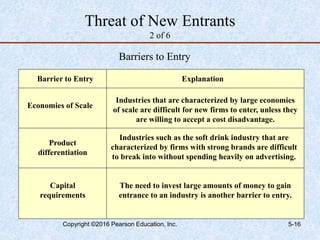
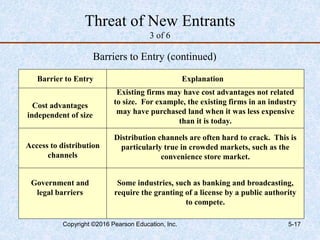
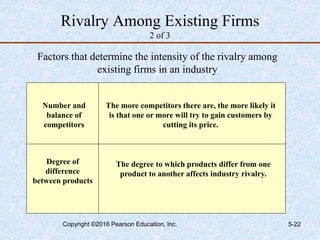
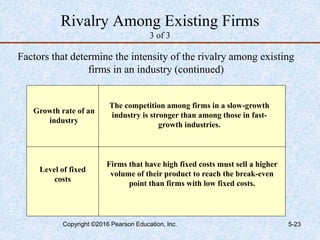
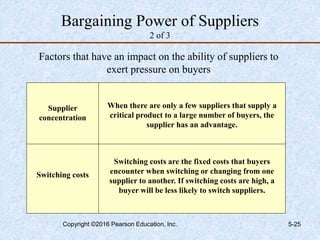
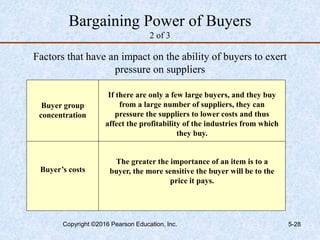
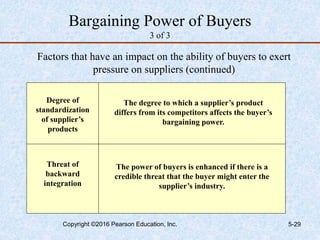
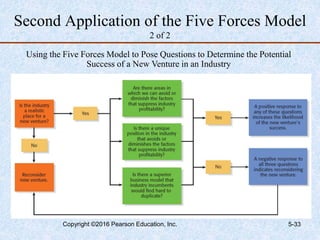
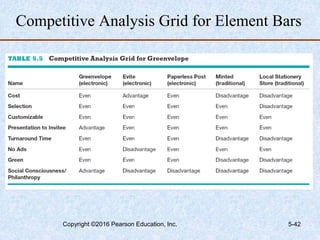
This document discusses industry and competitor analysis. It begins by explaining the purpose of industry analysis and identifying the five competitive forces that determine industry profitability. It then discusses techniques for assessing industry attractiveness, including studying trends and using Porter's five forces model to analyze the threat of new entrants, rivalry among existing firms, bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, and threat of substitutes. The document concludes by explaining the purpose of competitor analysis and how to complete a competitive analysis grid to organize information about competitors.