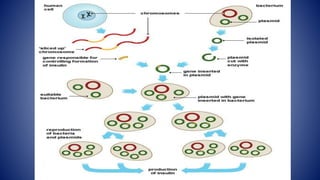
Modern biotechnology involves the use of living organisms and genetic engineering to modify DNA, creating products that enhance crops, medicine, and chemicals. Key processes include isolating genes, inserting them into vectors, transferring them into host organisms, and expressing desired traits. The scope of biotechnology spans medicine, food production, agriculture, and environmental control.