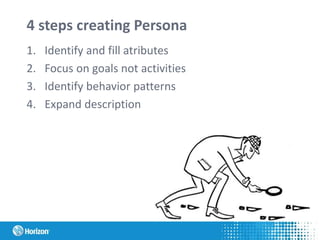
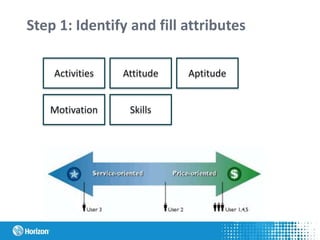
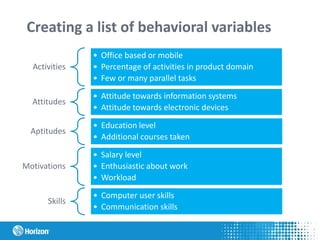
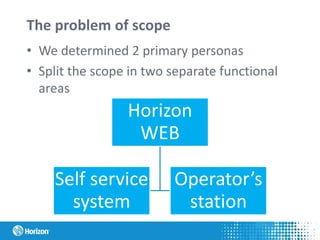
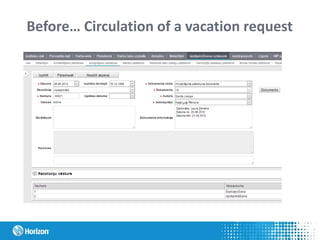
The document discusses the concept of personas in product development, emphasizing their importance in understanding and empathizing with users for creating more user-centric products. It outlines the steps for creating and using personas, provides a practical example related to the development of an ERP system in Latvia, and highlights the benefits of integrating personas into the design process. Additionally, it mentions the pros and challenges of using personas, as well as studying literature on the topic.