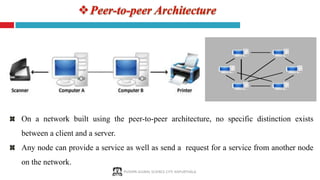
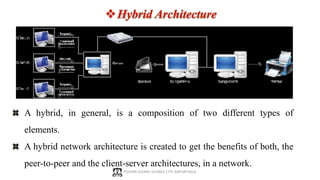
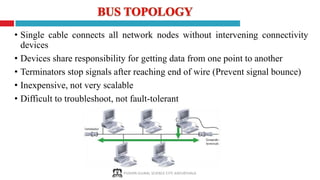
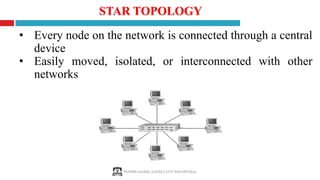
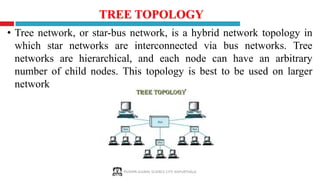
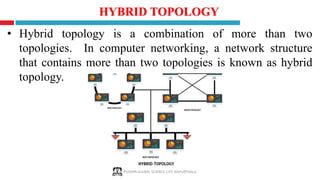
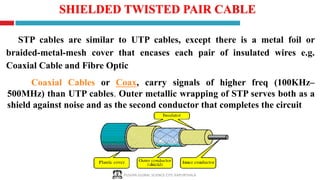
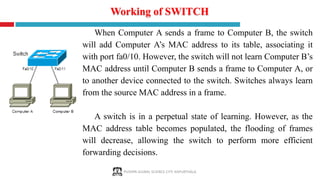
The document provides a comprehensive overview of computer networking, covering key concepts such as definitions, advantages, disadvantages, types of networks, architecture, protocols, and topologies. It outlines different network types including PAN, LAN, MAN, and WAN, and discusses various network protocols like TCP, HTTP, and FTP. Additionally, it details network terminologies, types of cabling, and specific topologies such as bus, ring, star, mesh, tree, and hybrid networks.