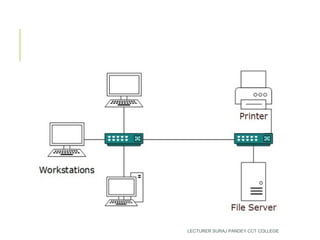
A computer network allows multiple computers to connect and share resources. It usually uses physical wires or cables to connect computers. There are different types of networks including local area networks (LANs), personal area networks (PANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), wide area networks (WANs), wireless local area networks (WLANs), and campus area networks. LANs connect computers within a building while WANs connect LANs over longer distances.