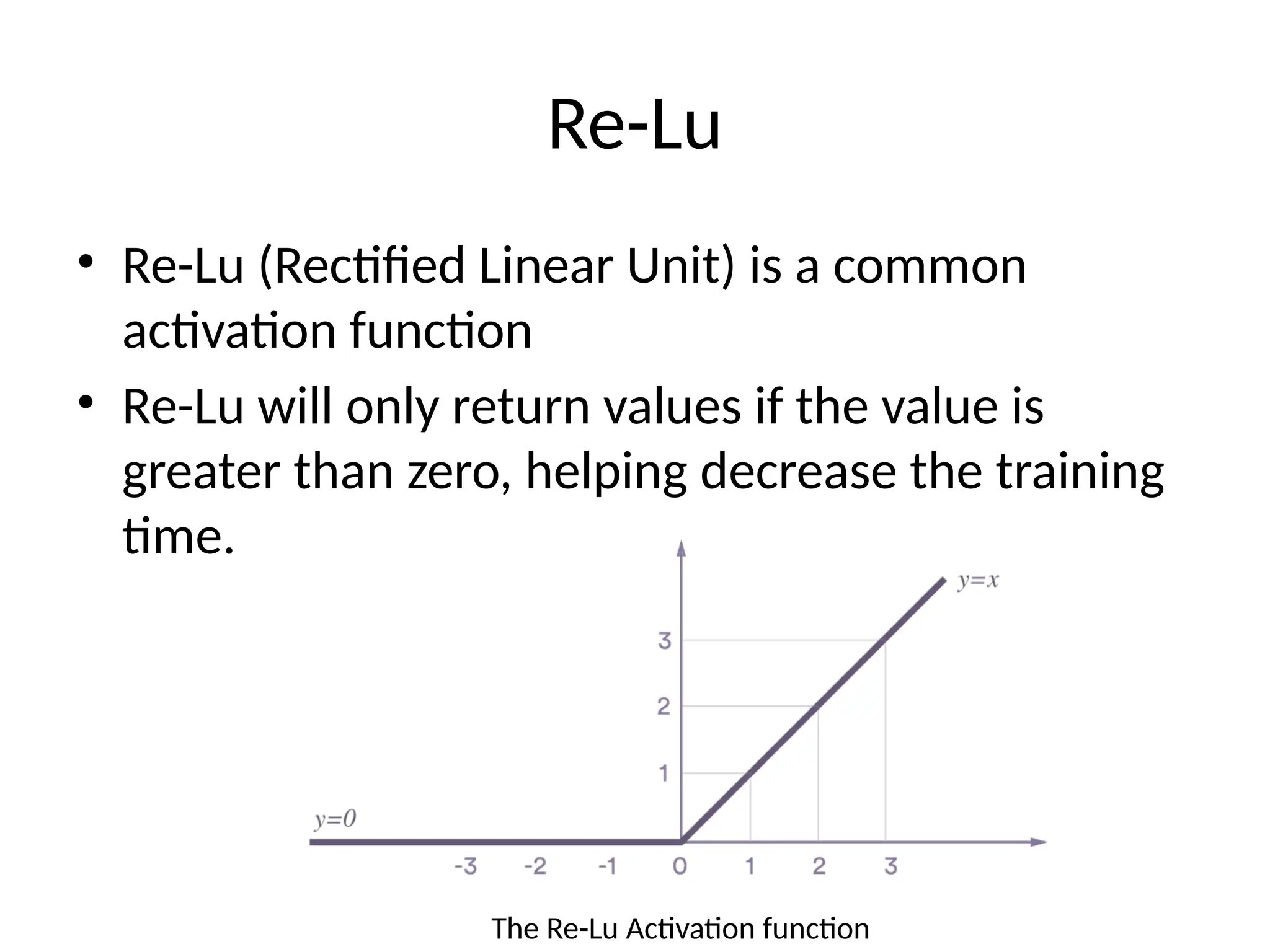
The document discusses convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and their architecture that enables image recognition, such as identifying swans. It describes the layers of CNNs—convolutional, pooling, and fully connected layers—highlighting their roles in feature extraction, size reduction, and classification. The document also mentions techniques like padding and the ReLU activation function to improve model efficiency and performance.